Stakeholder s may initially trust the provider with low-value contract s or non-critical services. Service management responds by delivering the performance expected of a strategic asset. The performance is rewarded with contract renewals, new services, and customers, which together represent a larger value of business . To handle this increase in value, service management must invest further in assets such as process , knowledge, people, application s and infrastructure. Successful learning and growth enables commitments of higher service level s as service management gets conditioned to handle bigger challenges.
Over time, this virtuous cycle results in higher capability levels and maturity in service management leading to a higher return on assets for the service provider . Service s play the role of a belt that engages service asset s with customer assets (Figure 4.15). Service agreement s or contract s define the rules of engagement. Unless properly defined the cost of service assets spent in support of customers’ assets may be difficult to account for and recover. This leads to situations where there is adequate creation of value for the customer but inadequate value capture for the provider.
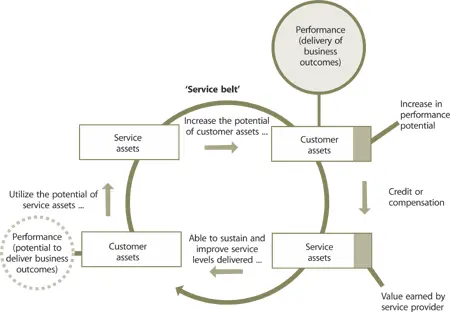
Figure 4.15 Mutual welfare when service assets are engaged in supporting customer outcomes
Value capture is an important notion for all types of service providers, internal and external. Good business sense discourages stakeholders from making major investments in any organizational capability unless it demonstrates value capture. Internal providers are encouraged to adopt this strategic perspective to continue as viable concerns within a business. Cost recovery is necessary but not sufficient. Profits or surpluses allow continued investments in service asset s that have a direct impact on capabilities.
Linking value creation to value capture is a difficult but worthwhile endeavour. In simplest terms customers buy services as part of plan s for achieving certain business outcomes. Say, for example, the use of a wireless messaging service allows the customer’s sales staff to connect securely to the sales force automation system and complete critical tasks in the sales cycle. This has a positive impact on cash flows from payments brought forward in time. By linking purchase orders and invoices expedited from use of the wireless service it is possible to sense the impact of the service on business outcomes. They can be measured in terms such as Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) and average time of the Order-to-Cash cycle. The total cost of utilizing the service can then be weighed against the impact on business outcomes.
It is difficult to establish the cause-and-effect relationship between the use of the service and the changes in cash flows. Quite often, there are several degrees of separation between the utilization of the service and the benefits customers ultimately realize. While absolute certainty is difficult to achieve, decision making nevertheless improves.
4.3.1 Service management as a closed-loop control system
As defined earlier, service management is a set of organizational capabilities specialized in providing value to customers in the form of services. The capabilities interact with each other to function as a system for creating value. Service assets are the source of value and customer assets are the recipients (Figure 4.16). Service s have the potential to increase the performance of customer assets and create value to the customer organization . Improvements in the design , transition and operation of the service increase this customer performance potential and reduce the risk s of variations on customer assets. This requires a clear and complete understanding of customer assets and desired outcomes.
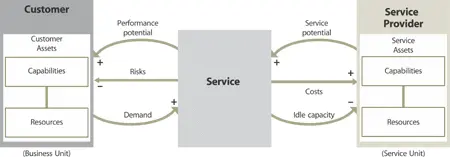
Figure 4.16 Service management as a closed-loop control system
Services derive their potential from service asset s. Service potential is converted into performance potential of customer assets. Increasing the performance potential frequently stimulates additional demand for the service in terms of scale or scope . This demand translates into greater use of service assets and justification for their ongoing maintenance and upgrades. Unused capacity is reduced. Cost s incurred in fulfilling the demand are recovered from the customer based on agreed terms and conditions.
From this perspective, service management is a closed-loop control system with the following function s, to:
Develop and maintain service asset s
Understand the performance potential of customer assets
Map service assets to customer assets through services
Design , develop, and operate suitable services
Extract service potential from service asset s
Convert service potential into performance potential
Convert demand from customer assets into workload for service assets
Reduce risk s for the customer
Control the cost of providing services.
4.3.2 Service management as a strategic asset
To develop service management as a strategic asset, define the value network within which service providers operate in support of their customers. This network may exist entirely within a business enterprise, as is often the case for Type I and Type II providers (Figure 4.17). More often the value network extends across organizational boundaries to include external customers, supplier s, and partners. By identifying the key relationships and interactions in the network, managers have better visibility and control over the system s and processes they operate. This allows managers to manage the complexity that exists in their business environment s as customers pursue their own business model s and strategies. It also helps account for all the costs and risk s involved in providing a service or supporting a customer.
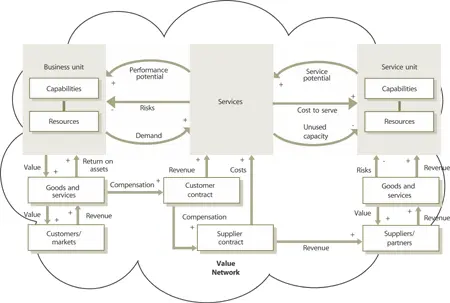
Figure 4.17 Service management as a strategic asset and a closed-loop system
Strategic assets are dynamic in nature. They are expected to continue to perform well under changing business conditions and objective s of their organization . That requires strategic assets to have learning capabilities. Performance in the immediate future should benefit from knowledge and experience gained from the past. This requires service management to operate as a closed-loop system that systematically creates value for the customer and captures value for the service provider . An important aspect of service management is controlling the interactions between customer assets and service assets.
4.3.2.1 Increasing the service potential
The capabilities and resource s ( service asset s) of a service provider represent the service potential or the productive capacity available to customers through a set of services (Figure 4.17). Project s that develop or improve capabilities and resources increase the service potential. For example, implementation of a Configuration Management System leads to improved visibility and control over the productive capacity of service assets such as networks, storage, and server s. It also helps quickly to restore such capacity in the event of failure s or outages. There is greater efficiency in the utilization of those assets and therefore service potential because of capability improvements in Configuration Management . Similar examples are given below in Table 4.4. One of the key objective s of service management is to improve the service potential of its capabilities and resources.
Читать дальше



