#define Plus '+'
#define Minus '−'
#define Multiply '*'
#define Divide '/'
//
// This function sends carriage-return and line-feed to USART
//
void Newline() {
Usart_Write(0x0D); // Send carriage-return
Usart_Write(0x0A); // Send line-feed
}
//
// This function sends a text to USART
//
void Text_To_Usart(unsigned char *m) {
unsigned char i;
i = 0;
while(m[i] != 0) { // Send TEXT to USART
Usart_Write(m[i]);
i++;
}
}
//
// Start of MAIN program
//
void main() {
unsigned char MyKey, i,j,kbd[5],op[12];
unsigned long Calc, Op1, Op2,Key;
unsigned char msg1[] = " CALCULATOR PROGRAM";
unsigned char msg2[] = " Enter First Number: ";
unsigned char msg3[] = "Enter Second Number: ";
unsigned char msg4[] = " Enter Operation: ";
unsigned char msg5[] = " Result = ";
//
// Configure the USART
//
Usart_Init(9600); // Baud=9600
//
// Program loop
//
for(;;) // Endless loop
{
MyKey = 0;
Op1 = 0;
Op2 = 0;
Newline(); // Send newline
Newline(); // Send newline
Text_To_Usart(msg1); // Send TEXT
Newline(); // Send newline
Newline(); // Send newline
//
// Get the first number
//
Text_To_Usart(msg2); // Send TEXT to USART
do // Get first number
{
if (Usart_Data_Ready()) // If a character ready
{
MyKey = Usart_Read(); // Get a character
if (MyKey == Enter) break; // If ENTER key
Usart_Write(MyKey); // Echo the character
Key = MyKey - '0';
Op1 = 10*Op1 + Key; // First number in Op1
}
} while(1);
Newline();
//
// Get the second character
//
Text_To_Usart(msg3); // Send TEXT to USART
do // Get second number
{
if (Usart_Data_Ready()) {
MyKey = Usart_Read(); // Get a character
if (Mykey == Enter) break; // If ENTER key
Usart_Write(MyKey); // Echo the character
Key = MyKey - '0';
Op2 = 10*Op2 + Key; // Second number in Op2
}
} while(1);
Newline();
//
// Get the operation
//
Text_To_Usart(msg4);
do {
if (Usart_Data_Ready()) {
MyKey = Usart_Read(); // Get a character
if (MyKey == Enter) break; // If ENTER key
Usart_Write(MyKey); // Echo the character
Key = MyKey;
}
} while(1);
//
// Perform the operation
//
Newline();
switch(Key) // Calculate
{
case Plus:
Calc = Op1 + Op2; // If ADD
break;
case Minus:
Calc = Op1 - Op2; // If Subtract
break;
case Multiply:
Calc = Op1 * Op2; // If Multiply
break;
case Divide:
Calc = Op1 / Op2; // If Divide
break;
}
LongToStr(Calc, op); // Convert to string
//
// Remove leading blanks
//
j=0;
for (i=0;i<=11;i++) {
if (op[i] != ' ') // If a blank
{
kbd[j]=op[i];
j++;
}
}
Text_To_Usart(msg5);
for(i=0; i
}
}

Figure 6.56: Program listing
At the beginning of the program various messages used in the program are defined as msg1 to msg5 . The USART is then initialized to 9600 baud using the mikroC library routine Usart_Init . Then the heading “CALCULATOR PROGRAM” is displayed on the PC monitor. The program reads the first number from the keyboard using the library function Usart_Read . Function Usart_Data_Ready checks when a new data byte is ready before reading it. Variable Op1 stores the first number. Similarly, another loop is formed and the second number is read into variable Op2 . The program then reads the operation to be performed (+ – * /). The required operation is performed inside a switch statement and the result is stored in variable Calc. The program then converts the result into string format by calling library function LongToStr . Leading blanks are removed from this string, and the final result is stored in character array kbd and sent to the USART to display on the PC keyboard.
The program can be tested using a terminal emulator software such as HyperTerminal, which is distributed free of charge with Windows operating systems. The steps to test the program follow (these steps assume serial port COM2 is used):
• Connect the RS232 output from the microcontroller to the serial input port of a PC (e.g., COM2)
• Start HyperTerminal terminal emulation software and give a name to the session
• Select File→New connection→Connect using and select COM2
• Select the baud rate as 9600, data bits as 8, no parity bits, and 1 stop bit
• Reset the microcontroller
An example output from the HyperTerminal screen is shown in Figure 6.57.
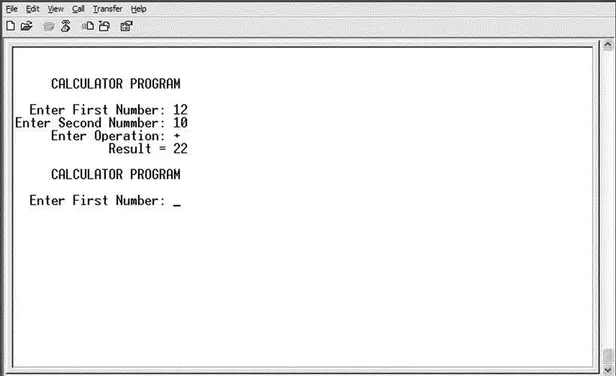
Figure 6.57: HyperTerminal screen
Using Software-Based Serial Communication
The preceding example made use of the microcontroller’s USART and thus its special serial I/O pins. Serial communication can also be handled entirely in software, without using the USART. In this method, any pin of the microcontroller can be used for serial communication.
The calculator program given in Project 10 can be reprogrammed using the mikroC software serial communications library functions known as the Software Uart Library .
The modified program listing is given in Figure 6.58. The circuit diagram of the project is same as in Figure 6.54 (i.e., RC6 and RC7 are used for serial TX and RX respectively), although any other port pins can also be used. At the beginning of the program the serial I/O port is configured by calling function Soft_Uart_Init . The serial port name, the pins used for TX and RX, the baud rate, and the mode are specified. The mode tells the microcontroller whether or not the data is inverted. Setting mode to 1 inverts the data. When a MAX232 chip is used, the data should be noninverted (i.e., mode = 0).
Читать дальше














