Tarso B. Ledur Kist - Open and Toroidal Electrophoresis
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Tarso B. Ledur Kist - Open and Toroidal Electrophoresis» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Open and Toroidal Electrophoresis
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Open and Toroidal Electrophoresis: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Open and Toroidal Electrophoresis»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The exact expressions of separation efficiency, resolution, peak capacity, and many other performance indicators of the open and toroidal layouts are presented and compared.
Featuring numerous illustrations throughout,
offers chapters covering: Solvents and Buffer Solutions; Fundamentals of Electrophoresis; Open Layout; and Toroidal Layout. Confronting Performance Indicators is next, followed by chapters on High Voltage Modules and Distributors; Heat Removal and Temperature Control; and Detectors. The book finishes with an examination of the applications of Toroidal Electrophoresis.
The first book to offer a detailed account of Toroidal Electrophoresis—written by one of its creators
Compares the toroidal layouts with the well-established open layouts of the three most used platforms (Capillary, Microchip, and Slab) Provides solutions to many of the experimental issues arising in electromigration techniques and discusses the voltage distributors and detectors that are compatible with the toroidal layouts Richly illustrated with a large number of useful equations showing the relationships between important operational parameters and the performance indicators
is aimed at method developers and separation scientists working in clinical analysis, and food analysis, as well as those in pharmacology, disease biomarker applications, and nucleic acid analysis using the Capillary, Microchip, or slab Platform. It will also benefit undergraduate and graduate students of inorganic analytical chemistry, organic analytical chemistry, bioanalysis, pharmaceutical sciences, clinical sciences, and food analysis.

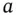 , in close contact with the crystal. The energy necessary to move this ion from this position (
, in close contact with the crystal. The energy necessary to move this ion from this position ( 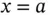 ) to infinity is found by replacing
) to infinity is found by replacing 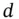 by
by 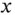 in equation 1.1and integrating it over
in equation 1.1and integrating it over 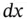 , from
, from 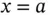 to infinity. The result is given by:
to infinity. The result is given by: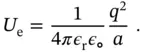
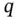 , and the resulting oppositely charged small crystal with charge
, and the resulting oppositely charged small crystal with charge 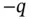 from
from 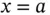 to infinity. From Table 1.1is possible to see that in water this required energy is 10 times smaller than what would be necessary, for instance, to perform the same operation in tetrahydrofuran, which has a relative permittivity of 7.6. All of this was calculated without counting the solvation phenomena, which favors water over most other solvents. In conclusion, both the electric forces among ions and the electrostatic energy change, which occurs when separating these ions from each other, is much smaller inside water than most of the solvents that are liquid at room temperature and one atmosphere of pressure.
to infinity. From Table 1.1is possible to see that in water this required energy is 10 times smaller than what would be necessary, for instance, to perform the same operation in tetrahydrofuran, which has a relative permittivity of 7.6. All of this was calculated without counting the solvation phenomena, which favors water over most other solvents. In conclusion, both the electric forces among ions and the electrostatic energy change, which occurs when separating these ions from each other, is much smaller inside water than most of the solvents that are liquid at room temperature and one atmosphere of pressure.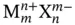 , are subjected to dissolution via a dissociation reaction when mixed in water. At the saturation point the following equilibrium is observed:
, are subjected to dissolution via a dissociation reaction when mixed in water. At the saturation point the following equilibrium is observed: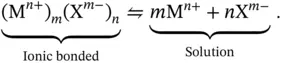
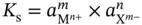 . This is also well recorded in the literature and is very useful for the theoretical modeling of problems in inorganic chemistry.
. This is also well recorded in the literature and is very useful for the theoretical modeling of problems in inorganic chemistry. of bulk water ( equation 1.1). At a given temperature there is a constant rate of ion production and recombination (H 3O ++ OH −→ 2H 2O), which leads to an equilibrium denoted by:
of bulk water ( equation 1.1). At a given temperature there is a constant rate of ion production and recombination (H 3O ++ OH −→ 2H 2O), which leads to an equilibrium denoted by: