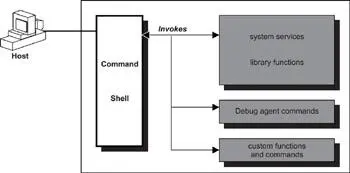
Figure 9.5: RTOS command shell.
Some command shell implementations provide a programming interface. A programmer can extend the shell's functionality by writing additional commands or functions using the shell's application program interface (API). The shell is usually accessed from the host system using a terminal emulation program over a serial interface. It is possible to access the shell over the network, but this feature is highly implementation-dependent. The shell becomes a good debugging tool when it supports available debug agent commands. A host debugger is not always available and can be tedious to set up. On the other hand, the programmer can immediately begin debugging when a debug agent is present on the target system, as well as a command shell.
Every good RTOS provides a target debug agent. Through either the target shell component or a simple serial connection, the debug agent offers the programmer a rich set of debug commands or capabilities. The debug agent allows the programmer to set up both execution and data access break points. In addition, the programmer can use the debug agent to examine and modify system memory, system registers, and system objects, such as tasks, semaphores, and message queues. The host debugger can provide source-level debug capability by interacting with the target debug agent. With a host debugger, the user can debug the target system without having to understand the native debug agent commands. The target debug agent commands are mapped into host debugger commands that are more descriptive and easier to understand. Using an established debug protocol, the host debugger sends the user-issued debug commands to the target debug agent over the serial cable or the Ethernet network. The target debug agent acts on the commands and sends the results back to the host debugger. The host debugger displays the results in its user-friendly debug interface. The debug protocol is specific to the host debugger and its supported debug agent. Be sure to check the host debugging tools against the supported RTOS debug agents before making a purchase.
What has been presented so far is a very small set of components commonly found in available RTOS. Other service components include the SNMP component. The target system can be remotely managed over the network by using SNMP. The standard I/O library provides a common interface to write to and read from system I/O devices. The standard system library provides common interfaces to applications for memory functions and string manipulation functions. These library components make it straightforward to port applications written for other operating systems as long as they use standard interfaces. The possible services components that an RTOS can provide are limited only by imagination. The more an embedded RTOS matures the more components and options it provides to the developer. These components enable powerful embedded applications programming, while at the same time save overall development costs. Therefore, choose the RTOS wisely.
9.3 Component Configuration
The available system memory in many embedded systems is limited. Therefore, only the necessary service components are selected into the final application image. Frequently programmers ask how to configure a service component into an embedded application. In a simplified view, the selection and consequently the configuration of service components are accomplished through a set of system configuration files. Look for these files in the RTOS development environment to gain a better understanding of available components and applicable configuration parameters.
The first level of configuration is done in a component inclusion header file. For example, call it sys_comp.h, as shown in Listing 9.1.
Listing 9.1: The sys_comp.h inclusion header file.
#define INCLUDE_TCPIP 1
#define INCLUDE_FILE_SYS 0
#define INCLUDE_SHELL 1
#define INCLUDE_DBG_AGENT 1
In this example, the target image includes the TCP/IP protocol stack, the command shell, and the debug agent. The file system is excluded because the sample target system does not have a mass storage device. The programmer selects the desired components through sys_comp.h.
The second level of configuration is done in a component-specific configuration file, sometimes called the component description file. For example, the TCP/IP component configuration file could be called net_conf.h, and the debug agent configuration file might be called the dbg_conf.h. The component-specific configuration file contains the user-configurable, component-specific operating parameters. These parameters contain default values. Listing 9.2 uses net_conf.h.
Listing 9.2: The net_conf.h configuration file.
#define NUM_PKT_BUFS 100
#define NUM_SOCKETS 20
#define NUM_ROUTES 35
#define NUM_NICS 40
Some points to remember include the following:
· Micro-kernel design promotes a framework in which additional service components can be developed to extend the kernel's functionalities easily.
· Debug agents allow programmers to debug every piece of code running on target systems.
· Developers should choose a host debugger that understands many different RTOS debug agents.
· Components can be included and configured through a set of system configuration files.
· Developers should only include the necessary components to safeguard memory efficiency.
Chapter 10: Exceptions and Interrupts
Exceptions and interrupts are part of a mechanism provided by the majority of embedded processor architectures to allow for the disruption of the processor's normal execution path. This disruption can be triggered either intentionally by application software or by an error, unusual condition, or some unplanned external event.
Many real-time operating systems provide wrapper functions to handle exceptions and interrupts in order to shield the embedded systems programmer from the low-level details. This application-programming layer allows the programmer to focus on high-level exception processing rather than on the necessary, but tedious, prologue and epilogue system-level processing for that exception. This isolation, however, can create misunderstanding and become an obstacle when the programmer is transformed from an embedded applications programmer into an embedded systems programmer.
Understanding the inner workings of the processor exception facility aids the programmer in making better decisions about when to best use this powerful mechanism, as well as in designing software that handles exceptions correctly. The aim of this chapter is to arm the programmer with this knowledge.
This chapter focuses on:
· the definitions of exception and interrupt,
· the applications of exceptions and interrupts,
· a closer look at exceptions and interrupts in terms of hardware support, classifications, priorities, and causes of spurious interrupts, and
· a detailed discussion on how to handle exceptions and interrupts.
10.2 What are Exceptions and Interrupts?
An exception is any event that disrupts the normal execution of the processor and forces the processor into execution of special instructions in a privileged state. Exceptions can be classified into two categories: synchronous exceptions and asynchronous exceptions.
Читать дальше













