Other models aim to mathematically describe the main features of an observation without necessarily understanding its deeper origin. The GARCH family of volatility models are phenomenological, and don't tell us why the GARCH effects exist. Because these models are designed to describe particular features, there will be many other things they totally ignore. For example, a GARCH process has nothing to say about the formation of the bid-ask spread. The GARCH model is limited, but not wrong .
The most ambitious models attempt to describe reality as it truly is. For example, the physicists who invented the idea that an atom was a nucleus around which electrons orbited thought this was actually what atoms were like. But they still had to make simplifying assumptions. For example, when formulating the theory, they had to assume that atoms were not subject to gravity. And, in only trivial situations could the equations be analytically solved. The Black-Scholes-Merton (BSM) model was meant to be of this type.
But it isn't used that way at all.
The inventors of the model envisaged that the model would be used to find a fair value for options. Traders would input the underlying price, strike, interest rate, expiration date, and volatility and the model would tell them what the option was worth. The problem was that the volatility input needed to be the volatility over the life of the option, an unknown parameter. Although it was possible for a trader to make a forecast of future volatility, the rest of the market could and did make its own forecast. The market's option price was based on this aggregated estimate. This is the implied volatility, which became the fundamental parameter. Traders largely didn't think of the model as a predictive valuation tool but just as an arbitrage-free way to convert the quickly changing option prices into a slowly changing parameter: implied volatility. For most traders, BSM is not a predictive model; it is just a simplifying tool.
This isn't to say that BSM can't be used as a pricing model to get a fair value. It absolutely can. But even traders who do this will think in volatility terms. They will compare the implied volatility to their forecast volatility, rather than use the forecast volatility to price the option and compare it to the market value. By using the model backwards, these traders still benefit from the way BSM converts the option prices into a slowly varying parameter.
We need to examine the effects of the model assumptions in light of how the model is used. Although the assumptions make the model less realistic, this isn't important. The model wasn't used because it was realistic; it was used because it was useful.
Obviously, it is possible to trade options without any valuation model. This is what most directional option traders do. We can also trade volatility without a model. Traders might sell a straddle because they think the underlying will expire closer to the strike than the value of the straddle. However, to move beyond directional trading or speculating on the value of the underlying at expiration we will need a model.
The BSM model is still the benchmark for option pricing models. It has been used since 1973 and has direct ancestors dating to the work of Bachelier (1900) and Bronzin (1906). In terms of scientific theory, this age makes it a dinosaur. But just as dinosaurs were the dominant life form for about 190 million years for a reason, BSM has persisted because it is good.
We want an option pricing model for two reasons.
The first is so we can reduce the many, fast-moving option prices to a small number of slow-moving parameters. Option pricing models don't really price options. The market prices options though the normal market forces of supply and demand. Pricing models convert the market's prices into the parameters. In particular, BSM converts option prices to an implied volatility parameter. Now we can do all analysis and forecasting in terms of implied volatility, and if BSM was a perfect model, we would have a single, constant parameter.
The second reason to use a pricing model is to calculate a delta for hedging. Model-free volatility trading exists. Buying or selling a straddle (or strangle, butterfly, or condor, etc.) gives a position that is primarily exposed to realized volatility. But it will also be exposed to the drift. The most compelling reason to trade volatility is that it is more predictable than returns (drift) and the only way to remove this exposure is to hedge. To hedge we need a delta and for this we need a model. This is the most important criterion for an option trader to consider when deciding if a model is good enough. Any vaguely sensible model will reduce the many option prices to a few parameters, but a good model will let us delta hedge in a way that captures the volatility premium.
In this chapter we will examine the BSM model and see if it can meet this standard. By BSM model I mean the partial differential equation rather than the specific solution for European vanilla options. The particular boundary conditions and solution methods aren't a real concern here.
Derivations of BSM can be found in many places (see Sinclair, 2013, for an informal derivation). Here we will look at how the model is used.
Here we will very briefly summarize the theory of option pricing and hedging. For more details refer to Sinclair (2010; 2013).
An option pricing model must include the following variables and parameters:
Underlying price and strike; this determines the moneyness of the option.
Time until expiration.
Any factors related to carry of either the option or the underlying; this includes dividends, borrow rates, storage costs, and interest rates.
Volatility or some other way to quantify future uncertainty.
A variable that is not necessary is the expected return of the underlying. Clearly, this is important to the return of an option, but it is irrelevant to the instantaneous value of the option. If we include this drift term, we will arrive at a contradiction. Imagine that we expect the underlying to rally. Naively, this means we would pay more for a call. But put-call parity means that an increase in call price leads to an increase in the price of the put with the same strike. This now seems consistent with us being bearish. Put-call parity is enough to make the return irrelevant to the current option price, but (less obviously perhaps) it is also enforced by dynamic replication.
This isn't an option-specific anomaly. There are many situations in which people agree on future price change, but this doesn't affect current price. For example, Ferrari would be justified in thinking that the long-term value of their cars is higher than their MSRP. But they can build the car and sell it at a profit right now. Their replication value as a manufacturer guarantees a profit without taking future price changes into account. Similarly, market-makers can replicate options without worrying about the underlying return. And if they do include the return, they can be arbed by someone else.
The canonical option-pricing model is BSM. Ignoring interest rates for simplicity, The BSM PDE for the price of a call, C, is
(1.1) 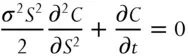
where S is the underlying price, σ is the volatility of the underlying, and t is the time until expiration of the option.
Or using the standard definitions where Γ is the second partial derivative of the option price with respect to the underlying and θ is the derivative of the option price with respect to time,
Читать дальше