1 ...7 8 9 11 12 13 ...23 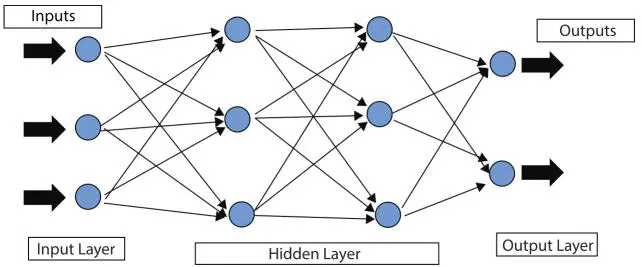
Figure 1.17Neural network (general).
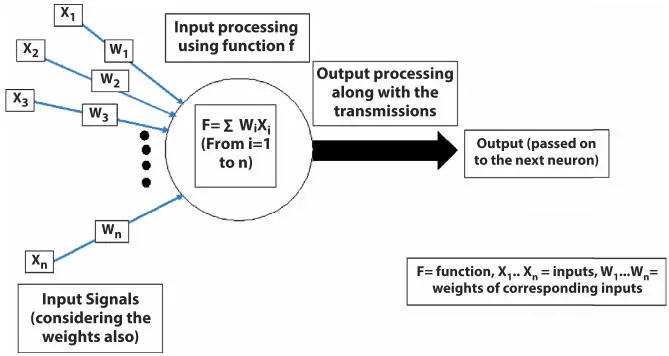
Figure 1.18Neural network (detailed).
Speech Recognition [94]
Signature Verification Application [95]
Human face Recognition [96]
Character Recognition [97]
Natural Language Processing [98].
A basic execution procedure of a neural network [99] is presented in Figure 1.15. In general, it has consisted of three layers. These are the Input layer, Hidden Layer, and the Output layer. These layers are consist of neurons and these neurons and are connected among themselves. In this figure, the input layer contains the health parameters. Depending on the number of inputs received, the hidden processing layer will work to provide an output. Here, only two hidden processing layers are considered but could be any depending on the nature of the purpose of the machine. The outputs are attained and these outputs will act as an input for the next neuron and this process goes on forever. A detailed form of the neural network is explained briefly below with the help of Figure 1.18 for easy understanding.
In Figure 1.16, x 1, x 2, x 3…. x nare the inputs, and the weights they carry are represented by w 1… w n. Their processing is done by the function F, where it performs summation with values up to n. After processing, the output is transmitted to the next neuron as an input. The AUC obtained after implementation of the neural network on the heart disease dataset is presented in Table 1.8. It shows that the model is performing excellently on the training dataset and outstanding on the testing dataset. The implementation is done on python (Google Colab).
Table 1.8AUC: Neural network.
| Parameter |
Data |
Value |
Result |
| The area under the ROC Curve (AUC) |
Training Data |
0.8366730 |
Excellent |
| Test Data |
0.9415238 |
Outstanding |
| Index: 0.5: No Discriminant, 0.6–0.8: Can be considered accepted, 0.8–0.9: Excellent, >0.9: Outstanding |
Some additional Points obtained from the implementation are also presented below:
Neural Score: 83.78
Neural Test Score: 90.24
Accuracy: 0.9024390.
Some other types of Neural Networks are available and listed below for reference:
Multilayer Perceptron [100]
Convolutional Neural Network [101]
Recursive Neural Network [102]
Recurrent Neural Network [103]
Long short term memory [104]
Sequence to Sequence Model [105]
Shallow neural Network [106].
1.10 Comparison of Numerical Interpretation
A summarized version of the AUC results of the above discussed supervised learning methods is given below in Table 1.9 as a comparison of methods. The result indicates that the performance of Random Forest, K-Nearest Neighbor, Decision Tree, and Support Vector Classifier performs outstandingly in both Train and test data sets. Whereas the Logistic Regression and Neural Network perform Outstanding on the testing data set only. It indicates that the models used in Logistic Regression and Neural Network need improvement in the training data set. Hence, the accuracy level will be achieved.
Table 1.9AUC: Comparison of numerical interpretations.
| S. No. |
Supervised Learning Parameter |
AUC Training Data Value (T1) |
AUC Test Data Value (T2) |
Result |
| 1 |
Logistic Regression |
0.8374022 |
0.9409523 |
T1: Excellent T2: Outstanding |
| 2 |
Random Forest |
1.0000000 |
1.0000000 |
T1: Outstanding T2: Outstanding |
| 3 |
K-Nearest Neighbor |
1.0000000 |
1.0000000 |
T1: Outstanding T2: Outstanding |
| 4 |
Decision Tree |
0.9588996 |
0.9773333 |
T1: OutstandingT2: Outstanding |
| 5 |
Support Vector Classifier |
1.0000000 |
0.9773333 |
T1: Outstanding T2: Outstanding |
| 6 |
Neural Networks |
0.8366730 |
0.9415238 |
T1: Excellent T2: Outstanding |
| Index: 0.5: No Discriminant, 0.6–0.8: Can be considered accepted, 0.8–0.9: Excellent, >0.9: Outstanding |
1.11 Conclusion & Future Scope
The contribution of AI has been significant from the past six decades. It consisted of the sub-domain, Machine Learning that has also made its mark in the field of research. Its main constituent Supervised Learning is highlighted in this chapter along with its different sub techniques such as a k-nearest neighbor algorithm, classification, regression, decision trees, etc. This chapter also depicts the analysis of a popular dataset of Heart Disease [41] along with its numerical interpretations. The implementation was done on python (Google Colab). A small introductory part of unsupervised learning along with reinforcement learning is also depicted in this chapter.
In the future, the research will be continued in the field of supervised learning (i.e. Logistic Regression and Neural Networks) and its subfields and will try to find out more similarities that may enhance the research perspective.
1. Guo, J., He, H., He, T., Lausen, L., Li, M., Lin, H., Zhang, A., Gluoncv and gluonnlp: Deep learning in computer vision and natural language processing. J. Mach. Learn. Res ., 21, 23, 1–7, 2020.
2. Abas, Z.A., Rahman, A.F.N.A., Pramudya, G., Wee, S.Y., Kasmin, F., Yusof, N., Abidin, Z.Z., Analytics: A Review Of Current Trends, Future Application And Challenges. Compusoft , 9, 1, 3560–3565, 2020.
3. Géron, A., Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems , O’Reilly Media, United State of America, 2019.
4. Alshemali, B. and Kalita, J., Improving the reliability of deep neural networks in NLP: A review. Knowl.-Based Syst ., 191, 105210, 2020.
5. Klaine, P.V., Imran, M.A., Onireti, O., Souza, R.D., A survey of machine learning techniques applied to self-organizing cellular networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut ., 19, 4, 2392–2431, 2017.
6. Abadi, M., Barham, P., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Davis, A., Dean, J., Kudlur, M., Tensorflow: A system for large-scale machine learning, in: 12th {USENIX} Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation ({OSDI} 16) , pp. 265–283, 2016.
7. Alpaydin, E., Introduction to machine learning , MIT Press, United Kingdom, 2020.
8. Larranaga, P., Calvo, B., Santana, R., Bielza, C., Galdiano, J., Inza, I., Robles, V., Machine learning in bioinformatics. Briefings Bioinf ., 7, 1, 86–112, 2006.
9. Almomani, A., Gupta, B.B., Atawneh, S., Meulenberg, A., Almomani, E., A survey of phishing email filtering techniques. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut ., 15, 4, 2070–2090, 2013.
10. Kononenko, I., Machine learning for medical diagnosis: History, state of the art and perspective. Artif. Intell. Med ., 23, 1, 89–109, 2001.
11. Kotsiantis, S.B., Zaharakis, I., Pintelas, P., Supervised machine learning: A review of classification techniques, in: Emerging Artificial Intelligence Applications in Computer Engineering , vol. 160, pp. 3–24, 2007.
Читать дальше














