Medical Statistics and Data Science
Because of the availability of large amounts of data over the last few decades, the term data science has emerged to describe the substantial current intellectual effort around research with the goal of extracting information from these data. The type of data currently available in all sorts of application domains is often massive in size, very heterogeneous and far from being collected under designed or controlled experimental conditions. Nonetheless, it contains information, often substantial information, and it has been argued that data science is a new interdisciplinary approach that makes maximal use of this information. However, data alone is typically not that informative and (machine) learning from data needs conceptual frameworks. Data science would seem to encompass statistics. However, we would argue that statistics is crucial for providing conceptual frameworks that enhance the understanding of fundamental phenomena, highlight limitations and provide a formalism for properly founded data analysis, information extraction and quantification of uncertainty, as well as for the analysis and development of algorithms that carry out these key tasks.
As taught at a number of universities, data science differs from statistics in a number of ways. Statistics originated before the computer and its core concern is with statistical models. However, no serious statistician is beguiled into confusing their model with reality (‘All models are wrong, but some are useful’ to quote the famous statistician John Tukey). However, models are very useful in describing how the world might be, and for making generalisations beyond the data. Data science is empirical, reliant on large data sets, whereas one of the key successes of statistics is doing inference on relatively small data sets, such as those available in agriculture and laboratories. Data science is often used for prediction, and the idea is that with the vast amounts of data now available electronically (such as that provided by national health services) one can look at empirical relationships and build up accurate predictors, such as how drugs will behave in individuals. These predictions are often highly successful, but lacking models it can be difficult to know why it makes some predictions, and how generalizable the predictions might be. Data science is related to the concept of ‘big data’. However, simply because a sample is large does not mean it is unbiased.
A case in point is the reported link between taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and lower heart disease rates observed in some large data sets. However, a key issue is whether women who use HRT are already more health conscious. It can be difficult to know whether this fact is adequately accounted for in conclusions drawn from the big data. Thus, it was only when the results of the randomised controlled trial of the use of HRT (Writing Group for the Women's Health Initiative Investigators 2002) became available that HRT was shown not to protect against heart disease. In fact, the trial identified an increased risk for total cardiovascular disease with hazard ratio 1.22 and 95% confidence interval 1.09 to 1.36 (the technical terms will be explained in Chapter 11). In this example, big data led to a wrong conclusion.
2 Displaying and Summarising Data
1 2.1 Types of Data
2 2.2 Summarising Categorical Data
3 2.3 Displaying Categorical Data
4 2.4 Summarising Continuous Data
5 2.5 Displaying Continuous Data
6 2.6 Within-Subject Variability
7 2.7 Presentation
8 2.8 Points When Reading the Literature
9 2.9 Technical Details
10 2.10 Exercises
This chapter describes different types of data that the reader is likely to encounter. It illustrates methods of summarising and displaying categorical data (bar charts, pie chart). It describes the different ways of summarising continuous data by measures of location or central tendency (mean, median, mode) and measures of spread or variability (range, variance, standard deviation, inter‐quartile range). It also illustrates how to display continuous data (dot‐plots, histograms, box‐and‐whisker plots).
Just as a farmer gathers and processes a crop, a statistician gathers and processes data. For this reason, the logo for the UK Royal Statistical Society is a sheaf of wheat. Like any farmer who knows instinctively the difference between oats, barley, and wheat, a statistician becomes an expert at discerning different types of data. Sections of this book will refer to different data types and so we start by considering these distinctions. Figure 2.1shows a basic summary of types, although some data do not fit neatly into these categories.
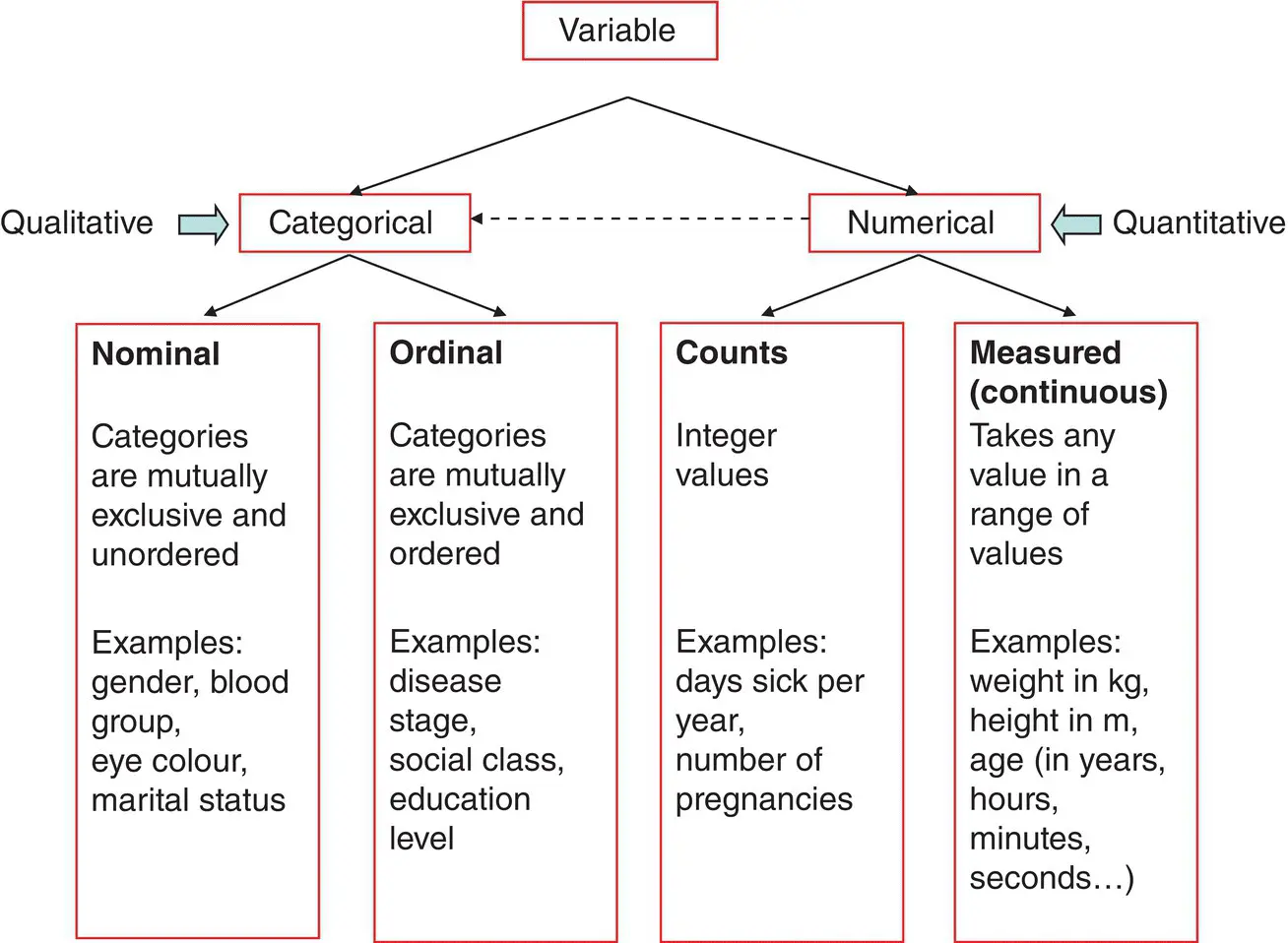
Figure 2.1 Broad classification of the different types of data with examples.
Example from the Literature – Salicylic Acid Plasters for Treatment of Foot Corns
Table 2.1gives a typical table reporting baseline characteristics of a set of patients entered into a randomised controlled trial that investigated the effectiveness of salicylic acid plasters compared with usual scalpel debridement for treatment of foot corns (Farndon et al. 2013). Corns and calluses are areas of hard, thickened skin that develop when the skin is exposed to excessive pressure or friction. They commonly occur on the feet and can cause pain and discomfort when you walk. We will discuss the different types of data given in this paper.
Table 2.1 Baseline characteristics of participants in a randomised control trial of the effectiveness of salicylic acid plasters compared with ‘usual’ scalpel debridement of foot corns by treatment group
( Source: Farndon et al. 2013).
|
Group |
|
|
Corn plaster |
Scalpel |
|
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
| Gender |
Male |
42 |
(42%) |
42 |
(42%) |
|
Female |
59 |
(58%) |
59 |
(58%) |
|
Total |
101 |
(100%) |
101 |
(100%) |
| Centre |
Central |
58 |
(58%) |
52 |
(52%) |
|
Manor |
13 |
(13%) |
20 |
(20%) |
|
Jordanthorpe |
10 |
(10%) |
14 |
(14%) |
|
Limbrick |
3 |
(3%) |
6 |
(6%) |
|
Firth Park |
7 |
(7%) |
4 |
(4%) |
|
Huddersfield |
5 |
(4%) |
4 |
(4%) |
|
Darnall |
5 |
(5%) |
1 |
(1%) |
|
Total |
101 |
(100%) |
101 |
(100%) |
| Smoking History |
Non‐Smoker |
34 |
(35%) |
40 |
(40%) |
|
Previous Smoker |
22 |
(22%) |
16 |
(16%) |
|
Current Smoker |
42 |
(43%) |
43 |
(43%) |
|
Missing |
3 |
(3%) |
2 |
(2%) |
|
Total |
101 |
(100%) |
101 |
(100%) |
| Number of corns evaluated |
1 |
48 |
(48%) |
66 |
(65%) |
|
2 |
28 |
(28%) |
23 |
(23%) |
|
3 |
24 |
(24%) |
12 |
(12%) |
|
Missing |
1 |
(1%) |
0 |
(0%) |
|
Total |
101 |
(100%) |
101 |
(100%) |
|
n |
Mean |
SD |
n |
Mean |
SD |
| Age |
101 |
58.5 |
15.6 |
101 |
59.7 |
17.5 |
| Size of index corn (mm) |
99 |
3.9 |
1.7 |
101 |
3.8 |
1.8 |
| VAS pain (0–10) |
100 |
5.7 |
2.9 |
101 |
4.9 |
3.0 |
|
n |
Median |
25–75th centile |
n |
Median |
25–75th centile |
| EQ‐5D tariff |
98 |
0.73 |
(0.59–0.80) |
101 |
0.73 |
(0.66–0.80) |
| EQ 5D VAS (0–100) |
100 |
80.0 |
(60.0–90.0) |
99 |
79 |
(60.0–90.0) |
Categorical or Qualitative Data
Читать дальше













