Subsequently, the combinations and interactions of identified subset of MAs and PPs are studied as part of the product development through DOE, which is regarded as a “toolkit” component of a QbD approach. The collective outcome from formulation and process design DOEs is utilized in finalizing the list of critical material attributes (CMAs) and CPPs, thereby establishing a design space and an overall control strategy. Based on current ICH Q8(R2), a design space is defined as the “multidimensional combination and interaction of input variables (e.g., material attributes) and process parameters that have been demonstrated to provide assurance of quality” [ICH Q8(R2) guideline 2009].
A generalized scheme representing the evolution of QbD and multidimensional combination and interaction of critical input variables (CMAs and CPPs) on CQAs of an output product is given in Flowchart 2.2. CMAs of input materials may include physical, chemical, or microbiological attributes of APIs, excipients, and other components (e.g., purified water, solvent) that are used in formulating a quality product.
2.5.1. Case Study for Optimizing Systematically a Formula to Make O/W Nanosized Emulsions
The case study initially starts with the risk assessment plan for o/w nanosized emulsions by utilizing Ishikawa fish‐bone diagram and RPN score.
2.5.1.1. Initial Quality Risk Assessment Studies
To find out the influence of CMAs and/or CPPs (independent variables) on CQAs (dependent variables) of topical ophthalmic emulsions, the initial risk assessment studies were performed. By employing the Mini tab 18software (M/s Minitab Inc., Philadelphia, PA, USA), an Ishikawa fish‐bone diagram was constructed to ascertain the potential cause–effect relationship among the product and process variables. Prioritization studies were carried out to select the CMAs/CPPs with high risk by constructing the Risk Estimation Matrix (REM) for qualitative analysis of risk by assigning low‐, medium‐, and high risk(s) levels to each MA and/or PP of topical ophthalmic emulsions ( Table 2.2). Furthermore, the quantitative estimation of risk(s) and detection of the plausibility of failure modes associated with the emulsions were assessed with the help of the FMEA ( Table 2.3). The rank order scores, ranging between 1 and 10 each, were allotted to the CMAs/CPPs (independent variables) for indicating severity, detectability, and occurrence of risks. The FMEA defines the RPN according to the formula already shown in Eq. (2.1)(Fahmy et al. 2012).
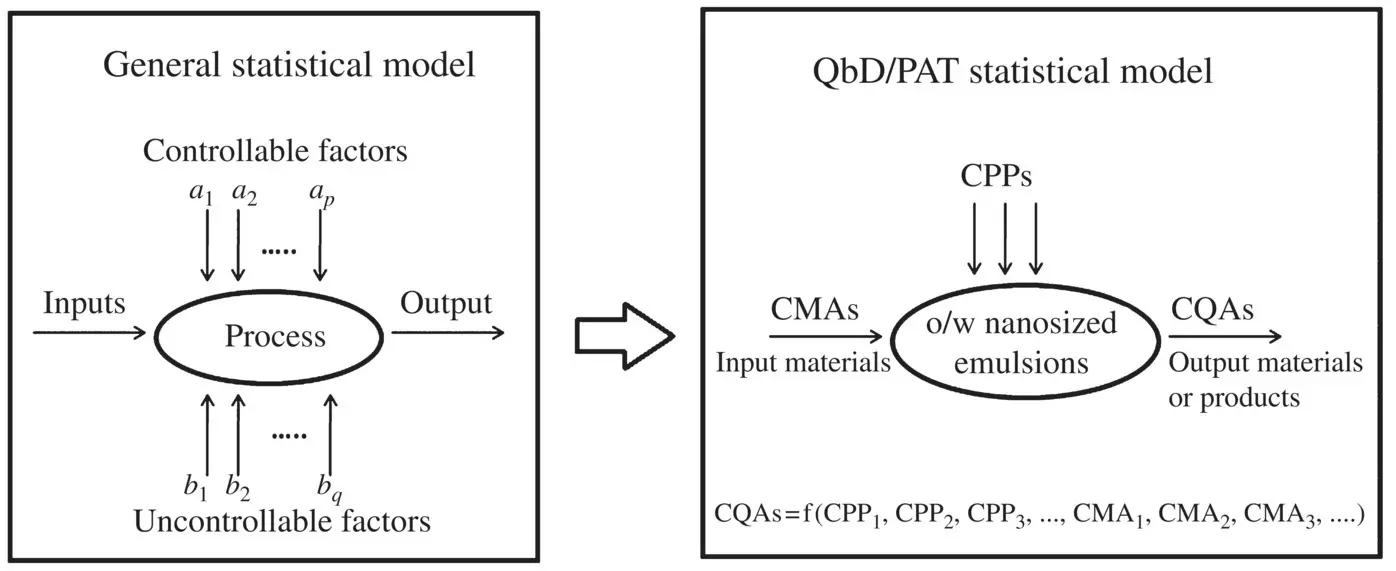
Flowchart 2.2. Evolution of QbD and multidimensional combination and interactions of critical input variables (CMAs and CPPs) on critical response variables (CQAs) for the preparation of o/w nanosized emulsions.
[Adapted from Montgomery (2013) and Yu et al. (2014).]
The parameter D is the ease that a failure mode can be detected because the more detectible a failure mode is, the less risk it presents to product quality. For D, the rank 1 is considered as easily detectable, 5 as moderately detectable, and 10 as hard to detect. The parameter O is the occurrence probability or the likelihood of an event occurring. For O, the rank 1 is considered as unlikely to occur, 5 as 50 : 50 chance of occurring, and 10 as likely to occur. The parameter S is a measure of how severe of an effect a given failure mode would cause. For S, the rank 1 is considered as no effect, 5 as moderate effect, and 10 as severe effect. Using this procedure, the REM carried out for qualitative analysis of risk associated with each MA and/or PP.
The Ishikawa fish‐bone diagram constructed for topical ophthalmic emulsions is simply portraying the cause–effect relationship among the factors that potentially affect the final product CQAs (shown in Fig. 2.4). The parameters outlined in the Ishikawa fish‐bone diagram assisted in the identification of the failure modes, i.e., the modes through which a system, process step, or piece of equipment might fail. Table 2.2illustrates the REM carried out for qualitative analysis of risk associated with each MA and/or PP. The REM suggested that factors such as amount of chitosan, speed and time of homogenization, and volume of castor oil were found to be high risk, while the factors like the amount of poloxamer, times for premixing, and probe sonication were associated with medium risk. An in‐house exercise employing extensive brain storming among the diverse research group members as well as the existing literature reports were used for prioritizing the factors or parameters and allotting the scores for RPN computation. Using FMEA, the modes of failure can be prioritized for risk management purposes according to their seriousness of their consequences (effects), how rottenly they occur, and how easily they can be detected. Through this information, the variables that are needed to be further studied and controlled were found out or short‐listed. In addition, the process of doing the FMEA analysis within a larger organization facilitates systematic gathering of current knowledge inside the organization. Furthermore, with the help of knowledge management system, the FMEA analysis allows the information on risk to be stored for future use. In this manner, it is important for the larger organization in which the turnover results in the loss of institutional memory. The outcomes of FMEA analysis are to define the RPN and further computation of RPN.
TABLE 2.2. Risk Estimation Matrix (REM) for Qualitative Analysis of Risk Constructed After Assigning Low, Medium, and High Risk(s) Levels to Each Material Attributes and Process Parameters of Topical Ophthalmic Emulsions
| Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) |
REM for Qualitative Analysis of Risk Assigned to |
| Volume of Castor Oil |
Amount of Chitosan |
Amount of Poloxamer 407 |
Premixing Time |
Homogenization Time |
Homogenization Speed |
Probe Sonication Time |
| Mean particle size |
High |
Medium |
Medium |
Medium |
High |
High |
Medium |
| Polydispersity index |
Low |
Low |
Medium |
Medium |
Medium |
High |
Medium |
| Zeta potential |
Low |
High |
Low |
Low |
Low |
Low |
Low |
TABLE 2.3. Summary of Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) Demonstrating Risk Priority Number (RPN) Scores for Various Materials and Process Variables Affecting the Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) Such As Mean Particle Size (MPS), Polydispersity Index (PDI), and Zeta Potential (ZP)
| Failure Modes |
Detection (D) |
Occurrence (O) |
Severity (S) |
RPN (=DOS) |
Consequences on CQAs |
| Volume of castor oil (ml) |
5 |
5 |
8 |
200 |
MPS |
| Amount of chitosan (mg) |
6 |
5 |
7 |
210 |
MPS and ZP |
| Amount of poloxamer (mg) |
5 |
5 |
5 |
125 |
MPS and PDI |
| Premixing time (min) |
5 |
7 |
7 |
245 |
MPS and PDI |
| Homogenization time (min) |
5 |
4 |
6 |
120 |
MPS and PDI |
| Homogenization speed (rpm) |
5 |
6 |
7 |
210 |
MPS and PDI |
| Probe sonication time (min) |
2 |
3 |
3 |
18 |
MPS and PDI |
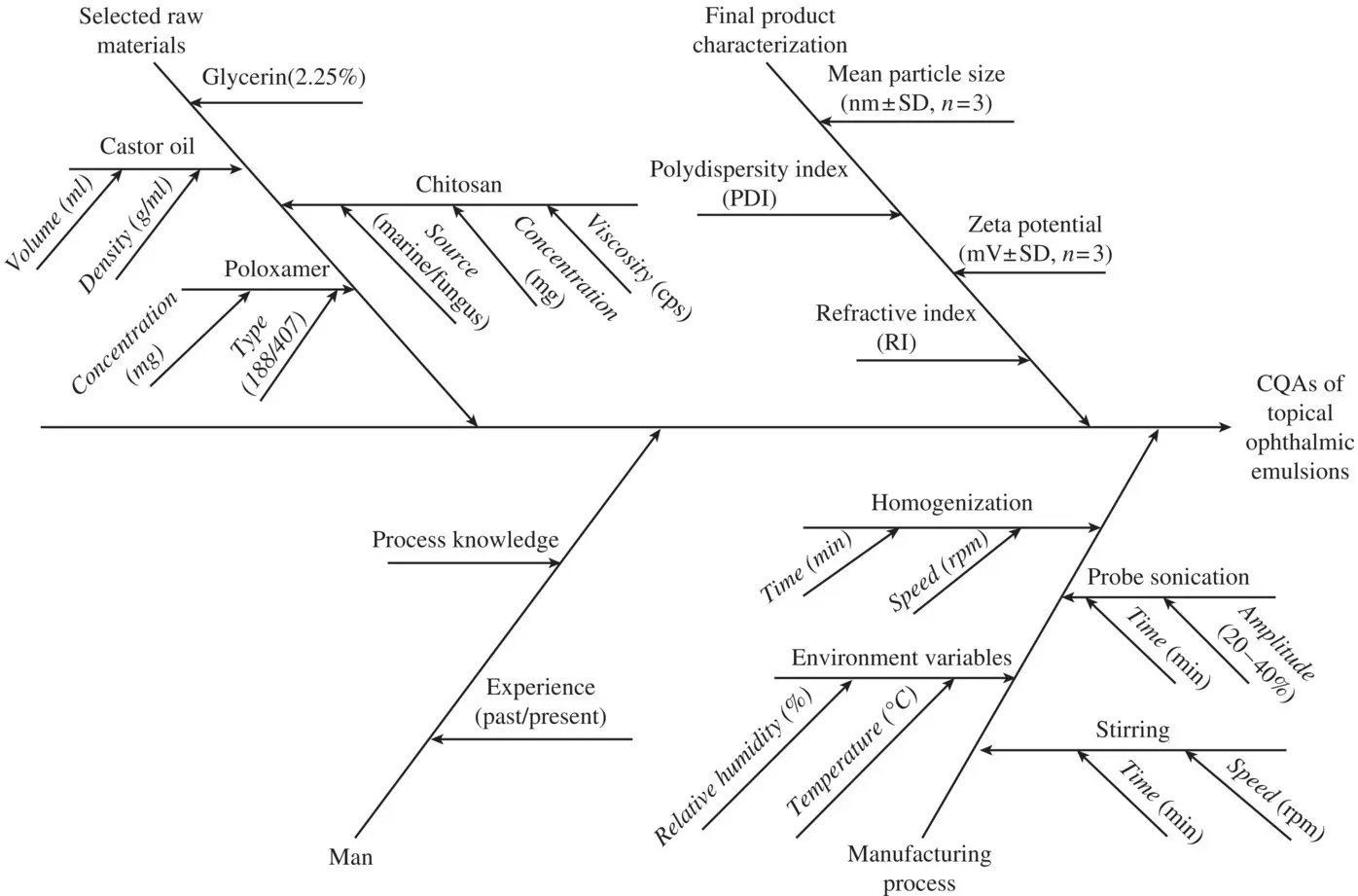
Figure 2.4. Ishikawa fish‐bone diagram made with the help of Mini tab 18software showcasing the potential cause–effect relationship among the product and process variables for topical ocular emulsions.
Читать дальше














