Chapter 5 examines the application of a measurement‐based analysis technique to identify voltage control areas in renewable integrated power systems. The proposed technique combines the inherent abilities of graph theoretical techniques with spectral clustering and visualization methods to identify voltage control areas and reconstruct system behavior. The evaluation of voltage stability problems is done using both static and dynamic techniques. Numerical relevant issues are also discussed.
Chapter 6 proposes advanced control schemes rely on inertia manipulation in the system to improve frequency, voltage, and small signal stabilities. The proposed control approaches, which use stochastic equivalent model of power system (to enable high penetration levels of MGs), combine an adaptive dispatch strategy for energy storage systems with an MG‐controlled islanding scheme to provide stability support for the host power grid.
Chapter 7 addresses some important issues in understanding the oscillatory performance of wind and solar PV penetrated power systems. A fundamental study of the characterization of power system dynamic behavior with increased RESs is presented. The study is motivated by the need to further clarify the participation of wind and PV farms in inter‐area oscillations. The performance of data‐driven model extraction techniques using two simple and complex power system examples is evaluated. Some analytical criteria to describe the energy relationships in the observed oscillations are derived, and a physical interpretation for the system modes is suggested.
Chapter 8 describes an experience in the analysis of wind and solar integration in a large‐scale practical power system to examine the impact of high variable renewable generation on power system security. Both active and reactive power control strategies are considered. The study assesses the impact of large amount of wind and PV on system dynamics and identifies ways of improving system dynamic performance and stability through control and operating practices.
Hêmin Golpîra, University of Kurdistan Arturo Román‐Messina, The Center for Research and Advanced Studies of IPN Hassan Bevrani, University of Kurdistan January 2021
Most of the contributions, outcomes, and insight presented in this book were achieved through a long-term teaching and research cooperation on the renewable integrated power systems over the last 15 years. The materials given in the present book are mainly the research outcomes and original results of authors in Smart/Micro Grids Research Center‐ SMGRC , University of Kurdistan (Sanandaj, Iran) and in The Center for Research and Advanced Studies‐ CINVESTAV of the National Polytechnic Institute of Mexico (Guadalajara, Mexico). It is a pleasure to acknowledge the received supports from these sources, and the awards from Iran Grid Management Company (IGMC), Iran National Science Foundation (INSF), and Alexander von Humboldt (AvH) Foundation.
The authors would like to thank their colleagues Prof. J. Raisch and Prof. Bruno Francois for their kind support. Finally, the authors offer their deepest personal gratitude to their families for their patience during the preparation of this book.
X,Ydata matricesεKernel bandwidthλeigenvalueσsingular valueξdamping υvector of natural modes ψ,φeigenvectors ΨΦmatrices of eigenvectors Γinflation operatorθphase angle Λdiagonal matrix of eigenvalues ∑diagonal matrix of singular valuesδsmechanical rotor angle (rad)δrotor angle position (rad) 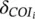 rotor angle position of the COI (rad)ωangular speed (rad/s)ωsmechanical rotor angular speed (rad/s)ω rated angular speed (rad/s)Tm(t)mechanical input torque (p.u.)Te(t)electrical output torque (p.u.)Minertia constant of the system (s)
rotor angle position of the COI (rad)ωangular speed (rad/s)ωsmechanical rotor angular speed (rad/s)ω rated angular speed (rad/s)Tm(t)mechanical input torque (p.u.)Te(t)electrical output torque (p.u.)Minertia constant of the system (s) 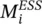 inertia of ESS in area i (s)
inertia of ESS in area i (s) 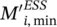 minimum required ESS inertia, in compliance with RoCof, in area i (s)
minimum required ESS inertia, in compliance with RoCof, in area i (s) 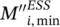 minimum required ESS inertia, in compliance with frequency nadir, in area i (s)Ddamping coefficientI(t)impulse response of the systemP(n)data sequence of interestPininjected power of ESS to the host gridKnumber of sinusoidal components in noiseLlength of P(n)Lx ,Lylatent variablesJmoment of inertiaakmagnitudeΦ kinitial phase angleωkharmonic frequency in radiusAkcomplex magnitude of the kth‐harmonicsieigenvectors associated with the noise subspaceesignal eigenvectoreUcomplex‐conjugate transpose of eCcapcapital costs ($/kW)CPCSpower conversion system costs ($/kW)Cstorstorage section costs ($/kWh)CBOPpower balance costs ($/kW)tchcharging/discharging time (h)CO & Moperation and maintenance costs ($/kW‐year)CR,aannualized replacement costs ($/kW‐year)Ccap,aannualized total capital costs ($/kW‐year)CLCC,aannualized life cycle costs ($/kW‐year)CRFcapital recovery factorCRreplacement costs ($/kWh)CFOM,afixed operation and maintenance costs ($/kW‐year)CVOM,avariable operation and maintenance costs ($/kWh)ncyclenumber of discharge cycles per yearζccharging efficiency of the battery (%)ζddischarging efficiency of the battery (%)ηpower angle‐based stability indexi (j)area (bus) indexffrequency (Hz)
minimum required ESS inertia, in compliance with frequency nadir, in area i (s)Ddamping coefficientI(t)impulse response of the systemP(n)data sequence of interestPininjected power of ESS to the host gridKnumber of sinusoidal components in noiseLlength of P(n)Lx ,Lylatent variablesJmoment of inertiaakmagnitudeΦ kinitial phase angleωkharmonic frequency in radiusAkcomplex magnitude of the kth‐harmonicsieigenvectors associated with the noise subspaceesignal eigenvectoreUcomplex‐conjugate transpose of eCcapcapital costs ($/kW)CPCSpower conversion system costs ($/kW)Cstorstorage section costs ($/kWh)CBOPpower balance costs ($/kW)tchcharging/discharging time (h)CO & Moperation and maintenance costs ($/kW‐year)CR,aannualized replacement costs ($/kW‐year)Ccap,aannualized total capital costs ($/kW‐year)CLCC,aannualized life cycle costs ($/kW‐year)CRFcapital recovery factorCRreplacement costs ($/kWh)CFOM,afixed operation and maintenance costs ($/kW‐year)CVOM,avariable operation and maintenance costs ($/kWh)ncyclenumber of discharge cycles per yearζccharging efficiency of the battery (%)ζddischarging efficiency of the battery (%)ηpower angle‐based stability indexi (j)area (bus) indexffrequency (Hz) 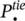 virtual transferred power (pu)
virtual transferred power (pu) 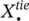 fictitious reactance (pu)TtieCOIi,japplied torques from bus j to COITtieCOIi,COGapplied torques from COG to COIAiarea iΔPisize of disturbance in area iξ−deviations from the target value in negative directionξ+deviations from the target value in positive directionξtarget valuepsprobability of each scenariosscenario counterICinternal combustionSMsynchronous machineMPslope of P‐ꞷ droopKPIintegral control gainKPPproportional control gainFCMDcommand fuel signalECMDexciter control signalPmeasmeasured value of real powerQmeasmeasured value of reactive powerI•line currentKtftorque to fuel conversion ratioηthrthermal constantKcvcalorific valueKfrfuel rate at rated speedKmmechanic losses constantτeexciter machine time constantPMGinjected power of MG to the host gridωMGsangular speed at the point of common couplingζDGs re‐dispatching time (s)υDGs islanding time (s)nnumber of areasβfrequency biasPGensetgeneration of GenstLlevel arm length (m)
fictitious reactance (pu)TtieCOIi,japplied torques from bus j to COITtieCOIi,COGapplied torques from COG to COIAiarea iΔPisize of disturbance in area iξ−deviations from the target value in negative directionξ+deviations from the target value in positive directionξtarget valuepsprobability of each scenariosscenario counterICinternal combustionSMsynchronous machineMPslope of P‐ꞷ droopKPIintegral control gainKPPproportional control gainFCMDcommand fuel signalECMDexciter control signalPmeasmeasured value of real powerQmeasmeasured value of reactive powerI•line currentKtftorque to fuel conversion ratioηthrthermal constantKcvcalorific valueKfrfuel rate at rated speedKmmechanic losses constantτeexciter machine time constantPMGinjected power of MG to the host gridωMGsangular speed at the point of common couplingζDGs re‐dispatching time (s)υDGs islanding time (s)nnumber of areasβfrequency biasPGensetgeneration of GenstLlevel arm length (m) 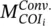 conventional synchronous inertia (s)TDdelivery time of primary frequency response (s)Kf(s)transfer function of the phase‐locked loopMMMGmuti‐micro‐grid inerta constant (s)Vinitial values of terminal voltage YHHankel matrix‖.‖norm
conventional synchronous inertia (s)TDdelivery time of primary frequency response (s)Kf(s)transfer function of the phase‐locked loopMMMGmuti‐micro‐grid inerta constant (s)Vinitial values of terminal voltage YHHankel matrix‖.‖norm
List of Abbreviations and Acronyms
AamplitudeAGCautomatic generation controlAQRautomatic reactive power regulatorAVRautomatic voltage regulatorBresidueBFVbest fitness valueCOGcenter of gravityCOIcenter of inertiaDERdistributed energy resourcesDFIGdoubly‐fed induction generatorDGdistributed generationDMdiffusion mapDMDdynamic mode decompositionEenergyEMTelectromagnetic transientESSenergy storage systemEVelectrical vehicleGAgenetic algorithmHVDChigh‐voltage direct currentKTKumaresan–TuftLCCline commutated converterMCLMarkov clusteringMGmicrogridMMGsmulti‐MGsNERCNorth American Electric Reliability CorporationNYNENew York New EnglandPCprincipal componentPCTVARpercentage of variationPFparticipation factorPIproportional‐integralPLLphase‐locked loopPLSpartial least squares regressionPLSCpartial least squares correlationPMSGpermanent magnet synchronous generatorsPMUphasor measurement unitPOISpoint of interconnection with the systemPSpseudo spectrumPSSpower system stabilizersPVphotovoltaicRESrenewable energy sourceRoCoFrate of change of frequencySCsynchronous condenserSCADAsupervisory control and data acquisitionSGsynchronous generatorSLBstatic load bankSOCstate of chargeSSstatic switchSVCstatic VAR compensatorSVDsingular value decompositionT‐Dtime domainTSOtransmission system operatorUCTEUnion for the Coordination of the Transmission of ElectricityUFLSunderfrequency load sheddingULTCunder load tap changerVARvolt–ampere reactiveVSCvoltage source converterVSGvirtual synchronous generatorV2Gvehicle‐to‐grid VvandVandermonde matrixWAMSwide‐area measurement systemWFwind farmWTwind turbinezcomplex amplitude
Читать дальше

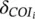 rotor angle position of the COI (rad)ωangular speed (rad/s)ωsmechanical rotor angular speed (rad/s)ω rated angular speed (rad/s)Tm(t)mechanical input torque (p.u.)Te(t)electrical output torque (p.u.)Minertia constant of the system (s)
rotor angle position of the COI (rad)ωangular speed (rad/s)ωsmechanical rotor angular speed (rad/s)ω rated angular speed (rad/s)Tm(t)mechanical input torque (p.u.)Te(t)electrical output torque (p.u.)Minertia constant of the system (s) 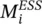 inertia of ESS in area i (s)
inertia of ESS in area i (s) 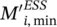 minimum required ESS inertia, in compliance with RoCof, in area i (s)
minimum required ESS inertia, in compliance with RoCof, in area i (s) 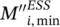 minimum required ESS inertia, in compliance with frequency nadir, in area i (s)Ddamping coefficientI(t)impulse response of the systemP(n)data sequence of interestPininjected power of ESS to the host gridKnumber of sinusoidal components in noiseLlength of P(n)Lx ,Lylatent variablesJmoment of inertiaakmagnitudeΦ kinitial phase angleωkharmonic frequency in radiusAkcomplex magnitude of the kth‐harmonicsieigenvectors associated with the noise subspaceesignal eigenvectoreUcomplex‐conjugate transpose of eCcapcapital costs ($/kW)CPCSpower conversion system costs ($/kW)Cstorstorage section costs ($/kWh)CBOPpower balance costs ($/kW)tchcharging/discharging time (h)CO & Moperation and maintenance costs ($/kW‐year)CR,aannualized replacement costs ($/kW‐year)Ccap,aannualized total capital costs ($/kW‐year)CLCC,aannualized life cycle costs ($/kW‐year)CRFcapital recovery factorCRreplacement costs ($/kWh)CFOM,afixed operation and maintenance costs ($/kW‐year)CVOM,avariable operation and maintenance costs ($/kWh)ncyclenumber of discharge cycles per yearζccharging efficiency of the battery (%)ζddischarging efficiency of the battery (%)ηpower angle‐based stability indexi (j)area (bus) indexffrequency (Hz)
minimum required ESS inertia, in compliance with frequency nadir, in area i (s)Ddamping coefficientI(t)impulse response of the systemP(n)data sequence of interestPininjected power of ESS to the host gridKnumber of sinusoidal components in noiseLlength of P(n)Lx ,Lylatent variablesJmoment of inertiaakmagnitudeΦ kinitial phase angleωkharmonic frequency in radiusAkcomplex magnitude of the kth‐harmonicsieigenvectors associated with the noise subspaceesignal eigenvectoreUcomplex‐conjugate transpose of eCcapcapital costs ($/kW)CPCSpower conversion system costs ($/kW)Cstorstorage section costs ($/kWh)CBOPpower balance costs ($/kW)tchcharging/discharging time (h)CO & Moperation and maintenance costs ($/kW‐year)CR,aannualized replacement costs ($/kW‐year)Ccap,aannualized total capital costs ($/kW‐year)CLCC,aannualized life cycle costs ($/kW‐year)CRFcapital recovery factorCRreplacement costs ($/kWh)CFOM,afixed operation and maintenance costs ($/kW‐year)CVOM,avariable operation and maintenance costs ($/kWh)ncyclenumber of discharge cycles per yearζccharging efficiency of the battery (%)ζddischarging efficiency of the battery (%)ηpower angle‐based stability indexi (j)area (bus) indexffrequency (Hz) 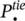 virtual transferred power (pu)
virtual transferred power (pu) 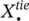 fictitious reactance (pu)TtieCOIi,japplied torques from bus j to COITtieCOIi,COGapplied torques from COG to COIAiarea iΔPisize of disturbance in area iξ−deviations from the target value in negative directionξ+deviations from the target value in positive directionξtarget valuepsprobability of each scenariosscenario counterICinternal combustionSMsynchronous machineMPslope of P‐ꞷ droopKPIintegral control gainKPPproportional control gainFCMDcommand fuel signalECMDexciter control signalPmeasmeasured value of real powerQmeasmeasured value of reactive powerI•line currentKtftorque to fuel conversion ratioηthrthermal constantKcvcalorific valueKfrfuel rate at rated speedKmmechanic losses constantτeexciter machine time constantPMGinjected power of MG to the host gridωMGsangular speed at the point of common couplingζDGs re‐dispatching time (s)υDGs islanding time (s)nnumber of areasβfrequency biasPGensetgeneration of GenstLlevel arm length (m)
fictitious reactance (pu)TtieCOIi,japplied torques from bus j to COITtieCOIi,COGapplied torques from COG to COIAiarea iΔPisize of disturbance in area iξ−deviations from the target value in negative directionξ+deviations from the target value in positive directionξtarget valuepsprobability of each scenariosscenario counterICinternal combustionSMsynchronous machineMPslope of P‐ꞷ droopKPIintegral control gainKPPproportional control gainFCMDcommand fuel signalECMDexciter control signalPmeasmeasured value of real powerQmeasmeasured value of reactive powerI•line currentKtftorque to fuel conversion ratioηthrthermal constantKcvcalorific valueKfrfuel rate at rated speedKmmechanic losses constantτeexciter machine time constantPMGinjected power of MG to the host gridωMGsangular speed at the point of common couplingζDGs re‐dispatching time (s)υDGs islanding time (s)nnumber of areasβfrequency biasPGensetgeneration of GenstLlevel arm length (m) 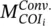 conventional synchronous inertia (s)TDdelivery time of primary frequency response (s)Kf(s)transfer function of the phase‐locked loopMMMGmuti‐micro‐grid inerta constant (s)Vinitial values of terminal voltage YHHankel matrix‖.‖norm
conventional synchronous inertia (s)TDdelivery time of primary frequency response (s)Kf(s)transfer function of the phase‐locked loopMMMGmuti‐micro‐grid inerta constant (s)Vinitial values of terminal voltage YHHankel matrix‖.‖norm










