In summary, the histological characteristics associated with the pathogenic variants of BRCA2 have been inconsistent.
Concerning the histological subtype, no correlation has been found with the most frequent germline variant in northern Europe, 1100delC of CHEK2. However, it has been shown that in Poland, where there are two other founder variants with a higher prevalence than 1100delC, the I157T mutation is associated with the lobular carcinoma subtype.
An examination of pathological features in 10 families with pathogenic RAD51C mutations revealed that nine patients (47%) developed carcinomas of the ovary and 12 (63%) developed carcinomas of the breast. This review also noted that, as a group, the RAD51C-associated mammary carcinomas were diagnosed at an early stage (89%) and were hormone receptor positive, HER2 negative, moderately differentiated invasive ductal carcinomas (IDC) and NST (80%).
In addition, RAD51C breast carcinomas were comparable to BRCA2-associated breast carcinomas in their lack of specific pathologic features and their tendency to be ER positive and HER2 negative, differing only in the Ki-67 proliferation index, which is significantly higher in BRCA2 tumors.
In terms of gynecological cancers, women with BRCA1 mutations have a 50% risk of developing ovarian, tubal or peritoneal carcinoma, while in BRCA2 carriers, the risk is about 25% for all ovarian cancer patients and about a quarter of patients with high-grade serous carcinoma (HGSC).
Carriers of BRCA mutations do not appear to have an increased risk of developing endometrial cancer, although there is some evidence to suggest that there may be an increased risk for serous/serous-like endometrial cancer.
BRCA1/2 carriers develop tumors that are almost always of high-grade serous histology, but the tumors may also be endometrioid and, more rarely, have clear cell histology.
Currently, there is a strong belief that the BRCA1/2 syndrome is almost exclusively associated with the histotype of ovarian cancer: HGSC.
Primary site histological features that have been found to be more common in HGSCs associated with BRCA1 (germinal or somatic) mutations include a solid, pseudo-endometrioid, transitional appearance (SET) , increased numbers of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), and higher mitotic index and necrosis.
BRCA2 mutations have also been associated with an increased risk of developing pancreatic and prostate cancer.
Table 1.1. Spectrum of cancers in carriers of BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic variants
| Cancer sites |
BRCA1 |
BRCA2 |
| Weight of evidence |
Absolute risk magnitude |
Weight of evidence |
Absolute risk magnitude |
| Breast (female) |
+++ |
High |
+++ |
High |
| Ovary, fallopian tubes, peritoneum |
+++ |
High |
+++ |
Moderate |
| Breast (male) |
+ |
Not defined |
+++ |
Low |
| Pancreas |
++ |
Very low |
+++ |
Low |
| Prostate |
+ |
Not defined |
+++ |
High |
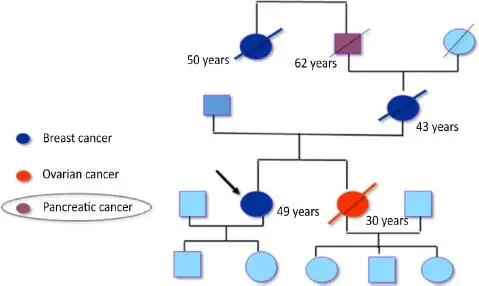
Figure 1.1. Familial pancreatic cancer in a syndromic context; identification of a mutation in the BRCA2 gene in the index case (indicated by an arrow). For a color version of this figure, see www.iste.co.uk/boukhatem/oncogenetics.zip
Figure 1.2. BRCA2 mutations are associated with breast and ovarian cancer, but also increase the risk of prostate cancer in men
Other genes in the BRCA1/2 pathway (repair of double-stranded DNA breaks) have also been implicated in hereditary ovarian cancer; in particular, mutations in RAD51C, RAD51D and BRIP1 confer ~10% increased risk of ovarian cancer.
Studies have identified RAD51C, RAD51D, BRIP1 and FANCM as likely susceptibility genes, particularly for the high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) histotype (high-grade epithelial tumors of the serous and endometrioid subtypes). In a subset of 10 families carrying RAD51C deleterious mutations, ovarian carcinomas histotypes were as follows: (56%), low-grade serous carcinoma (LGSC) (11%), high-grade endometrioid (11%) and unclassified (22%).
Deleterious mutations in the gene are associated with a moderate increase in the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). The relative risks associated with BRIP1 mutations have been estimated to be 11.22 for invasive EOC and 14.09 for high-grade serous.
The BRCA1 gene codes for a 220 kDa (1,863 amino acids) nuclear polypeptide. The BRCA1 protein has been implicated in various cellular processes, including repair of DNA damage and regulation of the transcription cycle, chromatin remodeling and ubiquitination. More recently, it has been shown to play a role in splicing and mediating estrogenic metabolites.
BRCA2 encodes a protein of 3418 amino acids and contains repeats of 39 amino acids that are critical for the binding of RAD51 recombinase (RAD51), a protein necessary for the repair of recombinant DNA. BRCA2 appears to have a more restricted role, largely limited to recombinant DNA repair and regulation of RAD51.
The CHEK2 gene codes for a cell cycle checkpoint regulatory protein and therefore this gene is a putative tumor suppressor. It contains an associated protein interaction domain at the fork head, essential for activation in response to DNA damage and is rapidly phosphorylated in response to replication blockages and DNA damage.
The partner and localizer gene of BRCA2 (PALB2) encodes a protein that can function in tumor suppression. This protein binds and colocalizes with the BRCA2 protein in nuclear foci and likely allows stable intranuclear localization and accumulation of BRCA2.
The nibrin gene (NBN) : mutations in this gene are associated with Nijmegen breakage syndrome, an autosomal recessive chromosomal instability syndrome characterized by microcephaly, growth delay, immunodeficiency and a predisposition to cancer. The coded protein is a member of the MRE11/RAD50 double-strand break repair that consists of five proteins. The protein is thought to be involved in the repair of double-stranded DNA breaks and in the activation of check points induced by DNA damage.
DEFINITION.– Microcephaly is an abnormality of the head (small size), a congenital condition associated with incomplete brain development .
The BRCA1 gene associated RING domain 1 (BARD1) encodes a protein that interacts with the N-terminal region of BRCA1. In addition to its ability to bind BRCA1 in vivo and in vitro , it shares homology with the two most conserved regions of BRCA1: the N-terminal RING pattern and the C-terminal BRCT domain. The formation of a stable complex between the BRCA1/BARD1 proteins may be an essential aspect of the tumor suppressor function of BRCA1.
The BRIP1 gene codes for a protein member of the RecQ DEAH helicase family and interacts with the BRCT repeats of the protein encoded by BRCA1. The attachment complex is important for the normal double-strand breaks repair function of BRCA1.
Читать дальше














