Another long-standing resource devoted to a specific organism is the Zebrafish Model Organism Database, or Zebrafish Information Network (ZFIN) (Howe et al. 2012) – a particularly attractive animal model given the experimental tractability of zebrafish in studying a wide variety of questions focused on vertebrate development, regeneration, inflammation, infectious disease, and drug discovery, to name a few. ZFIN provides a very simple search interface that allows free-text searches using any term. Using DCC once again as our search term brings the user to the summary page for the zebrafish dcc gene ( Figure 2.19), providing information on zebrafish mutants, sequence targeting reagents, transgenic constructs, orthology to other organisms, data on protein domains found within the Dcc protein product, and annotated gene expression and phenotype data derived from the literature or from direct submissions by members of the zebrafish community. Here, by following the link to the 19 figures in the Gene Expression section, one can examine full-size images illustrating expression patterns for dcc under various experimental conditions ( Figure 2.20).
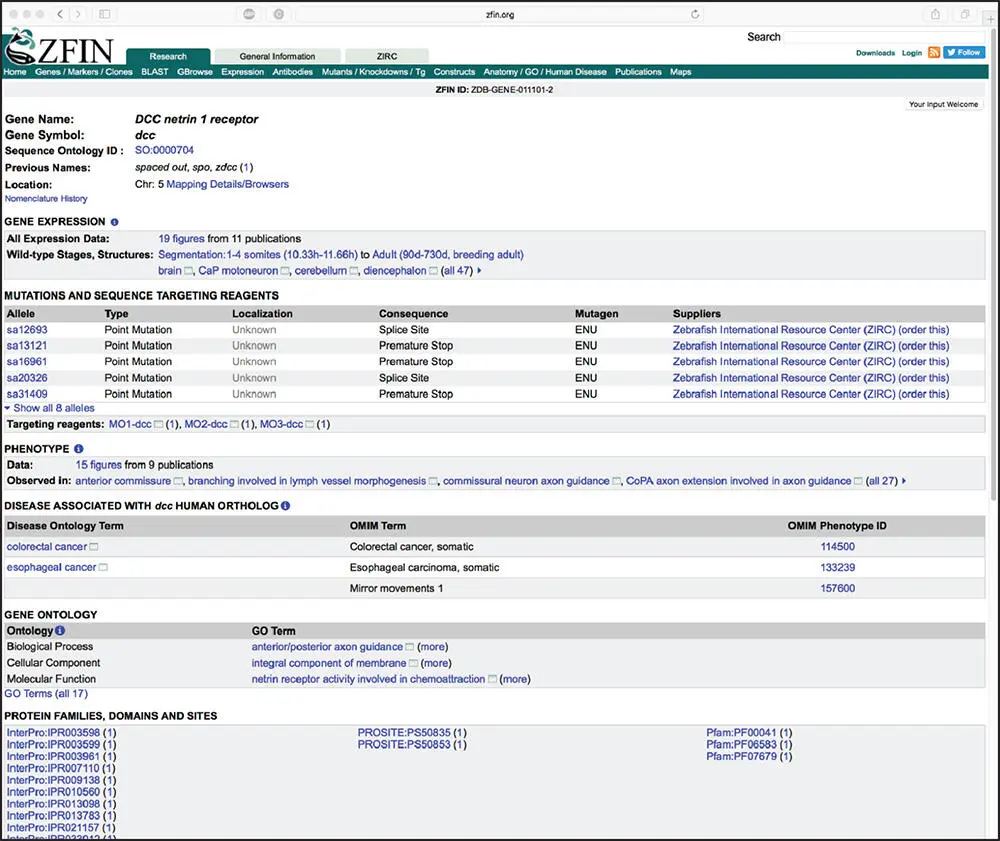
Figure 2.19 The Zebrafish Information Network (ZFIN) gene page for the dcc gene in zebrafish. This entry provides information on the ortholog to the human DCC gene. See text for details.
While MGD and ZFIN are excellent examples of model organism databases, every major model organism community maintains such a resource. These groups also collaborate to develop central portals to ease information retrieval across many of these resources through the Alliance of Genome Resources.
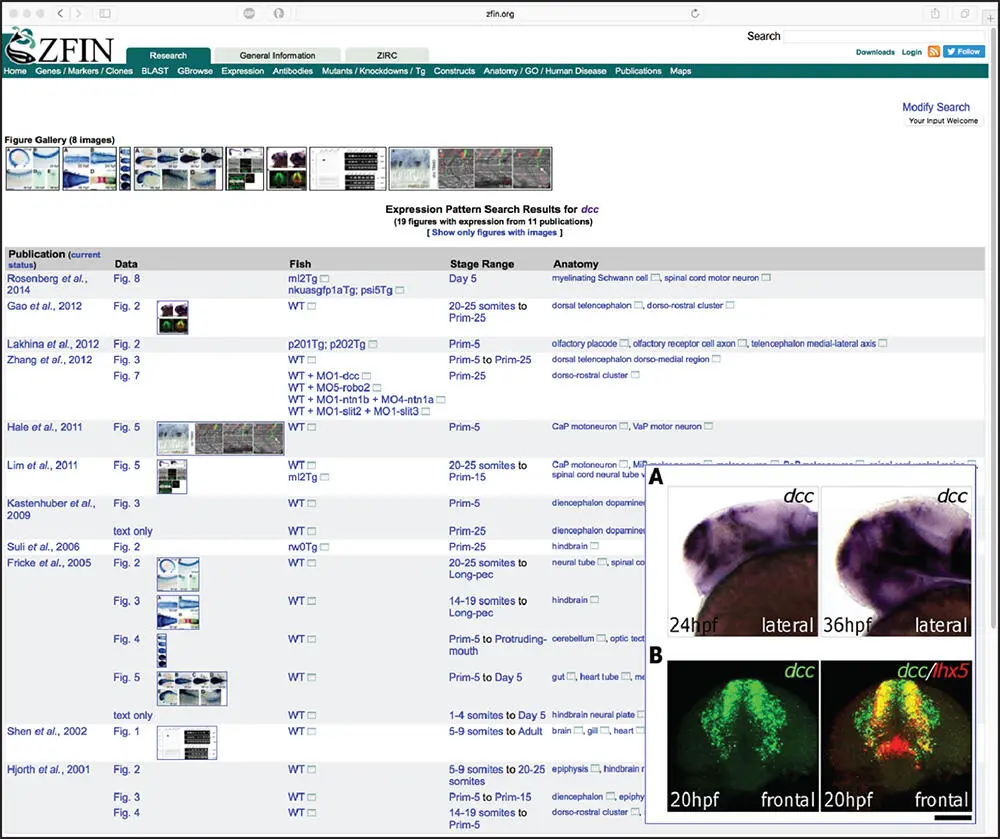
Figure 2.20 An example of gene expression data available through the Zebrafish Information Network (ZFIN), here showing the expression patterns for the zebrafish dcc gene under various experimental conditions. The inset displays a full-size image of data from Gao et al. (2012), showing the expression pattern for dcc in (panel A) and the co-expression of dcc and the Lim homeobox 5 gene ( lhx5 ; panel B).
As alluded to in the introduction to this chapter, the information space available to investigators will continue to expand at breakneck speed, with the size of GenBank alone doubling every year. Although the sheer magnitude of data can present a conundrum to the inexperienced user, mastery of the techniques covered in this chapter will allow researchers in all biological disciplines to make the best use of these data. The movement of modern science to “big data” approaches underscores the idea that both laboratory and computationally based strategies will be necessary in carrying out cutting-edge research. In the same way that investigators are trained in, for example, basic biochemistry and molecular biology methodologies, a basic understanding of bioinformatic techniques as part of the biologist's arsenal will be indispensable in the future. As is undoubtedly apparent at this point, there is no substitute for placing one's hands on the computer keyboard to learn how to search and use genomic sequence data effectively. Readers are strongly encouraged to take advantage of the resources presented here, to grow in confidence and capability by working with the available tools, and to begin to apply bioinformatic methods and strategies toward advancing their own research interests.
| Alliance of Genome Resources |
www.alliancegenome.org |
| Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) |
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST |
| ClinicalTrials.gov |
clinicaltrials.gov |
| DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ) |
www.ddbj.nig.ac.jp |
| European Molecular Biology Laboratory–European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) |
www.ebi.ac.uk |
| GenBank |
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank |
| iCn3D |
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/icn3d/docs/icn3d_about.html |
| Mouse Genome Database (MGD) |
informatics.jax.org |
| Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) |
omim.org |
| Protein Data Bank (PDB) |
www.rcsb.org/pdb |
| RefSeq |
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq |
| Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Database (dbSNP) |
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP |
| Vector Alignment Search Tool (VAST) |
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/VAST |
| Zebrafish Information Network (ZFIN) |
zfin.org |
1 Baxevanis, A.D. (2012). Searching Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) for information on genetic loci involved in human disease. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. Chapter 9, Unit 9.13.1–10. A protocol-driven description of the basic methodology for formulating OMIM searches and a discussion of the types of information available through OMIM, including descriptions of clinical manifestations resulting from genetic abnormalities.
2 Galperin, M.Y., Fernández-Suárez, X.M., and Rigden, D.J. (2017). The 24th annual Nucleic Acids Research database issue: a look back and upcoming changes. Nucleic Acids Res. 45: D1–D11. A curated, annual review of specialized databases of interest and importance to the biomedical research community.
1 Altschul, S., Gish, W., Miller, W. et al. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410.
2 Amberger, J.S., Bocchini, C.A., Schiettecatte, F. et al. (2014). OMIM.org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 43: D789–D798.
3 Benson, D.A., Cavanaugh, M., Clark, K. et al. (2017). GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 45: D37–D42.
4 Bult, C.J., Eppig, J.T., Blake, J.A. et al. (2016). Mouse genome database 2016. Nucleic Acids Res. 44: D840–D847.
5 Collins, F.S., Patrinos, A., Jordan, E. et al., and Members of the DOE and NIH Planning Groups (1998). New goals for the U.S. Human Genome Project: 1998–2003. Science. 282: 682–689.
6 Collins, F.S., Green, E.D., Guttmacher, A.E., and Guyer, M.S., on behalf of the U.S. National Human Genome Research Institute (2003). A vision for the future of genomics research. Nature. 422: 835–847.
7 Finci, L.I., Krüger, N., Sun, X. et al. (2014). The crystal structure of netrin-1 in complex with DCC reveals the bifunctionality of netrin-1 as a guidance cue. Neuron. 83: 839–849.
8 Galperin, M.Y., Fernández-Suárez, X.M., and Rigden, D.J. (2017). The 24th annual Nucleic Acids Research database issue: a look back and upcoming changes. Nucleic Acids Res. 45: D1–D11.
9 Gao, J., Zhang, C., Yang, B. et al. (2012). Dcc regulates asymmetric outgrowth of forebrain neurons in zebrafish. PLoS One. 7: e36516.
10 Gibrat, J.-F., Madej, T., and Bryant, S. (1996). Surprising similarities in structure comparison. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 6: 377–385.
11 Green, E.D. and Guyer, M.S., and The National Human Genome Research Institute (2011). Charting a course for genomic medicine from basepairs to bedside. Nature. 470: 204–213.
12 Howe, D.G., Bradford, Y.M., Conlin, T. et al. (2012). ZFIN, the Zebrafish Model Organism Database: increased support for mutants and transgenics. Nucleic Acids Res. 41: D854–D860.
Читать дальше






