2 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1. Partial response linear coding scheme Figure 2.2.Examples of binary RZ and NRZ codes. For a color version of this fig... Figure 2.3. Example of signal s(t) waveform with θ < T /2 Figure 2.4. First situation: 0 ≤ τ ≤ θ (with θ ≤ T/2) Figure 2.5. Second and third situations Figure 2.6. Autocorrelation function Rs (τ) and its decomposition Figure 2.7. Symmetrical triangular function Figure 2.8.Discrete spectral components of the power spectral density I2 (f) Fo... Figure 2.9.First situation: 0 < τ ≤ θ (with T/2 < θ ≤ T). For a color version o... Figure 2.10. Second situation: θ ≤ τ < T Figure 2.11.Third situation: T ≤ τ < T + θ . For a color version of this figure... Figure 2.12.Autocorrelation function Rs (τ) and its decomposition. For a color ... Figure 2.13.Example of a bipolar RZ signal waveform. For a color version of thi... Figure 2.14.First case: 0 < τ < T/2 and a positive impulsion at t. For a color ... Figure 2.15.First case: 0 ≤ τ ≤ T/2 and negative impulse at t . For a color ver... Figure 2.16.Second case: T/2 < τ ≤ T . For a color version of this figure, see ... Figure 2.17.Third case: T < τ ≤ T + T/2 . For a color version of this figure, s... Figure 2.18.Fourth case: 3T/2 < τ ≤ 2T . For a color version of this figure, se... Figure 2.19. (a) Autocorrelation function of the bipolar RZ code and (b) its dec... Figure 2.20.Trapezoidal function. For a color version of this figure, see www.i... Figure 2.21.Power spectral density of the bipolar RZ code. For a color version ... Figure 2.22.Transmission system with partial response linear encoder Figure 2.23.Basic pulse shape (type RZ) Figure 2.24.Block diagram of the partial response linear coder Figure 2.25.Structure of the partial response linear coder (D: D flip-flop sync... Figure 2.26. Block diagram of the baseband transmission system Figure 2.27. Power spectral density Γb0 (f) of noise b0 (t) Figure 2.28. Amplitude spectrum P (f) of p (t) Figure 2.29. Block diagram of the baseband digital transmission system Figure 2.30. Equivalent power spectral density of noise b0 (t) Figure 2.31. Amplitude spectrum P(f) of p(t) Figure 2.32. First-order R-C low pass filter Figure 2.33. Amplitude spectrum P(f) of p(t) Figure 2.34. Block diagram of the baseband transmission system on a cable Figure 2.35. Amplitude spectrum P(f) of p(t) Figure 2.36.Sample values akV, optimal thresholds and decision classes of ak : ... Figure 2.37.Sample values ak2V, optimal thresholds and decision classes of ak :... Figure 2.38.Practical chain of a digital baseband communication system with bip... Figure 2.39. Block diagram of RZ bipolar coder and decoder Figure 2.40. Amplitude spectrum P(f) of p(t) Figure 2.41.Sample values without ISI and noise, optimal thresholds and decisio... Figure 2.42.Baseband transmission and reception chain with partial response lin... Figure 2.43. Temporal diagrams of duobinary coding and decoding Figure 2.44. Duobinary precoder, transcoder and coder scheme Figure 2.45.Chronograms of duobinary coding and decoding. For a color version o... Figure 2.46.Values of sample ckV, optimum thresholds and decision classes of ck... Figure 2.47. Gaussian probability law and distribution intervals Figure 2.48. Partial response transmitter and receiver block diagram Figure 2.49. Details of the partial response transmitter block diagram Figure 2.50. Combined scheme of precoder, transcoder and encoder Figure 2.51.Values of sample ckV, optimum thresholds and decision classes of ck... Figure 2.52.Gaussian probability law with zero mean and unit standard deviation...
3 Chapter 3 Figure 3.1.General block diagram of a digital transmission system with carrier ... Figure 3.2.Supports of transfer function H (f) and He (f) . For a color version... Figure 3.3.General block diagram of a digital transmission system with quadratu... Figure 3.4.Block diagram of a digital transmission system with 2 -ASK modulatio... Figure 3.5.Block diagram of a digital transmission system with quadrature ampli... Figure 3.6.Sample value 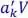 optimal threshold and estimation classes Figure 3.7. Block diagram of a digital transmission system with QAM modulation Figure 3.8. Constellation diagram of a 2-PSK modulation (reference) Figure 3.9.Constellation diagrams of 4 - ASK, 4 - QAM (QPSK) and16-QAM digital ... Figure 3.10. Fundamental frequency characteristics of a digital modulation Figure 3.11.Examples of positioning the points in the constellation diagram of ... Figure 3.12.Block diagram of the realization of the 16 -QAM modulator construct... Figure 3.13. Digital transmission system with quadrature amplitude modulation
optimal threshold and estimation classes Figure 3.7. Block diagram of a digital transmission system with QAM modulation Figure 3.8. Constellation diagram of a 2-PSK modulation (reference) Figure 3.9.Constellation diagrams of 4 - ASK, 4 - QAM (QPSK) and16-QAM digital ... Figure 3.10. Fundamental frequency characteristics of a digital modulation Figure 3.11.Examples of positioning the points in the constellation diagram of ... Figure 3.12.Block diagram of the realization of the 16 -QAM modulator construct... Figure 3.13. Digital transmission system with quadrature amplitude modulation
4 Chapter 4 Figure 4.1. Practical implementation of the TDR method Figure 4.2. Bitrate measurement scheme
5 Chapter 6 Figure 6.1. Block diagram of the ASK demodulation Figure 6.2. Block diagram of FSK modulation Figure 6.3. Block diagram of digital FSK demodulation Figure 6.4. Block diagram of a digital PSK modulation Figure 6.5. Block diagram of a digital PSK demodulation Figure 6.6.Block diagrams of a digital PSK modulation and demodulation by using...
6 Chapter 7 Figure 7.1. Block diagram of a QPSK modem “mqpsk.mdI” Figure 7.2. Decomposition of function “Map QPSK” Figure 7.3. Decomposition of function “transmitter1” Figure 7.4. Decomposition of function “up” Figure 7.5. Decomposition of function “down” Figure 7.6. Decomposition of function “receiver1” Figure 7.7. Parameter file “pmqpsk.m” Figure 7.8. QPSK map
7 Chapter 8 Figure 8.1. codec3f: cyclic coding and decoding Figure 8.2. Generation of the word information Figure 8.3. Encoding diagram Figure 8.4. Binary transmission channel generator Figure 8.5. Decoding diagram Figure 8.6. Example of simulation results Figure 8.7. coder based on linear feedback shift register (LFSR) Figure 8.8. Decoder based on linear feedback shift register (LFSR)
Читать дальше

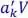 optimal threshold and estimation classes Figure 3.7. Block diagram of a digital transmission system with QAM modulation Figure 3.8. Constellation diagram of a 2-PSK modulation (reference) Figure 3.9.Constellation diagrams of 4 - ASK, 4 - QAM (QPSK) and16-QAM digital ... Figure 3.10. Fundamental frequency characteristics of a digital modulation Figure 3.11.Examples of positioning the points in the constellation diagram of ... Figure 3.12.Block diagram of the realization of the 16 -QAM modulator construct... Figure 3.13. Digital transmission system with quadrature amplitude modulation
optimal threshold and estimation classes Figure 3.7. Block diagram of a digital transmission system with QAM modulation Figure 3.8. Constellation diagram of a 2-PSK modulation (reference) Figure 3.9.Constellation diagrams of 4 - ASK, 4 - QAM (QPSK) and16-QAM digital ... Figure 3.10. Fundamental frequency characteristics of a digital modulation Figure 3.11.Examples of positioning the points in the constellation diagram of ... Figure 3.12.Block diagram of the realization of the 16 -QAM modulator construct... Figure 3.13. Digital transmission system with quadrature amplitude modulation










