12 Chapter 11Figure 11.1 Assembled DC machine [1].Figure 11.2 Disassembled DC machine [1] of Figure 11.1.Figure 11.3 Rotor lamination with rectangular slots to house the rotor windi...Figure 11.4 Types of rotor slots housing different winding coils: (a) single...Figure 11.5 Double‐layer lap winding with p = 4 poles and N = 24 full‐pitch ...Figure 11.6 Developed (straightened out) four‐pole rotor/armature winding of...Figure 11.7a Two‐pole direct‐current (DC) machine with slip rings consists o...Figure 11.7b Instantaneous magnetomotive forces (mmfs) F sand F r; flux densi...Figure 11.8a Two‐pole DC machine consisting of stationary stator (s) with an...Figure 11.8b Instantaneous magnetomotive forces (mmfs) F fand F a; flux densi...Figure 11.8c Application of the right‐hand‐side rule producing the mechanica...Figure 11.9a Schematic cross section of one pole pitch (half a period) of a ...Figure 11.9b Two‐dimensional magnetic field distribution of one pole pitch o...Figure 11.9c Air‐gap flux density of Figure 11.9, expanded rotor position 1 ...Figure 11.10 (a) Ward Leonard system [30] or generator/motor set applied to ...Figure 11.11 (a) Separately excited DC motor with armature reaction compensa...Figure 11.12 (a) Separately excited generator with cumulatively/differential...Figure 11.13 Self‐excited generator used when no independent voltage source ...Figure 11.14 (a) Series excited motor with one independent voltage source V aFigure E11.1.1 Equivalent circuit of a separately excited DC motor. For stea...Figure E11.2.1 Equivalent circuit of DC machine with (cumulative) flux addit...Figure E11.2.2 Applied terminal armature voltage V a( t ) as a function of time...Figure E11.2.3 Applied mechanical shaft torque T m( t ) as a function of time....Figure E11.2.4 Calculated armature current I a( t ) as a function of time.Figure E11.2.5 Calculated angular velocity ω m( t ) as a function of time....Figure E11.2.6 Calculated electrical torque T e( t ) as a function of time.Figure E11.2.7 Calculated output power P ( t ) as a function of time.Figure E11.2.8 Calculated armature current I a( t ) as a function of time.Figure E11.2.9 Calculated angular velocity ω m( t ) as a function of time....Figure E11.2.10 Calculated electrical torque T e( t ) as a function of time.Figure E11.2.11 Calculated output power P ( t ) as a function of time.Figure E11.2.12 Calculated armature current I a( t ) as a function of time.Figure E11.2.13 Calculated angular velocity ω m( t ) as a function of time...Figure E11.2.14 Calculated electrical torque T e( t ) as a function of time.Figure E11.2.15 Calculated output power P ( t ) as a function of time.Figure P11.1.1 Circuit [39] for measuring the armature resistance R a.Figure P11.1.2 Starting circuit [39] of separately excited DC motor includin...Figure P11.1.3 Separately excited DC motor with automatic starting box consi...Figure P11.1.4 Transient armature current i a( t ) in ampere (A) and transient ...Figure P11.3.1 Equivalent circuit of separately excited DC generator supplyi...Figure 11.A.1 Vector equipotential lines (specified by potential ϕ i) fo...Figure 11.A.2a Vectors used for flux calculation [3]. The potential A ois a ...Figure 11.A.2b Vectors used for flux calculation based on triangular first‐o...Figure 11.A.2c Equidistant vector potential ( A ℓ) solution [2] for a si...Figure 11.A.3 Relations used for flux calculation [2] based on rectangular (...Figure 11.A.3d Equidistant vector potential ( A o) solution [2] for a simple o...Figure 11.A.4a Definition of vertex coordinates used for flux calculation ba...Figure 11.A.4b Equidistant vector potential ( A ℓ) solution [2] for a si...Figure 11.B.1 Grid or node system for the numerical analysis of a 16‐pole DC...Figure 11.B.2 Magnetic field or vector potential distribution based on numer...
13 Chapter 12Figure 12.1 Two‐phase, two‐pole stator winding consisting of concentrated wi...Figure 12.2 Radial fundamental cosinusoidal magnetic field intensity H gof c...Figure 12.3a Instantaneous magnetic field intensity H g( ωt = 0) or F 1( ωt ...Figure 12.3b Instantaneous magnetic field intensity H g( ωt = π/2) or F 2(Figure 12.3c Instantaneous magnetic field intensity H g( ωt = π) or F 3( ωt ...Figure 12.4a Three‐phase stator winding and rotating DC winding on rotor. Th...Figure 12.4b Three‐phase stator winding and rotating DC winding on rotor. Th...Figure 12.5 Four‐pole configuration with concentrated two-phase windings. Th...Figure 12.6 Magnetic field intensity H gin the air gap around the circumfere...Figure 12.7 Magnetic field intensity H gin the air gap around the circumfere...Figure 12.8 Three‐phase, two‐pole distributed winding located in 18 stator s...Figure 12.9 Three‐phase, four‐pole distributed winding located in 24 stator ...Figure 12.10 Various permanent‐magnet material characteristics [8], where Ne...Figure 12.11 Typical demagnetization curves and temperature dependency of Nd...Figure 12.12 Load line 1: load line for small air‐gap and large flux density...Figure 12.13a Partial cross section of a 12‐pole wind power generator [13–18...Figure E12.2.1 Graphical interpretation of Ampere's law in three‐dimensional...Figure E12.2.2 Application of Ampere's law to a single wire in two‐dimension...Figure E12.2.3 Application of Ampere's law in two dimensions to permanent‐ma...Figure 12.13b No‐load magnetic field B ( r , φ ) of the 12‐pole generator o...Figure E12.3.1 Application of Ampere's law and specifications of geometrical...Figure E12.3.2 Measured (see figure 9 of Fingersh [18]) nonsinusoidal no‐loa...Figure E12.4.1a Symmetric no‐load field of 50 kW machine [10].Figure E12.4.1b Asymmetric rated full‐load field of 50 kW machine [10].Figure E12.5.1a Symmetric no‐load field of 20 kW PMM [16].Figure E12.5.1b Asymmetric rated‐load field of 20 kW PMM [16].Figure E12.5.1c Calculation of direct‐axis X dand stator leakage X s ℓr...Figure E12.5.1d Calculation of quadrature‐axis X qand stator leakage X sℓ...Figure E12.6.1 PMM with flux distribution at no load with flux‐weakening (FW...Figure 12.14a Brushless DC machine consisting of battery, inverter, and thre...Figure 12.14b Motor (stator) current waveshape based on full‐on motoring mod...Figure 12.14c Motor (stator) current waveshape based on PWM motoring mode [1...Figure 12.14d Current supplied during regeneration to battery, whereby the a...Figure E12.7.1a Sequence of gating signals for brushless DC motor in six‐ste...Figure E12.7.1b Upper graph, drain (D) current of upper MOSFET of phase a ID...Figure E12.7.1c Upper graph, drain current of upper MOSFET of phase a ID(Mau...Figure E12.7.1d Upper graph, drain current of upper MOSFET of phase a ID(Mau...Figure E12.7.1e Upper graph, drain current of upper MOSFET of phase a ID(Mau...Figure E12.7.1f Upper graph, drain current of upper MOSFET of phase a ID(Mau...Figure E12.7.1g Upper graph, drain current of upper MOSFET of phase a ID(Mau...Figure E12.7.1h Upper graph, drain current of upper MOSFET of phase a ID(Mau...Figure E12.7.1i Phase sequence of full‐on gating signals is not the same as ...Figure 12.15 Single inner magnet external fin‐cooled motor [11].Figure E12.8.1 Block diagram of 20 kW/30 kVA direct‐drive, variable‐speed wi...Figure E12.8.2 Phasor diagram of permanent‐magnet generator [18].Figure E12.8.3 Transient current during synchronization of inverter with pow...Figure 12.16 Cross section of three‐phase IM with three stator windings and ...Figure 12.17 Wye equivalent circuit of IM.Figure 12.18a Alternative wye equivalent circuit of IM.Figure 12.18b Phasor diagram (not to scale) at rated‐load operation based on...Figure 12.19 Power and loss distribution within a three‐phase IM, whereby th...Figure E12.9.1 Definition of phasor voltages and currents of stator for slip...Figure E12.9.2 Phasor diagram in the ( j , 1) complex number Gaussian plane (n...Figure E12.9.3 Saturated no‐load magnetic field of three‐phase squirrel‐cage...Figure E12.10.1 Saturated no‐load magnetic field [30–35] of a three‐phase IM...Figure E12.11.1 (a) The original stator circuit is replaced by (b) Thévenin ...Figure E12.11.1c Simplified equivalent circuit employing Thévenin equivalent...Figure E12.11.1d Phasor diagram (not to scale) for rated operation based on ...Figure E12.12.1a Magnetic field for the calculation of unsaturated (linear) ...Figure E12.12.1b Magnetic field for the calculation of unsaturated (linear) ...Figure E12.12.1c Magnetic field for the calculation of starting torque at ra...Figure E12.12.1d Starting current per phase 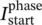 and total (three‐phase) torque...Figure 12.20a Current‐controlled PWM voltage source inverter [41] feeding a ...Figure 12.20b Phase input load voltage
and total (three‐phase) torque...Figure 12.20a Current‐controlled PWM voltage source inverter [41] feeding a ...Figure 12.20b Phase input load voltage 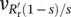 a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20c Phase input load voltage
a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20c Phase input load voltage 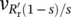 a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20d Phase input load voltage
a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20d Phase input load voltage 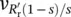 a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20e Phase input load voltage
a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20e Phase input load voltage 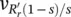 a(t) = v out1(t) = V(19) − V(123) and...Figure 12.21 (a) Equivalent circuit based on consumer (motor) reference fram...Figure 12.22 (a) Equivalent circuit based on generator reference frame (
a(t) = v out1(t) = V(19) − V(123) and...Figure 12.21 (a) Equivalent circuit based on consumer (motor) reference fram...Figure 12.22 (a) Equivalent circuit based on generator reference frame ( 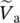 la...Figure 12.23 (a) d‐Axis equivalent circuit, (b) q‐axis equivalent circuit, a...Figure 12.24 Magnetic field distribution of two pole pitches or one period o...Figure 12.25 Six‐pole, three‐phase 250 kVA, 120/240 V, 400 Hz, and 8000 rpm ...Figure 12.26 Six-pole, three-phase 250 kVA, 120/240 V, 400 Hz, and 8000 rpm ...Figure 12.27a Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a nor...Figure 12.27b Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a lar...Figure 12.27c Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a sma...Figure 12.28 Two‐dimensional flux distribution of synchronous machine at ful...Figure 12.29a Two‐dimensional flux distribution for the calculation of the d...Figure 12.29b Two‐dimensional flux distribution for the calculation of the q...Figure E12.13.1 Phasor diagram for non‐salient pole synchronous motor at lag...Figure E12.14.1 Input induced phase voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and input...Figure E12.14.2 Input induced phase voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and input...Figure E12.14.3 Phase input induced voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and phase...Figure E12.15.1 Phasor diagram for generator operation with lagging (overexc...Figure E12.16.1 Non‐salient pole, three‐phase f = 400 Hz synchronous generat...Figure E12.16.2 DC load voltage V out= V (0) − V (b4) = 1.65 kV of three‐phase...Figure E12.16.3 DC load voltage V out= V (0) − V (b4) of three‐phase rectifier...
la...Figure 12.23 (a) d‐Axis equivalent circuit, (b) q‐axis equivalent circuit, a...Figure 12.24 Magnetic field distribution of two pole pitches or one period o...Figure 12.25 Six‐pole, three‐phase 250 kVA, 120/240 V, 400 Hz, and 8000 rpm ...Figure 12.26 Six-pole, three-phase 250 kVA, 120/240 V, 400 Hz, and 8000 rpm ...Figure 12.27a Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a nor...Figure 12.27b Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a lar...Figure 12.27c Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a sma...Figure 12.28 Two‐dimensional flux distribution of synchronous machine at ful...Figure 12.29a Two‐dimensional flux distribution for the calculation of the d...Figure 12.29b Two‐dimensional flux distribution for the calculation of the q...Figure E12.13.1 Phasor diagram for non‐salient pole synchronous motor at lag...Figure E12.14.1 Input induced phase voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and input...Figure E12.14.2 Input induced phase voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and input...Figure E12.14.3 Phase input induced voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and phase...Figure E12.15.1 Phasor diagram for generator operation with lagging (overexc...Figure E12.16.1 Non‐salient pole, three‐phase f = 400 Hz synchronous generat...Figure E12.16.2 DC load voltage V out= V (0) − V (b4) = 1.65 kV of three‐phase...Figure E12.16.3 DC load voltage V out= V (0) − V (b4) of three‐phase rectifier...
Читать дальше

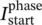 and total (three‐phase) torque...Figure 12.20a Current‐controlled PWM voltage source inverter [41] feeding a ...Figure 12.20b Phase input load voltage
and total (three‐phase) torque...Figure 12.20a Current‐controlled PWM voltage source inverter [41] feeding a ...Figure 12.20b Phase input load voltage 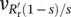 a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20c Phase input load voltage
a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20c Phase input load voltage 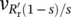 a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20d Phase input load voltage
a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20d Phase input load voltage 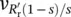 a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20e Phase input load voltage
a( t ) = v out1( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and...Figure 12.20e Phase input load voltage 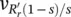 a(t) = v out1(t) = V(19) − V(123) and...Figure 12.21 (a) Equivalent circuit based on consumer (motor) reference fram...Figure 12.22 (a) Equivalent circuit based on generator reference frame (
a(t) = v out1(t) = V(19) − V(123) and...Figure 12.21 (a) Equivalent circuit based on consumer (motor) reference fram...Figure 12.22 (a) Equivalent circuit based on generator reference frame ( 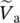 la...Figure 12.23 (a) d‐Axis equivalent circuit, (b) q‐axis equivalent circuit, a...Figure 12.24 Magnetic field distribution of two pole pitches or one period o...Figure 12.25 Six‐pole, three‐phase 250 kVA, 120/240 V, 400 Hz, and 8000 rpm ...Figure 12.26 Six-pole, three-phase 250 kVA, 120/240 V, 400 Hz, and 8000 rpm ...Figure 12.27a Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a nor...Figure 12.27b Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a lar...Figure 12.27c Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a sma...Figure 12.28 Two‐dimensional flux distribution of synchronous machine at ful...Figure 12.29a Two‐dimensional flux distribution for the calculation of the d...Figure 12.29b Two‐dimensional flux distribution for the calculation of the q...Figure E12.13.1 Phasor diagram for non‐salient pole synchronous motor at lag...Figure E12.14.1 Input induced phase voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and input...Figure E12.14.2 Input induced phase voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and input...Figure E12.14.3 Phase input induced voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and phase...Figure E12.15.1 Phasor diagram for generator operation with lagging (overexc...Figure E12.16.1 Non‐salient pole, three‐phase f = 400 Hz synchronous generat...Figure E12.16.2 DC load voltage V out= V (0) − V (b4) = 1.65 kV of three‐phase...Figure E12.16.3 DC load voltage V out= V (0) − V (b4) of three‐phase rectifier...
la...Figure 12.23 (a) d‐Axis equivalent circuit, (b) q‐axis equivalent circuit, a...Figure 12.24 Magnetic field distribution of two pole pitches or one period o...Figure 12.25 Six‐pole, three‐phase 250 kVA, 120/240 V, 400 Hz, and 8000 rpm ...Figure 12.26 Six-pole, three-phase 250 kVA, 120/240 V, 400 Hz, and 8000 rpm ...Figure 12.27a Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a nor...Figure 12.27b Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a lar...Figure 12.27c Two‐dimensional no‐load field of a rotating machine with a sma...Figure 12.28 Two‐dimensional flux distribution of synchronous machine at ful...Figure 12.29a Two‐dimensional flux distribution for the calculation of the d...Figure 12.29b Two‐dimensional flux distribution for the calculation of the q...Figure E12.13.1 Phasor diagram for non‐salient pole synchronous motor at lag...Figure E12.14.1 Input induced phase voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and input...Figure E12.14.2 Input induced phase voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and input...Figure E12.14.3 Phase input induced voltage e a( t ) = V (19) − V (123) and phase...Figure E12.15.1 Phasor diagram for generator operation with lagging (overexc...Figure E12.16.1 Non‐salient pole, three‐phase f = 400 Hz synchronous generat...Figure E12.16.2 DC load voltage V out= V (0) − V (b4) = 1.65 kV of three‐phase...Figure E12.16.3 DC load voltage V out= V (0) − V (b4) of three‐phase rectifier...










