2 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1 Dispersion curve, E ( k ), for electron waves in a crystal. Disconti... Figure 2.2 Extended zone scheme. Figure 2.3 Reduced zone scheme. Figure 2.4 Wigner–Seitzconstruction (in red). Lattice nodes are indic... Figure 2.5 Presentation of fcc (a) and bcc (b) lattices in a rhombohedral se... Figure 2.6 3D shapes of the first Brillouinzone: (a) – the truncated octahe... Figure 2.7 Definitions of a metal, a semiconductor, and an insulator via the... Figure 2.8 The location of a Fermilevel in a monovalent metal. Figure 2.9 Band structure of divalent Mg metal. Figure 2.10 3D lattices of cubic diamond (a) and hexagonal graphite (b). Figure 2.11 Hexagonal prism, comprising three unit cells of a graphite struc... Figure 2.12 Honeycomb-like graphene lattice composed of two sublattices colo... Figure 2.13 Reciprocal lattice of graphene with its first Brillouinzone (BZ... Figure 2.14 Illustration of electron hopping between graphene sublattices (c... Figure 2.15 Energy profiles between selected points in reciprocal space mark... Figure 2.16 3D structure of energy bands near the K-points in graphene. Figure 2.17 Examples of Fermisurfaces in selected metals: monovalent fcc Cu... Figure 2.18 Fermisurfaces in monovalent Na (a) and Cs (b), as well as in di...Figure 2.19 Individual electron orbit with respect to the Fermisurface.Figure 2.20 Scheme of the Azbel-Kanercyclotron resonance.Figure 2.21 Illustration to the de Haas-van Alphenresonance conditions upon...
3 Chapter 3Figure 3.1 Linear chain of the equidistantly positioned atoms of mass, M .Figure 3.2 Dispersion laws for acoustic waves in a discrete periodic chain (...Figure 3.3 Linear chain composed of two different types of atoms of mass M 1...Figure 3.4 Elastic wave frequencies, as functions of wavevector, q , for acou...Figure 3.5 Lattice heat capacity, C v, showing saturation (the Dulong–Petit...Figure 3.6 Schematic presentation of two contributions to X-ray diffraction ...Figure 3.7 Scheme of a triple-axis neutron diffractometer: 1, source of ther...Figure 3.8 Scheme of a time-of-flight (TOF) neutron spectrometer: 1, source ...Figure 3.9 There is no thermal expansion in harmonic approximation.Figure 3.10 Illustration of thermal expansion due to lattice anharmonicity....Figure 3.11 Mutual orientation of the three orthogonal polarizations in acou...
4 Chapter 4Figure 4.1 Fermi–Diracdistribution (4.16) at T = 0 (solid blue curve)...Figure 4.2 Illustration of the electrical resistivity calculations.Figure 4.3 Energy diagrams, illustrating the derivation of the Fermi-Diracd...
5 Chapter 5Figure 5.1 Only free electrons, having energy within an interval ∼ k B T ...Figure 5.2 Illustration of the delta function-like derivative (red curve) of...Figure 5.3 Scheme illustrating the working principle of a thermocouple.Figure 5.4 The last 25 years of progress in increasing the ZT record magnitu...Figure 5.5 The structure of skutterudite, CoAs 3. Purple and yellow balls rep...Figure 5.6 Crystal structure of half- Heusleralloys. The atoms marked as X, ...
6 Chapter 6Figure 6.1 Structure types of typical semiconductors showing tetrahedral ato...Figure 6.2 Energy scheme of an intrinsic semiconductor. A small amount of th...Figure 6.3 The position of the Fermilevel in an intrinsic semiconductor is ...Figure 6.4 Schematic illustration of the n -doped semiconductor: the four-val...Figure 6.5 Energy scheme of the n -doped semiconductor. The Fermilevel is lo...Figure 6.6 Schematic illustration of the p -doped semiconductor: the four-val...Figure 6.7 Energy scheme of the p -doped semiconductor. The Fermilevel is lo...Figure 6.8 Schematic illustration of charge distribution across a p - n juncti...Figure 6.9 Band bending near a p – n junction.Figure 6.10 Potential energy function, W ( x ), across a p – n junction: for elec...Figure 6.11 Sketch, indicating the opposite directions of the internal, 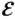 , a...Figure 6.12 I ( U ) characteristic of a p – n junction.Figure 6.13 Illustration of a p – n junction functioning as a diode.Figure 6.14 Illustration of the transistor effect obtained using a p – n junct...Figure 6.15 Scheme of a bipolar junction transistor.Figure 6.16 Scheme of a junction field-effect transistor (JFET).Figure 6.17 Illustration of the FET working principle. The letters S , G , and...Figure 6.18 Schematic design of a MOSFET.Figure 6.19 Schematics of a MOSFET working device: (a) no electric field; (b...Figure 6.20 Illustration to the calculation of the exciton radius and bindin...
, a...Figure 6.12 I ( U ) characteristic of a p – n junction.Figure 6.13 Illustration of a p – n junction functioning as a diode.Figure 6.14 Illustration of the transistor effect obtained using a p – n junct...Figure 6.15 Scheme of a bipolar junction transistor.Figure 6.16 Scheme of a junction field-effect transistor (JFET).Figure 6.17 Illustration of the FET working principle. The letters S , G , and...Figure 6.18 Schematic design of a MOSFET.Figure 6.19 Schematics of a MOSFET working device: (a) no electric field; (b...Figure 6.20 Illustration to the calculation of the exciton radius and bindin...
7 Chapter 7Figure 7.1 Illustration of the image charge method applied to the work funct...Figure 7.2 Graphical presentation of function (7.5).Figure 7.3 Energy scheme illustrating the concept of a work function.Figure 7.4 APRES measurement scheme.Figure 7.5 Changing the potential barrier for electron emission by applying ...Figure 7.6 Illustration of the basic principle that stands behind the work o...Figure 7.7 Energy schemes for a material being in contact with a vacuum: (a)...Figure 7.8 Illustration of the contact potential ( ϕ 0) concept.Figure 7.9 Illustration of band bending near the metal-semiconductor junctio...Figure 7.10 I – U characteristic of a Schottkydiode.Figure 7.11 Illustration of the image charge method applied for calculating ...Figure 7.12 Diagram illustrating the photon-electron interaction leading to ...
8 Chapter 8Figure 8.1 Coordinate system used for the skin-effect calculations. The meta...Figure 8.2 Direction of the Poyntingvector with respect to the light waveve...Figure 8.3 Application of Snell'slaw to light refraction in: (a) – righ...Figure 8.4 The action of a convex lens produced with conventional RH (a) and...Figure 8.5 Illustration with light focusing by a flat plate built of LH mate...Figure 8.6 Principal scheme of the split-ring resonator. The letter, C , indi...Figure 8.7 Illustration of the “invisible cloak” effect on propagating wave ...Figure 8.8 Illustration of light interference during its scattering within a...Figure 8.9 Illustration of the negative effective mass density in acoustic m...Figure 8.10 Schematics of the Helmholtzresonator.Figure 8.11 Scheme of the double “C” resonator (a) and membrane resonator (b...
9 Chapter 9Figure 9.1 The movement of light-induced electrons and holes across a p – n -ju...Figure 9.2 Sketch illustrating the working principle of the Grätzelcel...Figure 9.3 Energy scheme for the light/charge current conversion in the Grät...Figure 9.4 Main structural motifs in the RPphases: (a) – Sr 2RuO 4( n = 1) an...Figure 9.5 Schematic design of the silicon drift detector.Figure 9.6 An increase in the energy gap between mini-bands in the InAs/GaP ...Figure 9.7 Schematic presentation of the repeating block within the InAs/GaS...Figure 9.8 Sketch of a metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) capacitor.Figure 9.9 Sketch illustrating the working principle of a CCD. Note that for...Figure 9.10 Illustration of the LED action.Figure 9.11 The three-level scheme widely used for the stimulated light emis...Figure 9.12 Schematic illustration of the semiconductor laser principle.Figure 9.13 Schematic illustration of a photonic structure with periodic mod...
Читать дальше

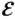 , a...Figure 6.12 I ( U ) characteristic of a p – n junction.Figure 6.13 Illustration of a p – n junction functioning as a diode.Figure 6.14 Illustration of the transistor effect obtained using a p – n junct...Figure 6.15 Scheme of a bipolar junction transistor.Figure 6.16 Scheme of a junction field-effect transistor (JFET).Figure 6.17 Illustration of the FET working principle. The letters S , G , and...Figure 6.18 Schematic design of a MOSFET.Figure 6.19 Schematics of a MOSFET working device: (a) no electric field; (b...Figure 6.20 Illustration to the calculation of the exciton radius and bindin...
, a...Figure 6.12 I ( U ) characteristic of a p – n junction.Figure 6.13 Illustration of a p – n junction functioning as a diode.Figure 6.14 Illustration of the transistor effect obtained using a p – n junct...Figure 6.15 Scheme of a bipolar junction transistor.Figure 6.16 Scheme of a junction field-effect transistor (JFET).Figure 6.17 Illustration of the FET working principle. The letters S , G , and...Figure 6.18 Schematic design of a MOSFET.Figure 6.19 Schematics of a MOSFET working device: (a) no electric field; (b...Figure 6.20 Illustration to the calculation of the exciton radius and bindin...










