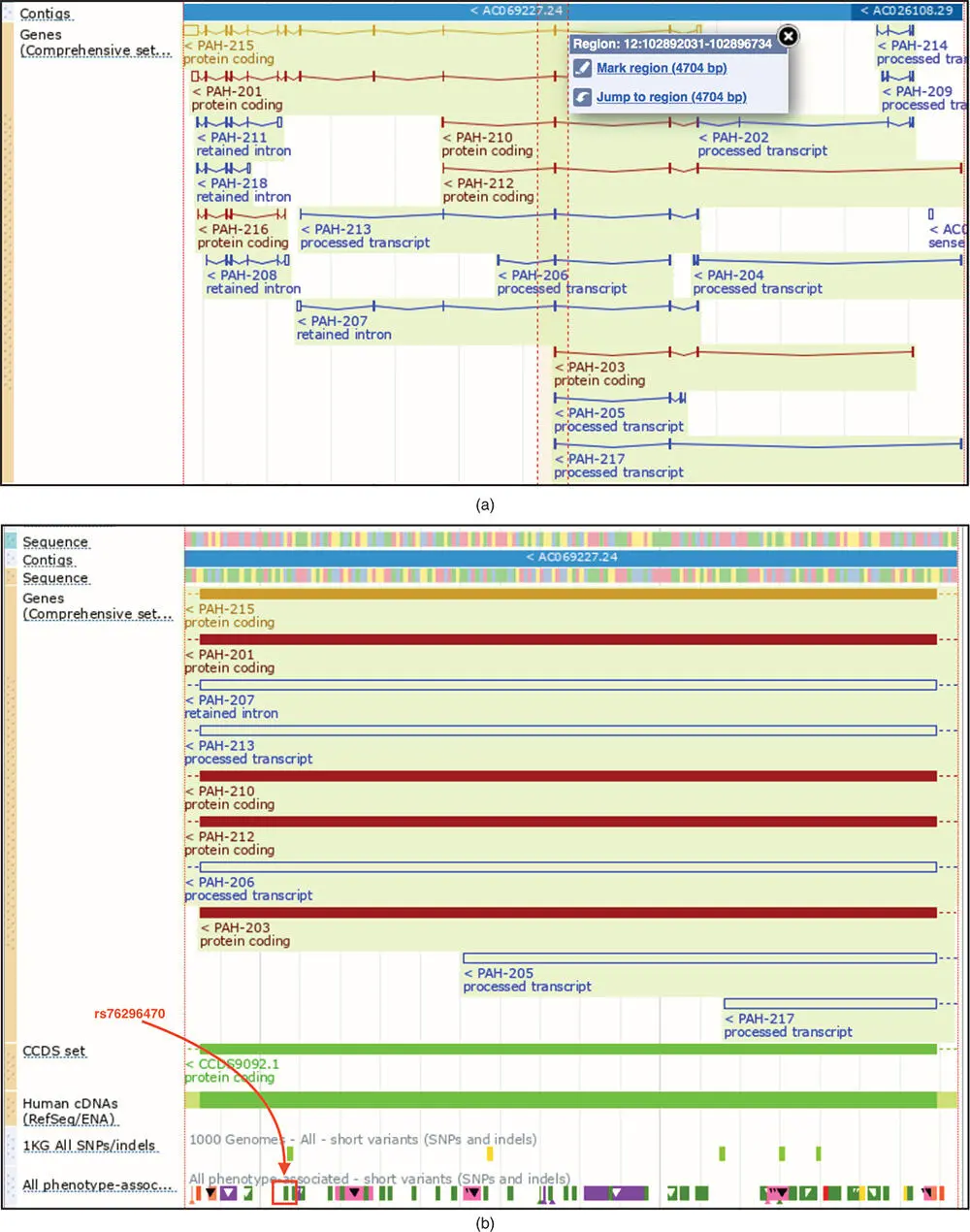
Figure 4.17 Zooming in on the bottom section of the Location tab from Figure 4.16. (a) Highlight a region of interest, the final exon of PAH transcript PAH-203 , by clicking the mouse and then scrolling to the left or right. In order to highlight the region, the Drag/Select toggle in the blue bar at the top of the section must first be set to Select . (b) To zoom in to the highlighted region, select Jump to region . It may take a few iterations to create the view in this figure. At the bottom of the window is a track labeled All phenotype-associated – short variants (SNPs and indels) . In this track, the SNP rs76296470 has been manually highlighted in red.
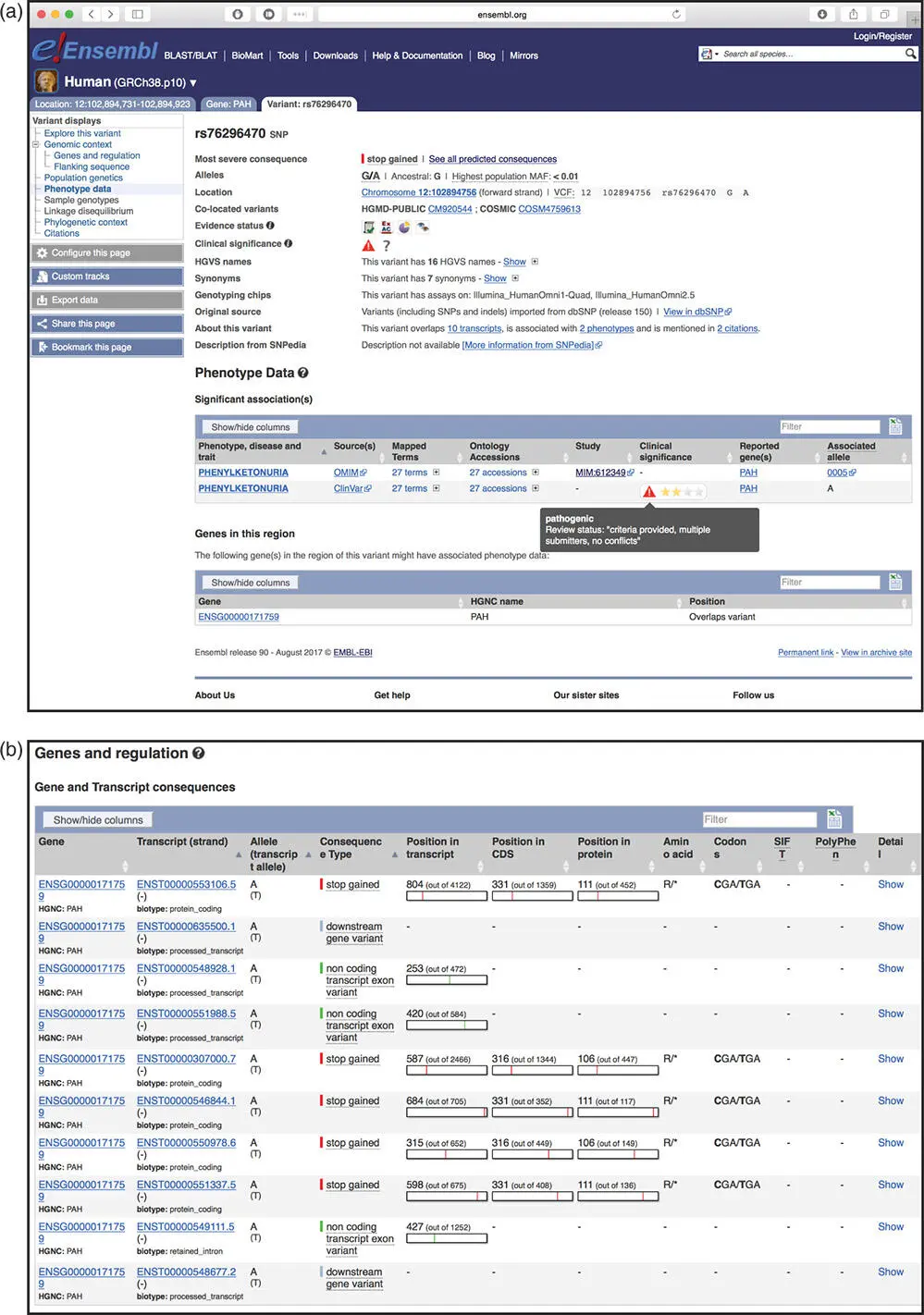
Figure 4.18 The Ensembl Variant tab. (a) To get more details about SNP rs76296470, click on the dark green SNP that is highlighted in red in the All phenotype-associated – short variants (SNPs and indels) track in Figure 4.17b. On the pop-up menu, click on more about rs76296470 . The Phenotype Data section of the Variant tab is available from the link in the blue sidebar. This variant is pathogenic for phenylketonuria. (b) The Genes and regulation section of the Variant tab shows the location and function of the variant in the transcripts that overlap it. Depending on the transcript, the SNP can change a codon to a stop codon (stop gained), map downstream of a gene, or map to a non-coding transcript. The transcripts in this view represent alternatively spliced forms of the gene PAH .
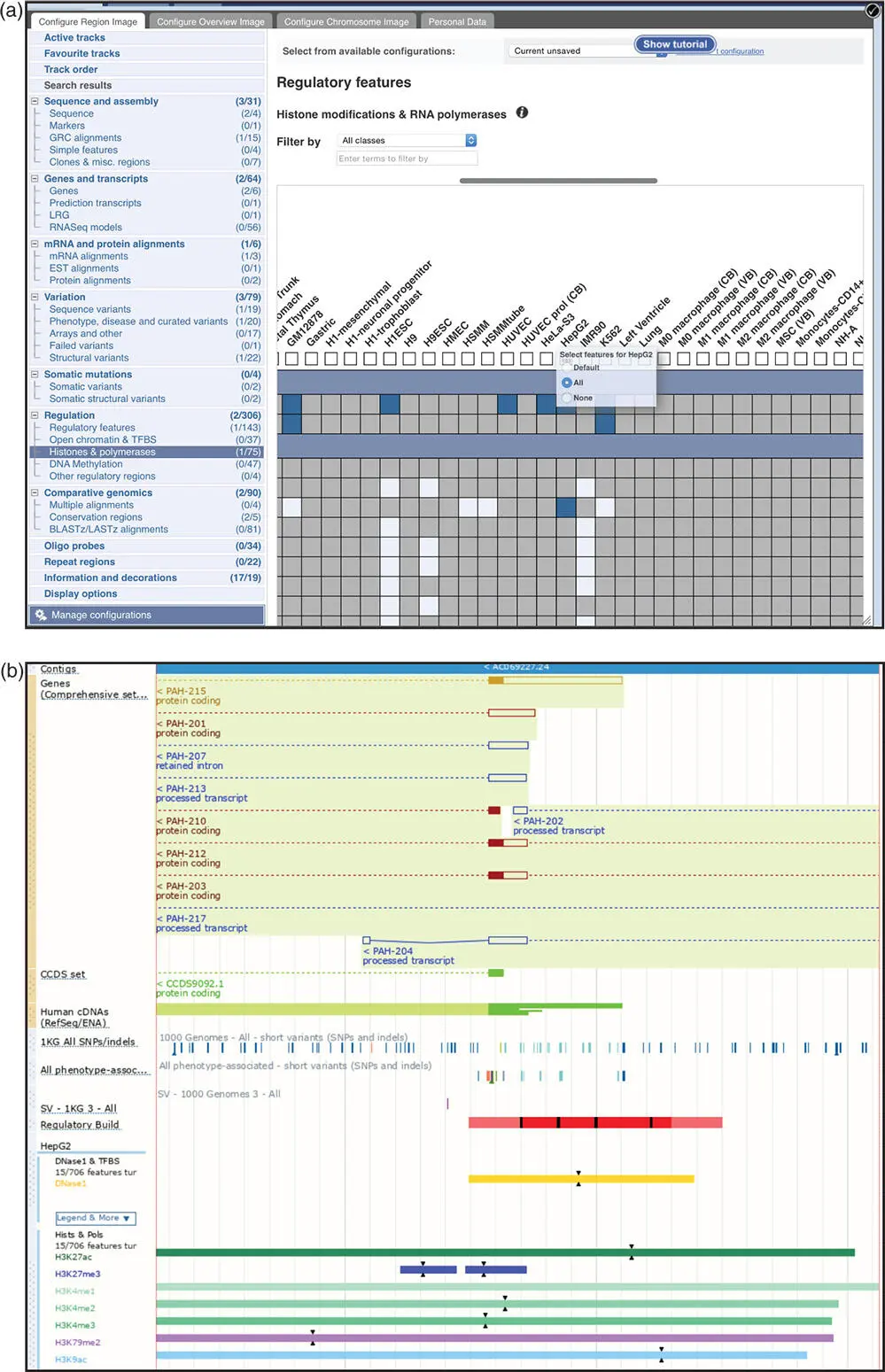
Figure 4.19 The Ensembl Regulatory Build track. (a) Go to Configure this page on the left side of the Location tab and select Regulation → Histones & polymerases . Scroll to the right to find the HepG2 (human liver cancer) cell type. Mouse over the text HepG2 and turn on all features. Clicking on the box under the cell type will change the track style; leave that set to the default of Peaks . Click on the black check mark on the upper right corner of the configuration window to save the settings and exit the setup. To turn on the DNase1 (DNaseI hypersensitive sites track), select Regulation → Open chromatin & TFBS and ensure that the DNase1 box in the HepG2 column is colored dark blue so that it is in the Shown configuration. Click on the black check mark on the upper right corner of the configuration window to save the settings again. (b) Back on the Region in detail section of the Location tab, zoom in to the first exon of transcript PAH-215. Note that the first exon is on the right end of the transcript, as the gene is transcribed from right to left. The resulting display shows the details of the Regulatory Build track. The figure legend (not shown) explains that the solid red box is a promoter. The DNaseI hypersensitive site and histone marks are also shown as colored boxes.
The left sidebar of the Location tab links to a number of additional useful resources. One of those, Comparative Genomics → Synteny displays blocks of synteny between the human chromosome featured in the Location tab and chromosomes from about 30 different organisms. In these syntenic blocks, the order of genes and other sequence features is conserved across the genomes being compared. Figure 4.20ashows the synteny between human chromosome 12 and the mouse genome. A cartoon of the human chromosome 12 is shown in the center of the display as a thick white rectangle, and mouse chromosomes are drawn on the sides as thinner white rectangles. Colored rectangles indicate regions of synteny between the human and mouse. For example, the light blue region on human chromosome 12 is syntenic to the light blue region on mouse chromosome 10. The region surrounding the PAH gene is outlined in red on both human chromosome 12 and mouse chromosome 10. Below the cartoon is a list of the human genes and corresponding mouse orthologs in the region of PAH . Selecting Region Comparison next to one of the genes opens a new Location tab that depicts the syntenic human and mouse chromosomes stacked on top of each other so that surrounding features can be compared directly ( Figure 4.20b). The upper panel shows the genomic context of the PAH gene on human chromosome 12 (top) and mouse chromosome 10 (bottom). Note that the genes are transcribed in opposite directions, so the order of the surrounding genes is flipped. The bottom panel is zoomed in on the PAH gene itself. The Regulatory Build track on the mouse assembly shows several regulatory features in this region. Further inspection of the regulatory feature that overlaps with the 5′ end of the mouse Pah gene reveals activating histone marks in liver and kidney cells, but not in other cell types (not shown), implying that the mouse Pah gene has similar expression patterns to its human ortholog. To reset the settings back to the default view, go to Configure this page in the left sidebar and select Reset configuration .
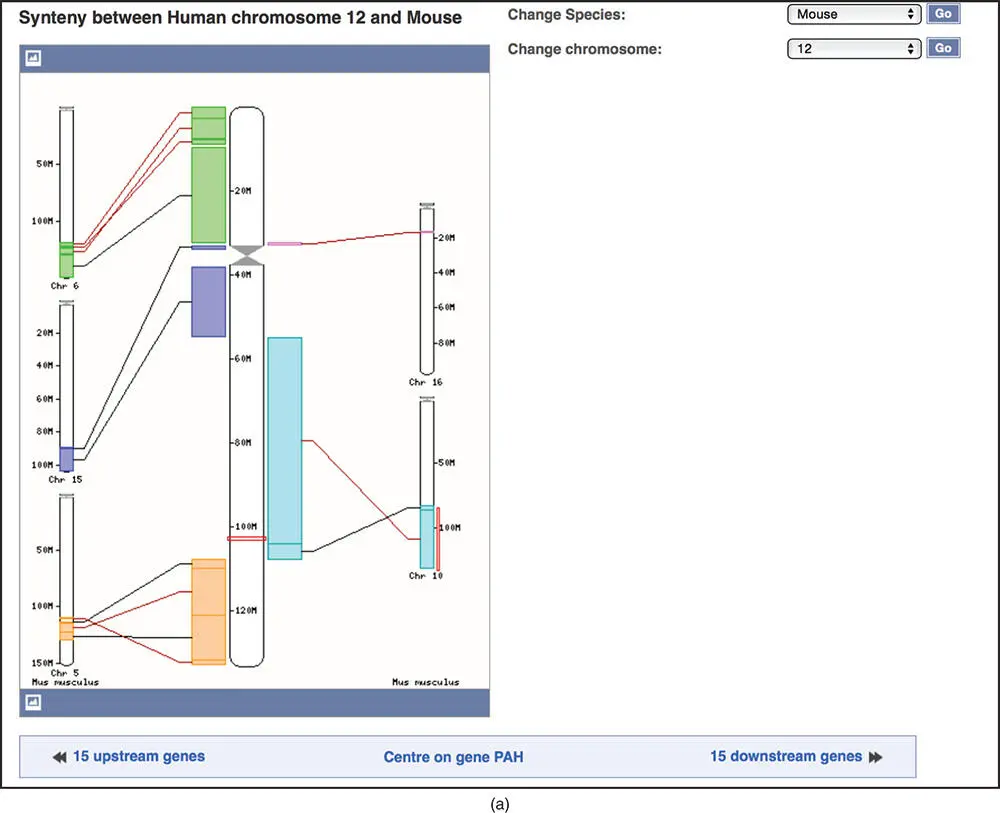
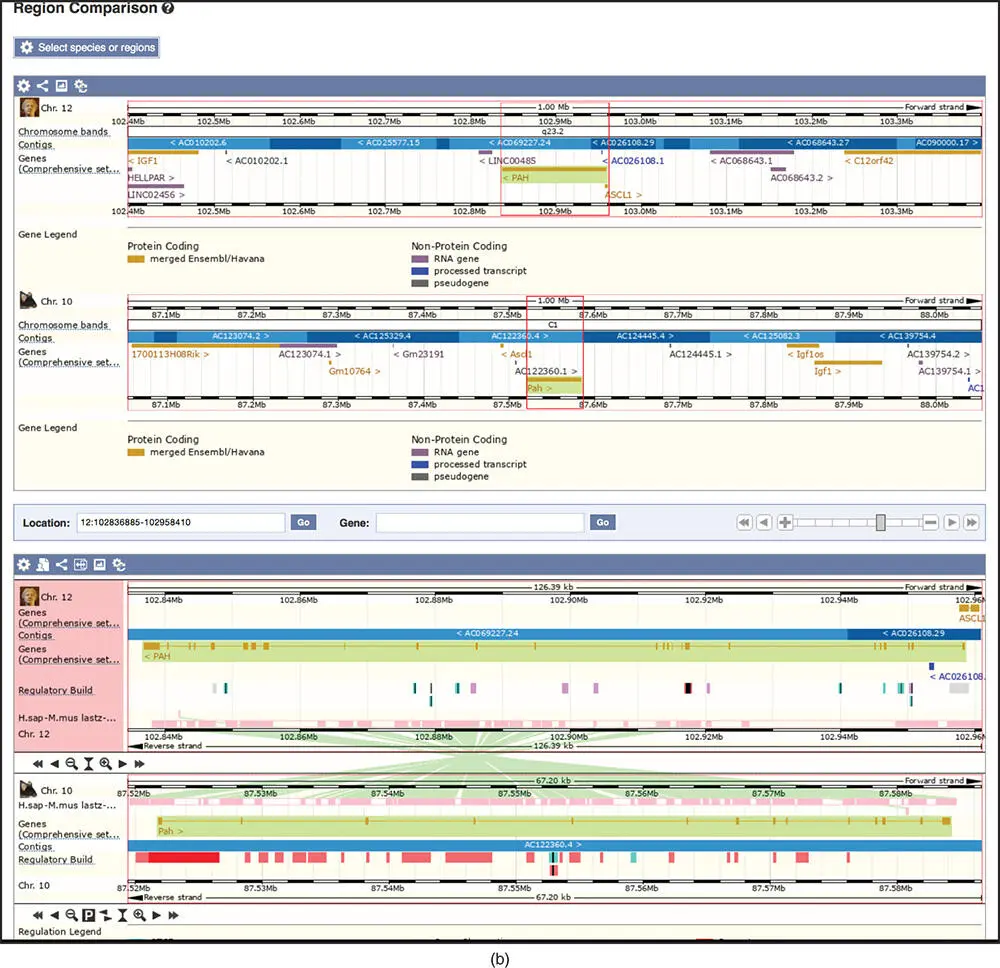
Figure 4.20 The Synteny view at Ensembl. (a) An overview of the syntenic blocks shared between human chromosome 12 and the mouse genome. The human chromosome is drawn in the middle of the display as a thick white box. The syntenic mouse chromosomes are represented by thinner white boxes along the side. The colored rectangles highlight regions of synteny between the human and mouse. A red outline illustrates the position of the PAH gene on the blue region of human chromosome 12 and on the blue region of mouse chromosome 10. (b) The Location tab for the PAH gene showing both the human and mouse syntenic regions. This is similar to the three-panel location tab shown in Figure 4.16, except that both the human and mouse genomes are depicted. The top panel (not shown) displays the full length human chromosome 12 and mouse chromosome 10. The second panel shows an overview of the genes in the region. The third panel focuses in on the PAH gene. Note that the regions in human and mouse appear to be presented in opposite orientations; in human, the PAH and IGF1 genes are both transcribed from right to left, while in mouse they are transcribed from left to right.
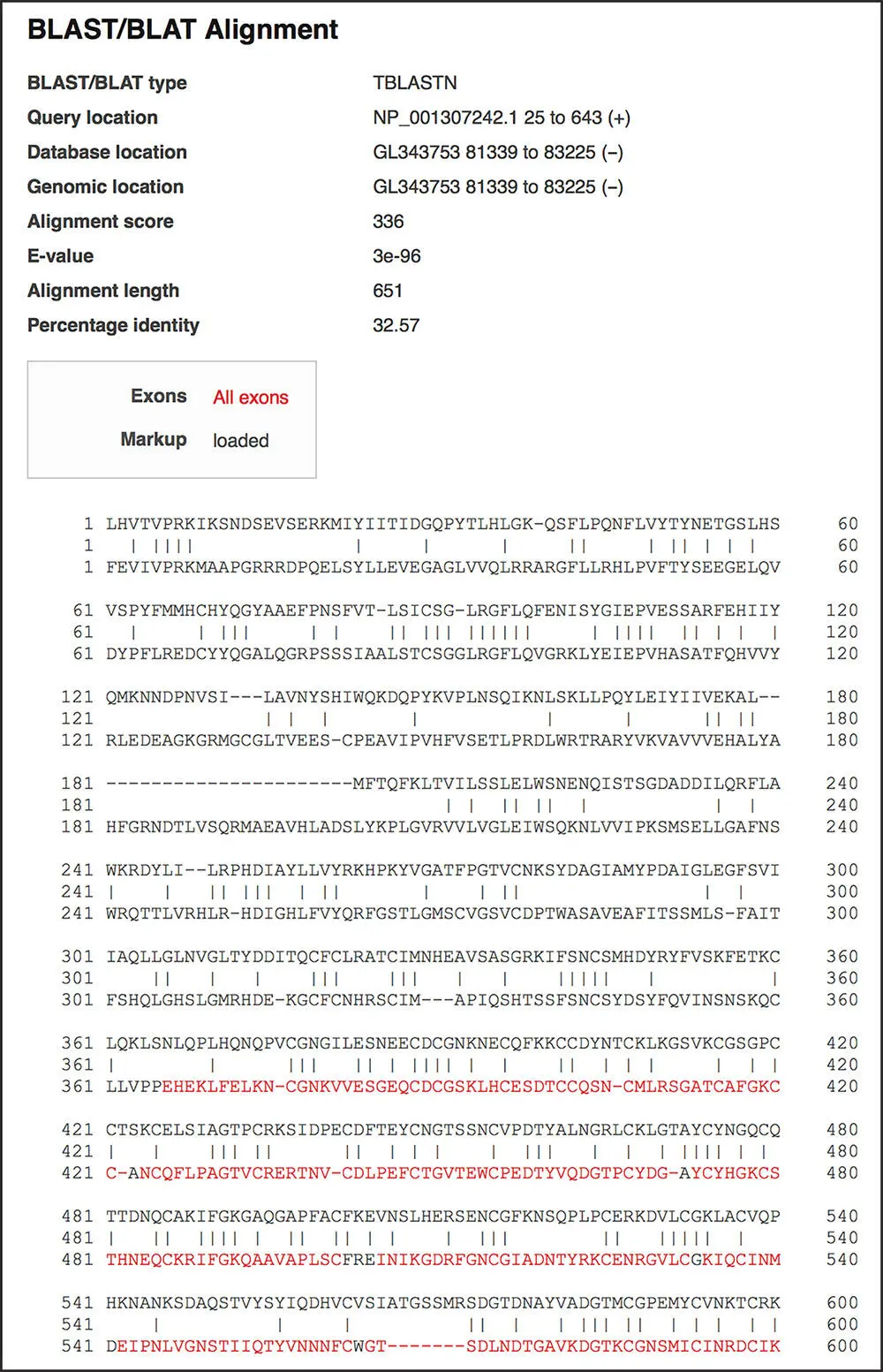
Figure 4.21 Ensembl BLAST output, showing an alignment between the human ADAM18 protein and the lizard genome translated in all six reading frames. On the BLAST/BLAT page at Ensembl, paste the FASTA-formatted sequence of human ADAM18, accession NP_001307242.1, into the Sequence data box. This sequence can be found at www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_001307242.1/?report=fasta. Select Genomic sequence from the anole lizard as the DNA database. On the results page, select the Alignment link next to the highest scoring hit in order to view the sequence alignment. The human protein sequence is on top, and the translated lizard genomic sequence is below. Lines indicate identical amino acids.
Читать дальше










