(2.5) 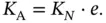
Hence, if Basil uses long frames and applies the law of large numbers, then he can have a good guess at the number of contending sensors and practically choose the reservation frame size 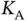 in an optimal way.
in an optimal way.
The equation (2.5)can give us further very important insights into the random access protocols. Let us, for a moment, put aside the frame structure considered until now, in which Basil first lets the sensors contend using short reservation frames and then allocates data slots to the successful contenders. Instead, consider the following situation. A very large population of sensors is synchronized to Basil. A periodic frame of 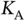 data slots and duration of
data slots and duration of 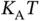 is used, without any additional overhead at the frame start, since all sensors and Basil are assumed to be perfectly synchronized and thus have a perfect knowledge about the moment at which a frame starts. Each sensor that got data to send before the start of the
is used, without any additional overhead at the frame start, since all sensors and Basil are assumed to be perfectly synchronized and thus have a perfect knowledge about the moment at which a frame starts. Each sensor that got data to send before the start of the 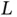 th frame, chooses a random number
th frame, chooses a random number 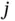 between 1 and
between 1 and 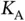 and sends its data in the
and sends its data in the 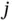 th slot of the
th slot of the 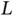 th frame. At the end of the frame, all sensors that sent data successfully receive feedback from Basil. This feedback is assumed to be sent extremely quickly, taking practically zero time. The sensors that did not send the data successfully, treat their data packet as a newly arrived one during the
th frame. At the end of the frame, all sensors that sent data successfully receive feedback from Basil. This feedback is assumed to be sent extremely quickly, taking practically zero time. The sensors that did not send the data successfully, treat their data packet as a newly arrived one during the 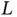 th frame and try again in the
th frame and try again in the 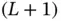 th frame. Looking again at the equation (2.5), we can interpret it as follows: if the number of newly arrived requests during each frame of duration
th frame. Looking again at the equation (2.5), we can interpret it as follows: if the number of newly arrived requests during each frame of duration 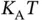 is
is 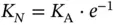 , then this number is equal to the number of successfully sent requests in a frame. Hence, the system is in equilibrium in the sense that each arrived request eventually gets served. Therefore the throughput of this system is, calculated in number of requests (packets) per unit time, is:
, then this number is equal to the number of successfully sent requests in a frame. Hence, the system is in equilibrium in the sense that each arrived request eventually gets served. Therefore the throughput of this system is, calculated in number of requests (packets) per unit time, is:
(2.6) 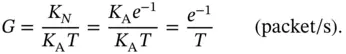
Note that, due to the absence of overhead, here the throughput is equal to the goodput. If we take 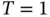 , then the throughput is conveniently expressed in packets per slot and we arrive at the well known formula for maximal throughput of a slotted ALOHA system equal to
, then the throughput is conveniently expressed in packets per slot and we arrive at the well known formula for maximal throughput of a slotted ALOHA system equal to  packets per slot.
packets per slot.
However, what does this theoretical value of the ALOHA throughput mean for a practical system? The randomized protocol coordinates the sensor transmissions, such that each sensor eventually transmits its request successfully. The presented analysis captures the following extreme case: the total population of sensors  is very large, practically infinite, and each new request comes from a new sensor, which also means that each sensor has only one request. Such a hypothetical scenario represents the most difficult case for coordination among the sensors. In the following we provide the reasoning behind the choice of the infinite-size sensor population.
is very large, practically infinite, and each new request comes from a new sensor, which also means that each sensor has only one request. Such a hypothetical scenario represents the most difficult case for coordination among the sensors. In the following we provide the reasoning behind the choice of the infinite-size sensor population.
Instead of 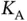 active sensors, each with a single request, we consider
active sensors, each with a single request, we consider 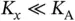 sensors, where each sensor has
sensors, where each sensor has 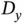 packets. The total number of packets to be sent in the system is
packets. The total number of packets to be sent in the system is 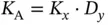 , which makes the overall traffic load equal to the case with
, which makes the overall traffic load equal to the case with 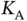 single-packet users. The following protocol is run by each sensor. The sensor Zoya applies the framed ALOHA protocol until it successfully sends her first request. After succeeding, Zoya records (a) the number of sensors
single-packet users. The following protocol is run by each sensor. The sensor Zoya applies the framed ALOHA protocol until it successfully sends her first request. After succeeding, Zoya records (a) the number of sensors 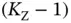 that sent their first requests successfully before Zoya, which she learns from Basil's feedback; (b) puts on hold her access until the remaining
that sent their first requests successfully before Zoya, which she learns from Basil's feedback; (b) puts on hold her access until the remaining 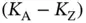 sensors have sent their first requests successfully. Note that, after this randomized contention is finalized, Zoya has a unique number
sensors have sent their first requests successfully. Note that, after this randomized contention is finalized, Zoya has a unique number 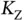 , where
, where 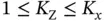 . Since every sensor applies the same protocol, each sensor has a unique token , which is a number between 1 and
. Since every sensor applies the same protocol, each sensor has a unique token , which is a number between 1 and 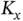 . After contending to send the first request and obtaining the token, the
. After contending to send the first request and obtaining the token, the 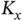 sensors no longer need to contend, but they are served through a TDMA frame with
sensors no longer need to contend, but they are served through a TDMA frame with 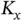 slots, where, for example, the slot number
slots, where, for example, the slot number 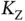 is allocated to Zoya. This is reminiscent of the use of random access as a technique for initial access, after which the transmissions are coordinated and scheduled.
is allocated to Zoya. This is reminiscent of the use of random access as a technique for initial access, after which the transmissions are coordinated and scheduled.
Читать дальше

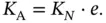
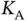 in an optimal way.
in an optimal way.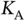 data slots and duration of
data slots and duration of 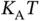 is used, without any additional overhead at the frame start, since all sensors and Basil are assumed to be perfectly synchronized and thus have a perfect knowledge about the moment at which a frame starts. Each sensor that got data to send before the start of the
is used, without any additional overhead at the frame start, since all sensors and Basil are assumed to be perfectly synchronized and thus have a perfect knowledge about the moment at which a frame starts. Each sensor that got data to send before the start of the 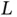 th frame, chooses a random number
th frame, chooses a random number 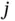 between 1 and
between 1 and 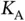 and sends its data in the
and sends its data in the 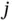 th slot of the
th slot of the 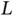 th frame. At the end of the frame, all sensors that sent data successfully receive feedback from Basil. This feedback is assumed to be sent extremely quickly, taking practically zero time. The sensors that did not send the data successfully, treat their data packet as a newly arrived one during the
th frame. At the end of the frame, all sensors that sent data successfully receive feedback from Basil. This feedback is assumed to be sent extremely quickly, taking practically zero time. The sensors that did not send the data successfully, treat their data packet as a newly arrived one during the 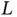 th frame and try again in the
th frame and try again in the 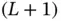 th frame. Looking again at the equation (2.5), we can interpret it as follows: if the number of newly arrived requests during each frame of duration
th frame. Looking again at the equation (2.5), we can interpret it as follows: if the number of newly arrived requests during each frame of duration 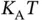 is
is 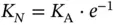 , then this number is equal to the number of successfully sent requests in a frame. Hence, the system is in equilibrium in the sense that each arrived request eventually gets served. Therefore the throughput of this system is, calculated in number of requests (packets) per unit time, is:
, then this number is equal to the number of successfully sent requests in a frame. Hence, the system is in equilibrium in the sense that each arrived request eventually gets served. Therefore the throughput of this system is, calculated in number of requests (packets) per unit time, is: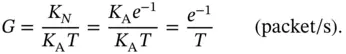
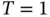 , then the throughput is conveniently expressed in packets per slot and we arrive at the well known formula for maximal throughput of a slotted ALOHA system equal to
, then the throughput is conveniently expressed in packets per slot and we arrive at the well known formula for maximal throughput of a slotted ALOHA system equal to  packets per slot.
packets per slot. is very large, practically infinite, and each new request comes from a new sensor, which also means that each sensor has only one request. Such a hypothetical scenario represents the most difficult case for coordination among the sensors. In the following we provide the reasoning behind the choice of the infinite-size sensor population.
is very large, practically infinite, and each new request comes from a new sensor, which also means that each sensor has only one request. Such a hypothetical scenario represents the most difficult case for coordination among the sensors. In the following we provide the reasoning behind the choice of the infinite-size sensor population. active sensors, each with a single request, we consider
active sensors, each with a single request, we consider 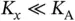 sensors, where each sensor has
sensors, where each sensor has 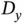 packets. The total number of packets to be sent in the system is
packets. The total number of packets to be sent in the system is 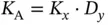 , which makes the overall traffic load equal to the case with
, which makes the overall traffic load equal to the case with 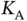 single-packet users. The following protocol is run by each sensor. The sensor Zoya applies the framed ALOHA protocol until it successfully sends her first request. After succeeding, Zoya records (a) the number of sensors
single-packet users. The following protocol is run by each sensor. The sensor Zoya applies the framed ALOHA protocol until it successfully sends her first request. After succeeding, Zoya records (a) the number of sensors 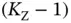 that sent their first requests successfully before Zoya, which she learns from Basil's feedback; (b) puts on hold her access until the remaining
that sent their first requests successfully before Zoya, which she learns from Basil's feedback; (b) puts on hold her access until the remaining 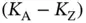 sensors have sent their first requests successfully. Note that, after this randomized contention is finalized, Zoya has a unique number
sensors have sent their first requests successfully. Note that, after this randomized contention is finalized, Zoya has a unique number 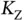 , where
, where 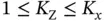 . Since every sensor applies the same protocol, each sensor has a unique token , which is a number between 1 and
. Since every sensor applies the same protocol, each sensor has a unique token , which is a number between 1 and 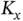 . After contending to send the first request and obtaining the token, the
. After contending to send the first request and obtaining the token, the 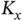 sensors no longer need to contend, but they are served through a TDMA frame with
sensors no longer need to contend, but they are served through a TDMA frame with 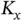 slots, where, for example, the slot number
slots, where, for example, the slot number 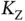 is allocated to Zoya. This is reminiscent of the use of random access as a technique for initial access, after which the transmissions are coordinated and scheduled.
is allocated to Zoya. This is reminiscent of the use of random access as a technique for initial access, after which the transmissions are coordinated and scheduled.










