While the word “Smart Building” (SB) may offer a focus on a futuristic intelligent space in science fiction films, the truth SBs still occur yet are its amount that. Standard buildings can be converted efficiently into SBs with limited infrastructural improvements due to recent developments in Machine intelligence (ML, large amounts of data Analysis, Items Network camera technology (IoT)) [51]. Smart workplaces, smart schools, intelligent residences, intelligent health facilities, intelligent hospitals and a broad range of other SBs provide digital systems that provide a vast assortment of value-added services, such as energy conservation, and often maintain occupant convenience, safety and protection.
1.10.1 Smart Building Appliances
SBs are also incorporated into a single framework, including a wide variety of programs and facilities including energy management systems, temperature controls, access protection systems, fire protection and defense, light and life regulation, telephone infrastructure, bureau automation, computer networks, region position systems, LANs, informatic management. The SB devices, including air temperatures, lighting systems, solar panels, energy storage systems, temperature sensors, power sensors and tracking cameras, will be shown in Figure 1.19.
Central management of these components, for example, will facilitate efficient energy consumption by smart monitoring of the air-conditioners and lights and good management of various sources of green and brown electricity. In most instances, SB requires a Controller Area Network (CAN) connection to Ethernet backend.
1.10.2 Intelligent Tools, Cameras and Electronic Controls in a Connected House (SRB)
Compared with commercial buildings, intelligent systems are simpler to incorporate in residential buildings because residential buildings have fewer technological infrastructure and less strict quality specifications. Because industrial buildings typically receive more public tourists, design projects are generally more complex than development models for private buildings [25].
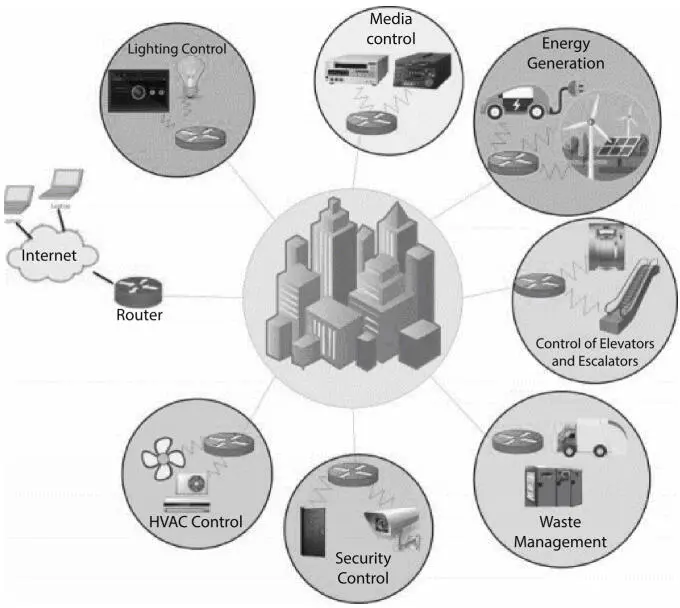
Figure 1.19Smart building appliances [52].
For apartment buildings typically have the bulk of the time with a small number of inhabitants. Rather than residential houses, the expenses involved with the procurement and development of intelligent equipment and services with industrial buildings are higher. Figure 1.20 shows an embedded socialized housing framework using an intelligent sensor network. Sensors include energy supply, estimation, HVAC, illumination and protection control systems. A building automation network operates a range of interconnected tools, sensors and actuators that together offer facilities for the well-being of citizens. Of starters, washers and drives, refrigerators, thermostats, lighting systems, power outlets, energy meters, smoke alarms, TVs, game consoles, window/door controls and alarms, air conditioning systems, video cameras and sound-detectors [36, 38, 39], are examples of these electronic appliances, sensors and actuators. These include advanced electronic systems like sophisticated floors and smart furnishings are continuously being built [40, 42].
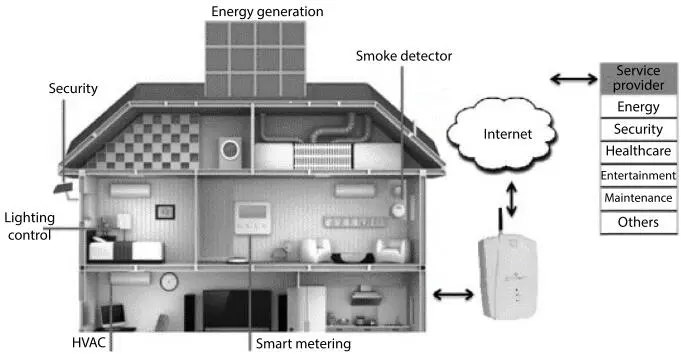
Figure 1.20Smart Residential Building Connected Sensors and Actuators.
1.10.3 Level if Clouds are the IoT Institute Level With SBs
To order to maintain optimum monitoring and activity of the design, the IoT enables the convergence Interconnection and transfer of data processing capacities in embedded devices to SBs in high definition. IoTs are based on a layer-dependent design as seen in Figure 1.21. Data collected from different sensing devices is obtained, which are able to track environmental conditions, gather data on the civilian community and identification of disturbances (e.g., bursts of flames and water pipes). This layer also contains actuators to be monitored for energy conservation, water usage minimization and so on.
In the network layer (second layer in Figure 1.21), there is a clear access and core networking potential. This layer is used to link the smart grid with the top layers accountable for the processing of data. An intermediate software layer known as the middleware layer (the third layer in Figure 1.21) is required to incorporate the design sensing layer smoothly into heteroscope devices and networks. The layer acts as a link between the embedded devices operating intelligent sensors and network backend services.
The context and the somaticized discovery layer (Figure 1.21, fourth layer) is responsible for the management of context and semanticized discovery, including context and semanticization generation. The analysis and reasoning layer (fifth layer in Figure 1.21) processes extracted knowledge from the middleware and takes decisions according to the application level. Various information retrieval systems are implemented in this layer to combine, retrieve and contextualize massive knowledge into practical know-how.
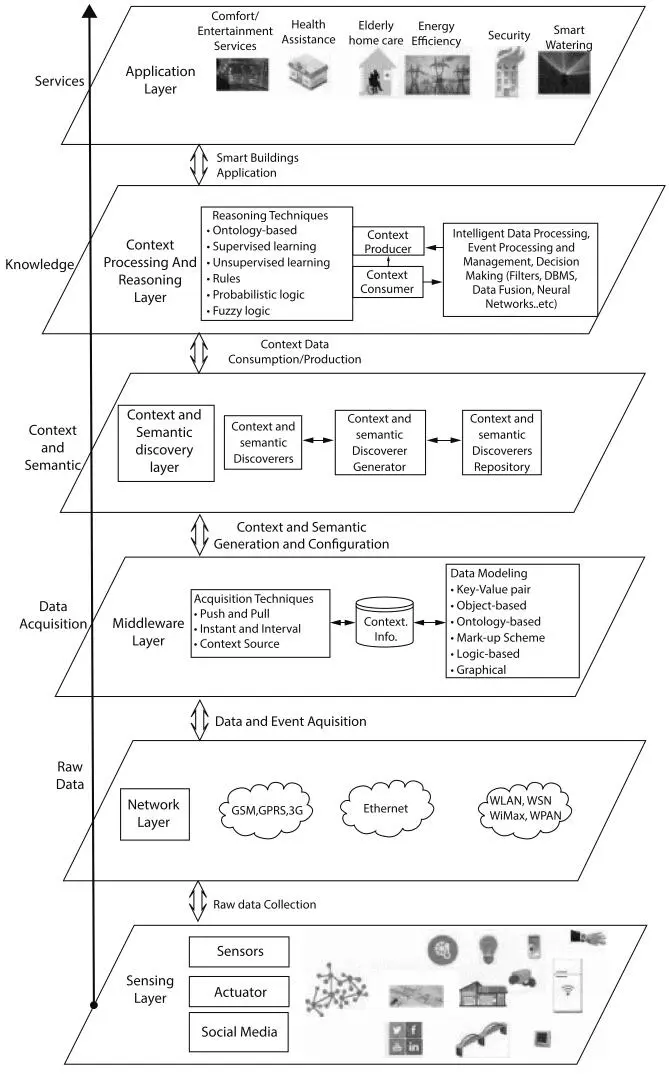
Figure 1.21IoT smart resilience building architecture.
These included exceptional facilities and initiatives, an OSI model (Figure 1.20’s biggest layer). This layer offers a context with clear links to the fundamental functions for various forms of applications. In addition, panels for managing automatic, the residence will create confined environments and infrastructure for a regional human–computer interface. The residence will create confined environments and infrastructure for a regional human–computer interface.
Knowledge and the retrieval of information in the sense of implementation and decision-making and the last layer of operation, including health care and home elderly care, convenience and entertainment facilities, protection, tele-management, intelligent watering, and resource output etc. analyze the core features of residential and industrial structures.
1.10.4 Component of Smart Buildings (SB)
Advances in intelligent design technologies contribute to widespread production of SBs, with the integration of IT and building automation systems, creating advantages for housing developers efficient and sustainable. The core elements of SB systems are seen in Figure 1.6, which involve vast sensors and drives, networks and connectivity structures, a software interface framework and a smart control device [54]. Figure 1.22 reveals different smart building components.
New solutions use smart sensors and control units attached to a central network. Such control systems and intelligent sensors are installed in the whole area. Each device has its own network and communications array that enables the central system to interact. SBs run linked networks that act for several structures as a connectivity backbone.
Sensors and Actuators for SBs
Mechanical elements calculating and monitoring environmental values of their system are sensors and actuators. Sensors collect and make information ready for the system from the environment. IR sensors can, for example, be used in a room for detecting human presence. While the actuator is an instrument for converting an electronic power signal for physical activity, determines and then executes ecological acts that enable automated interaction, remotely and with the environment. For examples, one or more control lights may be turned on and off by an actuator.
Читать дальше




![Чарльз Диккенс - A Tale of Two Cities [С англо-русским словарем]](/books/26616/charlz-dikkens-a-tale-of-two-cities-s-anglo-thumb.webp)










