7 Chapter 8Table 8.1 Accident types.Table 8.2 Causes of airplane accidents 1992–2001.Table 8.3 Causes of car accidents (Example 8.4).Table 8.4 Basic risk factors.Table 8.5 Attributes of interactive complexity.Table 8.6 Attributes of tight coupling.Table 8.7 Characteristics of tight and loose coupling systems.Table 8.8 A brief comparison of accident models.
8 Chapter 9Table 9.1 A simple data dossier for a risk analysis.
9 Chapter 10Table 10.1 Hazards for a ship (Example 10.1).Table 10.2 List of generic hazardous events on offshore oil and gas installat...Table 10.3 Process/system checklist for the design phase.Table 10.4 Questions used to identify hazards (partly based on CCOHS (2009)).Table 10.5 Generic HAZOP guidewords.Table 10.6 Extract of interpretation of HAZOP guidewords for use in CHAZOP (C...Table 10.7 Generic causes of unsafe control actions.
10 Chapter 11Table 11.1 Some basic causes of hazardous events.Table 11.2 Fault tree symbols.Table 11.3 Criticality ranking of minimal cut sets of order 2.Table 11.4 Example of a conditional probability table (CPT) for a node with t...Table 11.5 Truth table for a fault tree with a singleAND‐gate and two basic e...Table 11.6 Conditional probability table corresponding to a fault tree with a...Table 11.7 Conditional probability table corresponding to a fault tree with a...Table 11.8 Possible states of a system of two pumps.Table 11.9 Possible states for the pumping system in Example 11.3 .
11 Chapter 13Table 13.1 Comparison of the 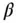 ‐factor model, the MGL model, and the
‐factor model, the MGL model, and the 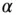 ‐fact...
‐fact...
12 Chapter 14Table 14.1 Intervals of the average probability of failure on demand ( 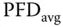 ) an...Table 14.2 Survey of relevant risk‐influencing factors (RIFs).Table 14.3 State scores for RIFs.
) an...Table 14.2 Survey of relevant risk‐influencing factors (RIFs).Table 14.3 State scores for RIFs.
13 Chapter 15Table 15.1 Typical human errors.Table 15.2 Errors of omission and errors of commission.Table 15.3 Performance‐influencing factors (not exhaustive).Table 15.4 Human HAZOP guidewords.Table 15.5 Human HAZOP guidewords.Table 15.6 SHERPA error mode taxonomy.
14 Chapter 16Table 16.1 Examples of activity types in the MIRMAP risk models
15 Chapter 17Table 17.1 Examples of potential internal and external threat actors.Table 17.2 Simple threat rating.Table 17.3 Procedure for rating threat actors (constructed example).Table 17.4 Vulnerability rating.Table 17.5 Procedure for rating vulnerabilities (constructed example).
1 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 The Beauvais Cathedral (Source: Photo by David Iliff. License: CC...
2 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1 Hazard (a), event (b), and consequence (c) (Example 2.4). Figure 2.2 An accident scenario and related concepts illustrated in a bow‐ti... Figure 2.3 Two different choices of hazardous events, (a) early in the event... Figure 2.4 Failure and fault of a degrading item. Figure 2.5 Consequence spectrum for a hazardous event. Figure 2.6 Loss spectrum for a hazardous event 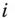 . Figure 2.7 The concepts of threat, threat actor, and vulnerability.
. Figure 2.7 The concepts of threat, threat actor, and vulnerability.
3 Chapter 3 Figure 3.1 Risk assessment as a combination of risk analysis and risk evalua... Figure 3.2 The six steps of a risk assessment. Figure 3.3 Step 1: Plan the risk assessment. Figure 3.4 Risk assessment in the decision‐making process. Figure 3.5 Step 2: Define the study. Figure 3.6 Step 3: Identify hazards and initiating events. Figure 3.7 Step 4: Develop accident scenarios and describe consequences. Figure 3.8 Step 5: Determine and assess the risk.
4 Chapter 4 Figure 4.1 System breakdown structure (simplified). Figure 4.2 A system and its boundary. Figure 4.3 Black box model for a component function. Figure 4.4 The system modeling and analysis process. Figure 4.5 Analysis versus synthesis.
5 Chapter 5 Figure 5.1 The ALARP principle.
6 Chapter 6 Figure 6.1 The application of a risk metric and a safety performance metric.Figure 6.2 Risk contour plot where several people are exposed to hazards.Figure 6.3 Risk contour plot example.Figure 6.4 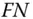 curve example.Figure 6.5
curve example.Figure 6.5 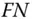 curve example.Figure 6.6
curve example.Figure 6.6 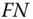 criterion lines (example).Figure 6.7 Risk matrix.
criterion lines (example).Figure 6.7 Risk matrix.
7 Chapter 7Figure 7.1 Risk management process.Figure 7.2 Decision framework.Figure 7.3 Elements of RIDM.
8 Chapter 8Figure 8.1 Three main categories of accidents.Figure 8.2 The hazard‐barrier‐asset model.Figure 8.3 Haddon's matrix (example for a traffic accident).Figure 8.4 The domino model.Figure 8.5 The main elements of the loss causation model.Figure 8.6 Rasmussen and Svedung's accident model.Figure 8.7 STEP diagram (main elements).Figure 8.8 Reason's Swiss cheese model.Figure 8.9 The three feet of Tripod‐Delta: basic risk factors, hazards and u...Figure 8.10 The Tripod accident causation model.Figure 8.11 Updated Tripod‐Delta accident causation model.Figure 8.12 The basic HEMP model as part of Tripod‐Beta.Figure 8.13 MTO diagram (main elements).Figure 8.14 The top structure of a generic MORT chart.Figure 8.15 Hierarchical model of sociotechnical system involved in risk man...Figure 8.16 Boundaries of safe operation.Figure 8.17 AcciMap structure and symbols.Figure 8.18 Interactions and coupling.Figure 8.19 Standard control loop.
9 Chapter 9Figure 9.1 Example of a reliability data dossier.
10 Chapter 10Figure 10.1 Analysis workflow for PHA.Figure 10.2 Hazards and threats in various locations of the study object.Figure 10.3 Sample PHA worksheet.Figure 10.4 Sample HAZID worksheet.Figure 10.5 Analysis workflow for JSA.Figure 10.6 JSA worksheet (example).Figure 10.7 Alternative JSA worksheet.Figure 10.8 Analysis workflow for FMECA.Figure 10.9 Example of an FMECA worksheet.Figure 10.10 Analysis workflow for HAZOP.Figure 10.11 HAZOP worksheet for “filling a bucket with water.”Figure 10.12 Analysis workflow for STPA.Figure 10.13 Tables for reporting the STPA.Figure 10.14 Analysis workflow for SWIFT.Figure 10.15 Example of a SWIFT worksheet for Example 10.14 .Figure 10.16 Comparison of hazard identification methods.Figure 10.17 Analysis workflow for change analysis.Figure 10.18 Simple hazard log (example).Figure 10.19 Hazard log (example).Figure 10.20 Building site (example). Figure 10.21 Water tank.
11 Chapter 11Figure 11.1 The main elements of a cause and effect diagram.Figure 11.2 Oil and gas separator in Example 11.1 .Figure 11.3 Fault tree for the shutdown system in Example 11.1 .Figure 11.4 Primary failure, secondary failure, and command fault for a pres...Figure 11.5 Explicit modeling of a common‐cause failure in a system of two p...Figure 11.6 Relationship between some simple fault tree diagrams and reliabi...Figure 11.7 The TOP event will occur if at least one of the 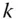 minimal cut ...Figure 11.8 Example of a fault tree.Figure 11.9 Reliability block diagram corresponding to the fault tree in Fig...Figure 11.10 Fault tree with a single AND‐gate.Figure 11.11 Fault tree with single OR‐gate.Figure 11.12 Fire water system (Example 11.3).Figure 11.13 Fault tree for the fire water system in Example 11.3 .Figure 11.14 Reliability block diagram for the fire water system in Example ...Figure 11.15 Alternative fault tree for the fire water system in Example 11....Figure 11.16 A simple Bayesian network.Figure 11.17 Example of a Bayesian network showing technical, human, and org...Figure 11.18 Bayesian network.Figure 11.19 Fault tree with single AND‐gate and the corresponding Bayesian ...Figure 11.20 Fault tree with single OR‐gate and the corresponding Bayesian n...Figure 11.21 Bayesian network for Example 11.7 .Figure 11.22 State transition diagram for the pump system in Example 11.8 .Figure 11.23 State transition diagram for a single component (function‐repai...Figure 11.24 The availability and the survivor function of a single componen...Figure 11.25 Water supply system.Figure 11.26 Gas detection system.
minimal cut ...Figure 11.8 Example of a fault tree.Figure 11.9 Reliability block diagram corresponding to the fault tree in Fig...Figure 11.10 Fault tree with a single AND‐gate.Figure 11.11 Fault tree with single OR‐gate.Figure 11.12 Fire water system (Example 11.3).Figure 11.13 Fault tree for the fire water system in Example 11.3 .Figure 11.14 Reliability block diagram for the fire water system in Example ...Figure 11.15 Alternative fault tree for the fire water system in Example 11....Figure 11.16 A simple Bayesian network.Figure 11.17 Example of a Bayesian network showing technical, human, and org...Figure 11.18 Bayesian network.Figure 11.19 Fault tree with single AND‐gate and the corresponding Bayesian ...Figure 11.20 Fault tree with single OR‐gate and the corresponding Bayesian n...Figure 11.21 Bayesian network for Example 11.7 .Figure 11.22 State transition diagram for the pump system in Example 11.8 .Figure 11.23 State transition diagram for a single component (function‐repai...Figure 11.24 The availability and the survivor function of a single componen...Figure 11.25 Water supply system.Figure 11.26 Gas detection system.
Читать дальше

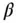 ‐factor model, the MGL model, and the
‐factor model, the MGL model, and the 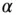 ‐fact...
‐fact...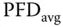 ) an...Table 14.2 Survey of relevant risk‐influencing factors (RIFs).Table 14.3 State scores for RIFs.
) an...Table 14.2 Survey of relevant risk‐influencing factors (RIFs).Table 14.3 State scores for RIFs.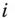 . Figure 2.7 The concepts of threat, threat actor, and vulnerability.
. Figure 2.7 The concepts of threat, threat actor, and vulnerability.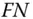 curve example.Figure 6.5
curve example.Figure 6.5 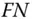 curve example.Figure 6.6
curve example.Figure 6.6 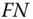 criterion lines (example).Figure 6.7 Risk matrix.
criterion lines (example).Figure 6.7 Risk matrix.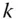 minimal cut ...Figure 11.8 Example of a fault tree.Figure 11.9 Reliability block diagram corresponding to the fault tree in Fig...Figure 11.10 Fault tree with a single AND‐gate.Figure 11.11 Fault tree with single OR‐gate.Figure 11.12 Fire water system (Example 11.3).Figure 11.13 Fault tree for the fire water system in Example 11.3 .Figure 11.14 Reliability block diagram for the fire water system in Example ...Figure 11.15 Alternative fault tree for the fire water system in Example 11....Figure 11.16 A simple Bayesian network.Figure 11.17 Example of a Bayesian network showing technical, human, and org...Figure 11.18 Bayesian network.Figure 11.19 Fault tree with single AND‐gate and the corresponding Bayesian ...Figure 11.20 Fault tree with single OR‐gate and the corresponding Bayesian n...Figure 11.21 Bayesian network for Example 11.7 .Figure 11.22 State transition diagram for the pump system in Example 11.8 .Figure 11.23 State transition diagram for a single component (function‐repai...Figure 11.24 The availability and the survivor function of a single componen...Figure 11.25 Water supply system.Figure 11.26 Gas detection system.
minimal cut ...Figure 11.8 Example of a fault tree.Figure 11.9 Reliability block diagram corresponding to the fault tree in Fig...Figure 11.10 Fault tree with a single AND‐gate.Figure 11.11 Fault tree with single OR‐gate.Figure 11.12 Fire water system (Example 11.3).Figure 11.13 Fault tree for the fire water system in Example 11.3 .Figure 11.14 Reliability block diagram for the fire water system in Example ...Figure 11.15 Alternative fault tree for the fire water system in Example 11....Figure 11.16 A simple Bayesian network.Figure 11.17 Example of a Bayesian network showing technical, human, and org...Figure 11.18 Bayesian network.Figure 11.19 Fault tree with single AND‐gate and the corresponding Bayesian ...Figure 11.20 Fault tree with single OR‐gate and the corresponding Bayesian n...Figure 11.21 Bayesian network for Example 11.7 .Figure 11.22 State transition diagram for the pump system in Example 11.8 .Figure 11.23 State transition diagram for a single component (function‐repai...Figure 11.24 The availability and the survivor function of a single componen...Figure 11.25 Water supply system.Figure 11.26 Gas detection system.










