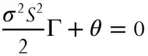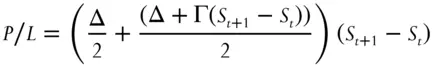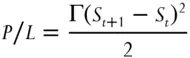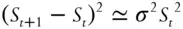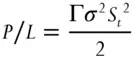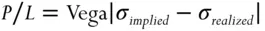(1.2) 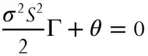
This is then solved using standard numerical or analytical techniques and with the final condition being the payoff of the particular option.
This relationship between Γ and θ is crucial for understanding how to make money with options. Imagine we are long a call and the underlying stock moves from S tto S t+1.The delta P/L of this option will be the average of the initial delta, Δ, and the final delta, all multiplied by the size of the move. Or
(1.3) 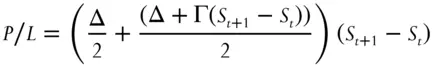
If this option was initially delta-hedged, the P/L over this price move would be
(1.4) 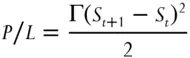
Next note that
(1.5) 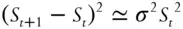
so that the profit in hedging over each time interval is
(1.6) 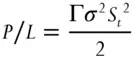
(Although equation 1.6is only asymptotically true, if we worked with an infinitesimal price change, this derivation would be exact.
This is the first term of the BSM differential equation. Literally, BSM says that these profits from rebalancing due to gamma are exactly equal to the theta of the option. Expected movement cancels time decay. The only way a directionally neutral option position will make money is if the option's implied volatility (which governs theta) is not the same as the underlying's realized volatility (which determines the rebalancing profits). This is true no matter which structure is chosen and the particulars of the hedging scheme.
If we can identify situations where this volatility mismatch occurs, the expected profit from the position will be given by
(1.7) 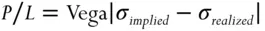
This is the fundamental equation of option trading. All the “theta decay” and “gamma scalping” profits and losses are tied up in this relationship.
Note also that this vega P/L will affect directional option trades. If we pay the wrong implied volatility level for an option, we might still make money but we would have been better off replicating the option in the underlying.
The BSM equation depends on a number of financial and mathematical assumptions.
The underlying is a tradable asset.
There is a single, risk-free interest rate.
The underlying can be shorted.
Proceeds from short sales can be invested at the risk-free rate.
All cash flows are taxed at the same rate.
The underlying's returns are continuous and normally distributed with a constant volatility.
Traders have devised various workarounds to address these limiting assumptions (see Appendix One). The most important of these is the concept of the implied volatility surface. If the BSM were an accurate descriptive theory, all options on a given underlying would have one volatility. This is not true. For the BSM equation to reproduce market option prices, options with different strikes have different implied volatilities (the smile ) and options with different maturities have different implied volatilities (the term structure ). These implied volatilities make up the IV surface. An example is in shown in Figure 1.1.
The IV surface exists partially because the BSM is mathematically misspecified. The underlying does not have returns that are continuous and normally distributed with a constant volatility. However, even a model that perfectly captured the underlying dynamics would need a fudge factor like the implied volatility surface. Some of the reasons for its existence have nothing to do with the underlying. Different options have different supply and demand, and these distort option prices. Because of this, there is often an edge in selling options with high volatilities relative to others on the same underlying (see the section on the implied skewness premiumin Chapter Four).
Equation 1.7gives the average PL of any hedged option position, but there is a wide dispersion of results for this mean, and the spread of this distribution decreases with the number of hedges. Figure 1.2shows the PL distribution of a short straddle that is never re-hedged, and Figure 1.3shows the distribution when the straddle is re-hedged every day. The underlying paths were generated from 10,000 realizations of a GBM. The implied and realized volatility were equal so we expect an average PL of zero.
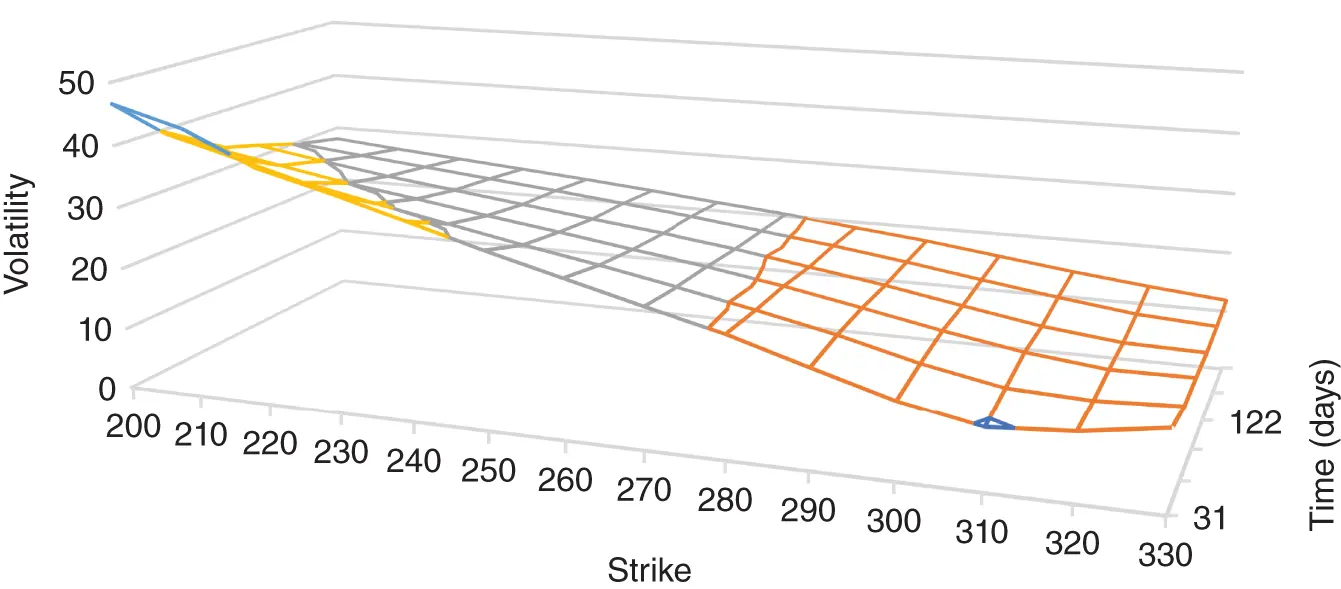
FIGURE 1.1 The implied volatility surface for SPY on September 10, 2019.
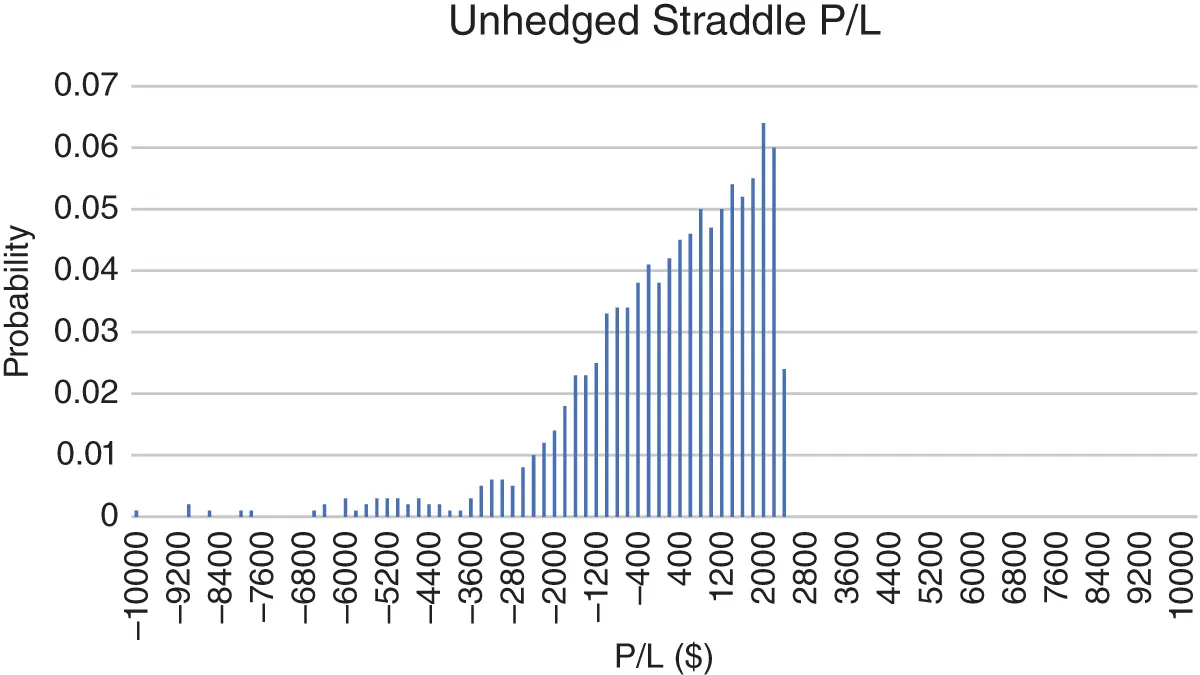
FIGURE 1.2 The terminal PL distribution of a single short one-year ATM straddle that is never re-hedged. Stock price is $100, rates are zero, and both realized and implied volatilities are 30%.
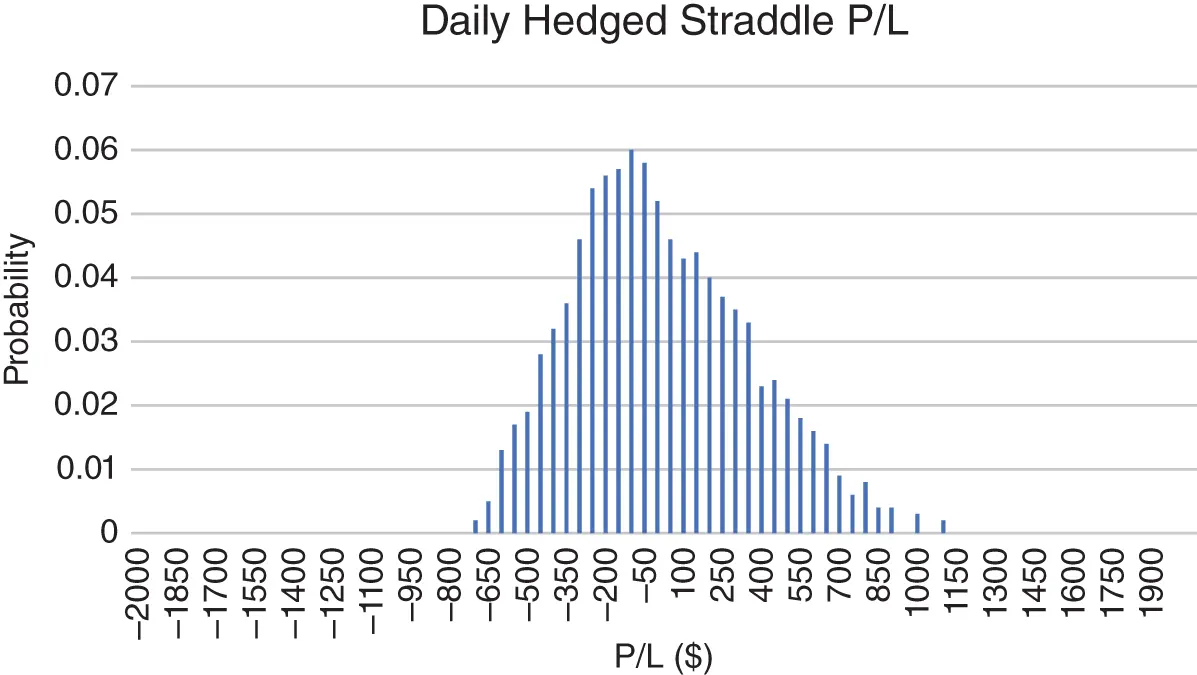
FIGURE 1.3 The terminal PL distribution of a single one-year ATM straddle that is hedged daily. Stock price is $100, rates are zero, and both realized and implied volatilities are 30%.
The dependence of the standard deviation of the PL distribution on the number of hedges is shown in Figure 1.4.
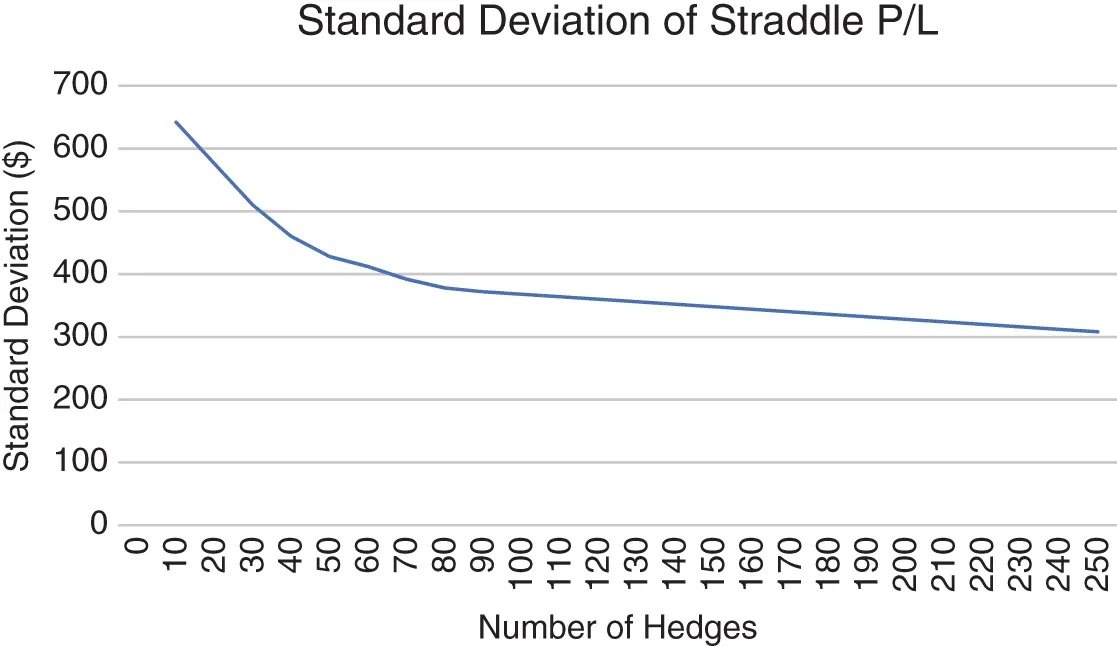
FIGURE 1.4 The standard deviation of the terminal PL distribution of a single one-year ATM straddle as a function of the number of hedges. Stock price is $100, rates are zero, and both realized and implied volatilities are 30%.
The reason to hedge less frequently and accept a wider standard deviation of results is that hedging costs money. All hedges incur transaction costs (brokerage, exchange fees, and infrastructure costs). Costs like this are an easily forgotten drain on a portfolio. Individually they are small, but they accumulate. To emphasize this point, Table 1.1 compares the summary statistics of results for the daily hedged short straddle when there is a transaction cost of $.10 per share and when hedges are costless.
The difference between these two cases is roughly equivalent to misestimating volatility by two points.
In practice, aggressive re-hedging is done by market-making firms and some volatility specialists. The vast majority of retail and buy-side users seldom or never hedge. The relevant theory for those hoping to approximate continuous hedging is discussed in Sinclair (2013). In this book we will generally assume that no re-hedging takes place. These results are also applicable to those who hedge infrequently. They can just assume that the original position has been closed and a new one opened. So, a one-year position that is hedged after a month would thereafter have the expected distribution of an 11-month option.
Читать дальше