KDE configuration options are stored in text files in ~/.kde/share/config . The format of these files varies slightly, but most take the form of name and value pairs divided into sections denoted by section titles in square brackets:
[$Version]
update_info=kfmclient_3_2.upd:kfmclient_3_2
[HTML Settings]
AutomaticDetectionLanguage=0
[KonqMainWindow Toolbar Speech Toolbar]
IconText=IconOnly
Index=4
...(snip)...
[SearchBar]
Mode=1
Since these are text files, they may be copied from one account to another.
2.3.3.1. ...setting the defaults for new users?
The directory /etc/skel acts as a template, or skeleton , for new account creation. Any KDE configuration files placed in /etc/skel/.kde/share/config will get copied to new user accounts automatically.
2.3.4. Where Can I Learn More?
Start with the KDE online manual, accessed through the Help option on the K menu. The first time you access the KDE online manual, you will be asked if you wish to create the index; select the Application Manual and click Build Index to create the index (this takes only a minute or two).
KDE home page: http://kde.org
freedesktop.org: http://freedesktop.org
2.4. Fine-Tuning Your Display Configuration
Fedora's Anaconda installer detects and configures most display hardware optimally. However, there are some situations where it's necessary to override the default configuration to set up a desired display resolution and color depth.
Fedora's display configuration program is called system-config-display .
If you have a working graphical display, you can start this program by selecting System→Administration→Display from the panel menus (System Settings→Display in KDE). You'll need to enter the root password when prompted.
If you don't have a working graphical display, or you've booted into character mode (see Lab 4.5, "Using Runlevels "), you can start this program from the command line:
$ system-config-display
You are attempting to run "system-config-display" which requires administrative privileges, but more information is needed in order to do so.
Password for root:
secret
The graphical display will be started in a very basic mode so that the graphical configuration dialog can be displayed.
system-config-display uses the existing display configuration as a starting point. If the existing configuration does not work at all, you may need to delete it to force system-config-display to start from scratch:
# rm /etc/X11/xorg.conf
Whether started from the menu or the command line, the window shown in Figure 2-15 will be displayed.
Figure 2-15. system-config-display window
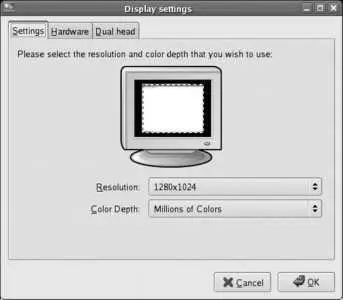
This dialog has three tabs:
Settings
Selects the default resolution and color depth for the system. The maximum display resolution is limited by the monitor setting on the Hardware tab; the color depth should almost always be set to "Millions of Colors," which enables 24-bit color.
Hardware
Selects the monitor and video card type installed in your system. The Anaconda installer will have preselected the best match in most cases, but in some display configurationsincluding those with keyboard-video-mouse (KVM) switches, video splitters, or old monitorsthe monitor type cannot be determined automatically. If your monitor does not appear on the list, select the closest option from the Generic CRT or Generic LCD categories.
In most cases, the exact video card model is not important; it's the chipset that counts. From your video card documentation, find out the chipset manufacturer and model (such as NVIDIA GeForce 4 MX) and select that option from the list. In many cases, an exact match is not required because one video driver is used for a wide range of chipsets.
If there are no options that work for your video card, select the VESA driver, which will provide basic capabilities on almost any modern video card.
Dual head
The X.org server used in Fedora can drive multiple monitors. If you have a second monitor connected to a second video card , you can enable it here. Select the checkbox labeled "Use dual head," then specify the video card, resolution, and color depth to be used. You can also specify the desktop layout as "Individual desktops" or "Spanning desktops"; for most applications, "Spanning desktops" is most versatile, since it enables you to move windows between desktops or even have a window fill both desktops. The second monitor is assumed to be to the right of the primary monitor.
Once you have selected the desired configuration, click OK. The new configuration will take effect the next time you start the graphical user interface.
If you logged in graphically, the GUI won't restart until you restart the system. You can force it to restart sooner by pressing Ctrl-Alt-Backspacebut you will lose any unsaved data, so exit from all applications first. (This key sequence abruptly aborts the X server process and normally should not be used to exit from a graphical session).
system-config-display changes the X server configuration file, /etc/X11/xorg.conf . If necessary, it creates an entirely new file. Most of the information for this file is determined from the hardware by probing.
The xorg.conf file contains configuration information for four types of devices:
Video card
Monitor
Keyboard
Pointer (typically a mouse, but possibly a trackball, graphics tablet, touch screen, light pen, or some other positional input device)
The xorg.conf file is a plain-text file and can be edited by hand (see Lab 4.4, "Basic Text Editing Using vi "). Be sure to make a backup copy before making any changes. You can find a detailed description of the configuration options in xorg.conf 's manpage (see Lab 4.2, "Accessing Online Documentation "):
$ man xorg.conf
The file is divided into sections, each of which looks like this:
Section " SectionName "
Configuration Directives
EndSection
The most commonly used sections in this file are shown in Table 2-3.
Table 2-3. Common xorg.conf section names
| Name |
Description |
| Monitor |
Monitor specifications. |
| InputDevice |
Keyboard configuration. |
| Pointer device configuration (mice, graphics tablets, touch screens). |
| Device |
Video card configuration. |
| Screen |
Associates a Device with a Monitor and defines the available resolutions and color depth. |
| ServerLayout |
Associates one or more Screen sections with two or more InputDevice sections. Different ServerLayouts can be defined to combine devices in different ways for use at different times; for example, a laptop can have a ServerLayout that specifies that the internal+external displays should be used, and another one that specifies only the internal display. |
| Files |
Location of auxiliary files such as fonts, drivers, and color tables. |
| ServerFlags |
Flags to control the overall operation of the X server. The flags may alternatively be placed in the ServerLayout sections if they apply to some ServerLayouts but not to others. |
| Extensions |
Enables/disables extensions to the server capabilities. |
| Module |
Loads additional modules. (Modules may provide extensions, but extensions don't have to exist as separate modules.) |
| Modes |
Defines special video modes (rarely required). |
| DRI |
Direct Render Interface (DRI) device configuration, used for some 3-D gaming. |
Here is a typical xorg.conf file:
Читать дальше













