Ewald F. Fuchs - Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Ewald F. Fuchs - Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A combination of analytical and software solutions in order to relate aspects of electric circuits at an accessible level A thorough description of compensation of flux weakening (CFW) applied to inverter-fed, variable-speed drives not seen anywhere else in the literature Numerous application examples of solutions using PSPICE, Mathematica, and finite difference/finite element solutions such as detailed magnetic flux distributions Manufacturing of electric energy in power systems with integrated renewable energy sources where three-phase inverter supply energy to interconnected, smart power systems Connecting the energy-related technology and application discussions with urgent issues of energy conservation and renewable energy—such as photovoltaics and ground-water heat pump resulting in a zero-emissions dwelling—
crafts a truly modern and relevant approach to its subject matter.
Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
9 Chapter 8Figure 8.1 Linear ideal operational amplifier with input ( v in1, v in2) and o...Figure 8.2 Linear ideal operational amplifier with input voltages v in2, v in...Figure 8.3 Power supply voltages V DDand V SSof linear, ideal operational ...Figure 8.4 Noninverting OP amplifier with resistor R 2as negative feedback ...Figure E8.1.1 (a) Input and (b) output voltage of noninverting linear OP amp...Figure 8.5 Unity‐gain OP amplifier with zero (short‐circuited) negative feed...Figure E8.2.1 Unity‐gain (UG) linear OP amplifier with power supply voltages...Figure 8.6 Inverting OP linear amplifier with resistor R 2as negative feedb...Figure E8.3.1 Inverting linear OP amplifier with power supply voltages of V Figure 8.7 Linear ideal differential amplifier with input voltages v in1and...Figure 8.8 Summing network with two inputs.Figure 8.9 Integrating circuit.Figure 8.10 Differentiating circuit.Figure E8.6.1 (a) Definition of input step voltage v in( t ) via the functions...Figure E8.7.1 (a) Definition of input voltage v in( t ) via linear functions f...Figure 8.11 Low‐pass (LP) active filter.Figure 8.12 Low‐pass (LP) active filter frequency response.Figure 8.13 Frequency‐selective high‐pass (HP) active filter.Figure 8.14 High‐pass (HP) active filter frequency response 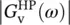 (pu).Figure 8.15 Current–voltage converter.Figure 8.16 (a) P‐controller network with closed‐loop voltage gain G v= v o...Figure E8.9.1 Block diagram of separately excited DC machine drive where the...Figure E8.9.2 Definition of the parameter i outmaxof the current limiter.Figure E8.9.3 DC machine armature I a(A) with current limiter of Figure E8....Figure E8.9.4 DC machine angular velocity ω m(rad/s) with current limi...Figure E8.9.5 DC machine torque T (Nm) with current limiter of Figure E8.9.2...Figure E8.9.6 DC machine output power P (W) with current limiter of Figure E...Figure E8.9.7 DC machine armature I anew(A) with current limiter of Figure ...Figure E8.9.8 DC machine angular velocity ω m(rad/s) with current limi...Figure E8.9.9 DC machine torque T (Nm) with current limiter of Figure E8.9.2...Figure E8.9.10 DC machine output power P (W) with current limiter of Figure ...Figure E8.9.11 DC machine armature I a(A) with current limiter of Figure E8...Figure E8.9.12 DC machine angular velocity ω m(rad/s) with current lim...Figure E8.9.13 DC machine torque T (Nm) with current limiter of Figure E8.9....Figure E8.9.14 DC machine output power P (W) with current limiter of Figure ...Figure E8.9.15 DC machine armature I anew(A) with current limiter of Figure...Figure E8.9.16 DC machine angular velocity ω m(rad/s) with current lim...Figure E8.9.17 DC machine torque T (Nm) with current limiter of Figure E8.9....Figure E8.9.18 DC machine output power P (W) with current limiter of Figure ...Figure E8.9.19 Steady‐state error ε ωm=
(pu).Figure 8.15 Current–voltage converter.Figure 8.16 (a) P‐controller network with closed‐loop voltage gain G v= v o...Figure E8.9.1 Block diagram of separately excited DC machine drive where the...Figure E8.9.2 Definition of the parameter i outmaxof the current limiter.Figure E8.9.3 DC machine armature I a(A) with current limiter of Figure E8....Figure E8.9.4 DC machine angular velocity ω m(rad/s) with current limi...Figure E8.9.5 DC machine torque T (Nm) with current limiter of Figure E8.9.2...Figure E8.9.6 DC machine output power P (W) with current limiter of Figure E...Figure E8.9.7 DC machine armature I anew(A) with current limiter of Figure ...Figure E8.9.8 DC machine angular velocity ω m(rad/s) with current limi...Figure E8.9.9 DC machine torque T (Nm) with current limiter of Figure E8.9.2...Figure E8.9.10 DC machine output power P (W) with current limiter of Figure ...Figure E8.9.11 DC machine armature I a(A) with current limiter of Figure E8...Figure E8.9.12 DC machine angular velocity ω m(rad/s) with current lim...Figure E8.9.13 DC machine torque T (Nm) with current limiter of Figure E8.9....Figure E8.9.14 DC machine output power P (W) with current limiter of Figure ...Figure E8.9.15 DC machine armature I anew(A) with current limiter of Figure...Figure E8.9.16 DC machine angular velocity ω m(rad/s) with current lim...Figure E8.9.17 DC machine torque T (Nm) with current limiter of Figure E8.9....Figure E8.9.18 DC machine output power P (W) with current limiter of Figure ...Figure E8.9.19 Steady‐state error ε ωm= 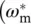 − ω m)/
− ω m)/ 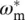 = 1/(1 +...Figure 8.17 (a) I‐controller network with time constant T = R 1 C and closed...Figure 8.18 (a) PI‐controller network with proportional–integral control con...Figure 8.19 (a) D controller. (b) Symbolic representation of D controller of...Figure 8.20 (a) PID controller with P, I, and D circuits connected in parall...Figure E8.10.1 PID control of current through load resistor R Lwith seven i...Figure E8.10.2 Controlled voltage response v Rload= V (17) across R L= R l...Figure E8.10.3 Controlled voltage v Rload= V (17) response through R L= R Figure E8.10.4 Controlled voltage v Rload= V (17) response through R L= R Figure E8.10.5 Controlled voltage v Rload= V (17) response through R L= R Figure 8.21 (a) PD controller with P and D circuits connected in parallel us...Figure P8.1.1 Noninverting (NI) OP amplifier.Figure P8.2.1 (a–c) Determination of closed‐loop voltage gain
= 1/(1 +...Figure 8.17 (a) I‐controller network with time constant T = R 1 C and closed...Figure 8.18 (a) PI‐controller network with proportional–integral control con...Figure 8.19 (a) D controller. (b) Symbolic representation of D controller of...Figure 8.20 (a) PID controller with P, I, and D circuits connected in parall...Figure E8.10.1 PID control of current through load resistor R Lwith seven i...Figure E8.10.2 Controlled voltage response v Rload= V (17) across R L= R l...Figure E8.10.3 Controlled voltage v Rload= V (17) response through R L= R Figure E8.10.4 Controlled voltage v Rload= V (17) response through R L= R Figure E8.10.5 Controlled voltage v Rload= V (17) response through R L= R Figure 8.21 (a) PD controller with P and D circuits connected in parallel us...Figure P8.1.1 Noninverting (NI) OP amplifier.Figure P8.2.1 (a–c) Determination of closed‐loop voltage gain 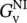 for various ...Figure P8.3.1 Determination of closed‐loop voltage gain
for various ...Figure P8.3.1 Determination of closed‐loop voltage gain 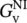 of noninverting (N...Figure P8.4.1 Noninverting (NI) OP amplifier supplying ohmic load R Lwith A...Figure P8.5.1 Calculation of load resistor R 2of noninverting (NI) OP ampli...Figure P8.6.1 Unity‐gain (UG) buffer network.Figure P8.7.1 Inverting (IN) OP amplifier circuit.Figure P8.8.1 Inverting (IN) OP amplifier with DC voltages V DC1= 10 V and Figure P8.9.1 Differential amplifier with equal input resistances R 1.Figure P8.10.1 Differential amplifier with unequal input resistances R 1and...Figure P8.11.1 OP amplifier with positive and negative feedback paths.Figure P8.12.1 Summing circuit.Figure P8.13.1 Temperature sensing network consisting of Wheatstone bridge a...Figure P8.14.1 (a) Integrating network. (b) Given output voltage.Figure P8.15.1 (a) Differentiating network. (b) Given input voltage.Figure P8.16.1 Low‐pass filter circuit or proportional–integral (PI) control...Figure P8.17.1 Band‐pass filter circuit or proportional–integral–differentia...Figure P8.18.1 Small photovoltaic power plant with DC transmission network s...
of noninverting (N...Figure P8.4.1 Noninverting (NI) OP amplifier supplying ohmic load R Lwith A...Figure P8.5.1 Calculation of load resistor R 2of noninverting (NI) OP ampli...Figure P8.6.1 Unity‐gain (UG) buffer network.Figure P8.7.1 Inverting (IN) OP amplifier circuit.Figure P8.8.1 Inverting (IN) OP amplifier with DC voltages V DC1= 10 V and Figure P8.9.1 Differential amplifier with equal input resistances R 1.Figure P8.10.1 Differential amplifier with unequal input resistances R 1and...Figure P8.11.1 OP amplifier with positive and negative feedback paths.Figure P8.12.1 Summing circuit.Figure P8.13.1 Temperature sensing network consisting of Wheatstone bridge a...Figure P8.14.1 (a) Integrating network. (b) Given output voltage.Figure P8.15.1 (a) Differentiating network. (b) Given input voltage.Figure P8.16.1 Low‐pass filter circuit or proportional–integral (PI) control...Figure P8.17.1 Band‐pass filter circuit or proportional–integral–differentia...Figure P8.18.1 Small photovoltaic power plant with DC transmission network s...
10 Chapter 9Figure 9.1 Quasi‐three‐dimensional representation of materials with (a) 4 (e...Figure 9.2 (a) Quasi‐three‐dimensional representation of material with 4 val...Figure 9.3 (a) Silicon‐based pn junction [19] doped/implanted into the silic...Figure 9.4 Characteristic of pn junction diode (d), LED [20, 21], photodiode...Figure 9.5 (a) Circuit symbol of a pn junction diode. (b) Circuit for a ligh...Figure 9.6 (a) Circuit symbol of a Zener (Z) diode; note that V Zis positive...Figure 9.7 (a) Varistor symbol. (b) Varistor characteristic ( i varistor− v va...Figure 9.8 (a) pnp bipolar junction transistor (BJT). (b) Amplifier/switch c...Figure 9.9 (a) Enhancement‐type NMOSFET with a positive voltage applied to t...Figure 9.10 (a) Circuit symbol of a thyristor or SCR. (b) Current–voltage ( I Figure 9.11 (a) Two anti‐parallel‐connected thyristors or SCRs, which are tw...Figure 9.12 (a) Simplified equivalent circuit of IGBT consisting of Darlingt...Figure 9.13 (a) Circuit symbol of GTO with anode (A), cathode (C), and gate ...
11 Chapter 10Figure 10.1 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase AC vo...Figure 10.2 Common approximations [1] for diode characteristics: (a) ideal c...Figure E10.1.1 (a) Source voltage v s( t ), load output voltage v out( t ) = v s( t )...Figure E10.2.1 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), diode voltage v d( t ) = V (2...Figure E10.3.1 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), diode voltage v d( t ) = V (1...Figure E10.4.1 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase vo...Figure E10.4.2 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), output load voltage v out(Figure E10.4.3 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), output voltage v out( t ) = Figure E10.4.4 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), output load voltage v out(Figure E10.5.1 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase vo...Figure E10.5.2 Top plot: source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0); source current Figure E10.5.3 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase vo...Figure E10.5.4 Top plot: source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) and source curre...Figure E10.6.1 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) as well as the output volt...Figure E10.6.2 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) as well as the output volt...Figure E10.7.1 (a, b) A Zener diode with the voltage V zcan be applied to a ...Figure E10.8.1 (a, b) Single‐phase Zener diode applied to a circuit to limit...Figure E10.9.1 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase vo...Figure E10.9.2 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), output load voltage v out(Figure E10.10.1 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase v...Figure E10.10.2 Top plot: source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) and input sourc...Figure E10.11.1 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase v...Figure E10.11.2 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), output load voltage v outFigure E10.12.1 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase v...Figure E10.12.2 Top plot: source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) and output load...Figure E10.13.1 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase v...Figure E10.13.2 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), output load voltage v outFigure E10.14.1 Rectifier supplying pulsating DC current from single‐phase v...Figure E10.14.2 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), output load voltage v outFigure E10.15.1 Full‐wave, single‐phase half‐controlled diode/thyristor brid...Figure E10.15.2 Top plot: source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) and source curr...Figure E10.15.3 Full‐wave, single‐phase half‐controlled diode/thyristor brid...Figure E10.15.4 Top plot: source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) and source curr...Figure E10.16.1 Full‐wave, single‐phase rectifier with a diode bridge, MOSFE...Figure E10.16.2 Top plot: source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) and input or so...Figure E10.17.1 Controller supplying AC current with variable magnitude from...Figure E10.17.2 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), output load voltage v outFigure E10.18.1 Controller supplying AC current from single‐phase voltage so...Figure E10.18.2 Source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0), source current i s( t ) = i Figure E10.19.1 Controller supplying variable AC current from single‐phase v...Figure E10.19.2 Top plot: source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) and input or so...Figure E10.19.3 Top plot: source voltage v s( t ) = V (1) − V (0) and input sourc...Figure E10.20.1 Clipping circuit limiting the positive and negative excursio...Figure E10.20.2 Input v in( t ) = V (1) − V (0) and output v out( t ) = V (2) − V (0) ...Figure E10.20.3 Positive clamping circuit maintaining at the output voltage ...Figure E10.20.4 Top plot: rectangular input v in( t ) = V (1) − V (0). Bottom plo...Figure E10.20.5 Negative clamping circuit maintaining at the output voltage ...Figure E10.20.6 Top plot: input v in( t ) = V (1) − V (0). Bottom plot: rectangul...Figure E10.21.1 Full‐wave, three‐phase rectifier employing a diode bridge fe...Figure E10.21.2 Top plot: source voltages v an( t ) = V (1) − V (0), v bn( t ) = V (2...Figure E10.22.1 Full‐wave, three‐phase thyristor rectifier supplying power t...Figure E10.22.2 Top plot: source voltages v an( t ) = V (1) − V (0), v bn( t ) = V (2...Figure E10.22.3 Top plot: source voltages v an( t ) = V (1) − V (0), v bn( t ) = V (2...Figure E10.23.1 Full‐wave, three‐phase rectifier with diode bridge employing...Figure E10.23.2 Top plot: source voltages v an( t ) = V (1) − V (0), v bn( t ) = V (2...Figure E10.23.3 Full‐wave, three‐phase MOSFET rectifier employing six self‐c...Figure E10.23.4 Top plot: source voltages v an( t ) = V (1) − V (0), v bn( t ) = V (2...Figure E10.24.1 Three‐phase ∆/(ungrounded Y) step‐down transformer supplying...Figure E10.24.2 Top plot: line‐to‐line voltages v AB( t ) = V (1) − V (2), v BC( t )...Figure E10.24.3 Top plot: line‐to‐line voltages v AB( t ) = V (1) − V (2), v BC( t )...Figure E10.25.1 Brushless DC machine consisting of battery, inverter, and th...Figure E10.25.2 Sequence of gating signals for brushless DC motor/machine in...Figure E10.25.3 Top plot: motor (stator) current i MA( t ) = I ( R 1) and applied ...Figure E10.25.4 Top plot: reverse conducting current of diode i Dau( t ) = I (Da...Figure E10.26.1 Full‐wave, three‐phase current‐controlled voltage source inv...Figure E10.26.2 Battery voltage V bat= V (2) − V (0) and battery current or in...Figure E10.26.3 Reference currents of inverter v ref1( t ) = V (12) − V (0), v ref...Figure E10.26.4 Power system phase voltages v an( t ) = V (19) − V (123), v bn( t ) ...Figure E10.27.1 Equivalent circuit of a solar cell.Figure E10.27.2 Nonlinear convex ( V c− I c) characteristic of a solar cell.Figure E10.27.3 Equivalent circuit of a solar PV array or panel with bypass ...Figure E10.27.4 Battery voltage V bat= V (2) − V (0) and battery current or in...Figure E10.27.5 Reference currents of inverter v ref1( t ) = V (12) − V (0), v ref...Figure E10.27.6 Power system phase voltages v an( t ) = V (19) − V (123), v bn( t ) ...Figure E10.28.1 Block diagram of direct‐drive, variable‐speed wind power pla...Figure E10.28.2 Direct‐drive (without mechanical gear), variable‐speed three...Figure E10.28.3 Three‐phase ∆/(ungrounded Y) step‐up transformer supplying t...Figure E10.28.4 Three‐phase current‐controlled voltage source inverter suppl...Figure E10.28.5 Top plot: steady‐state line‐to‐neutral voltages v an( t ) = V (1...Figure E10.28.6 Top plot: required (given) rectifier output unipolar voltage...Figure E10.28.7 Reference line currents v ref1( t ) = V (12) − V (0), v ref2( t ) = Figure E10.28.8 Top plot: required (given) rectifier output unipolar voltage...Figure E10.28.9 Top plot: secondary phase transformer currents i aph( t ) = I ( L Figure E10.28.10 Top plot: primary line transformer currents i genA( t ) = I (Rg...Figure E10.28.11 Design dimensions of tower of wind power plant.Figure 10.3 Voltage–current (v‐i) diagram of motoring and regeneration modes...Figure 10.4 Block diagram of motoring mode converting electric energy of con...Figure 10.5 Block diagram of regeneration mode converting mechanical braking...Figure E10.29.1 Input transformer ( N 1: N 2) with diode bridge PWM MOSFET swi...Figure E10.29.2 Current‐controlled PWM voltage source inverter [7, 8, 17] fe...Figure E10.29.3 Top plot: input DC voltage to inverter v out( t ) = V bat( t ) ≈ V Figure E10.29.4 Harmonic current through DC input source of inverter i bat( t )...Figure E10.29.5 Top plot: induced voltages of induction machine e a( t ) = v out...Figure E10.29.6 Comparison of reference currents v ref1( t ) = V (12) − V (0), v r...Figure E10.29.7 Input AC voltage to primary of step‐up transformer v syst( t ) ...Figure E10.29.8 Secondary transformer voltage v sec( t ) = V (10) − V (11) and cu...Figure E10.29.9 Top plot: unipolar output voltage of diode bridge v Cbridge( t Figure E10.29.10 Current through MOSFET switch i DMosfet( t ) = ID(mosfet) oper...Figure E10.29.11 Top plot: unipolar (or DC) output voltage v out( t ) ≈ V bat=
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












