Figure 2.6 The device configuration of (a) direct and (b) plasmonic enhanced plasmonic solar cell and (c) plasmonic DSSC.
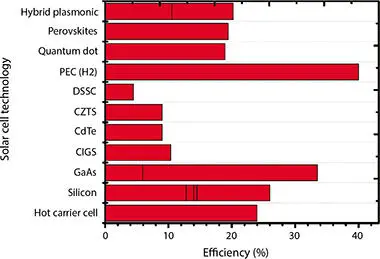
Figure 2.7 Efficiency for various plasmonic solar cell technology.
Table 2.3 Effect of various plasmonic nanostructures on solar cell technologies.
| Solar cell technology |
Plasmonic nanostructure |
Mechanism |
Efficiency (%) |
Reference |
| Hot carrier cell |
Au@TiO 2/PEDOT |
Direct plasmonic transparent active layer |
0.2 |
[46] 2019 |
| Au |
Direct plasmonic as active layer |
24 |
[59] Wu, 2013 |
| Silicon |
Ag with diameter 14-100 nm |
At top surface |
26 |
[27] Atwater HA, 2010 et al ., 2010 |
| Al |
At top of surface |
14.5 |
[53] 2013 |
| Au |
At top of surface |
14 |
[115] Jacak, 2018 |
| Ag |
At top of surface |
12.8 |
[115] Jacak, 2018 |
| GaAs |
Ag |
At top of surface |
22.15 |
[94] 2019 |
| Ag |
At top surface |
5.9 |
[51] 2008 |
| CIGS |
Au |
At top surface |
4 |
[61] Londhe, 2016 |
| Ag |
At top surface |
9.44 |
[115] Jacak, 2018 |
| Au |
At top surface |
10.34 |
[115] Jacak, 2018 |
| CdTe |
Au |
At top surface |
9 |
[62] Kim, 2015 |
| CZTS |
Au |
At back surface |
9 |
[64] Omar, 2018 |
| DSSC |
Ag |
Embedded with TiO 2 |
3.62 |
[85] 2017 |
| Au (15 nm) |
Embedded with TiO 2 |
4.46 |
[73] 2014 |
| PEC |
Au@TiO 2 |
Emdded with TiO 2for oxygen evolution |
40 (H atom per electron) |
[88] 2012 |
| Quantum dot |
Ag@PdS |
At top surface |
6.03 |
[114] Kawawaki, 2015 |
| Au@PbS |
At top surface |
9.58 |
[81] Chen, 2018 |
| CdS@GaAs |
At top surface |
18.9 |
[82] Lin, 2012 |
| Perovskites |
Ag |
At top surface |
13.46 |
[107] Aliaksandr, 2018 |
| Ag@TiO 2 |
Embedded with TiO 2 |
16.3 |
[113] Saliba, 2015 |
| Au@coreshell |
Embedded with core-shell structure |
19.42 |
[87] 2020 |
| Hybrid plasmonic |
Au@AuQD:organic |
At top surface |
13 |
[83] Phetsang, 2019 |
| Ag@TiO 2@Pa |
Embedded with core-shell structure |
20.2 |
[86] 2019 |
| Au@ZnO:OEC |
Embedded |
10.5 |
[89] 2016 |
2.4.2 Plasmonic-Enhanced Solar Cell
They are considered as simple plasmonic solar cells. The crystalline or amorphous silicon and thin film solar cells can be developed using SPR of metal nanoparticles. The plasmonic nanostructure can act as light harvesting antennas to enhance optical path length of photon through scattering that resulting in enhanced absorption and generation of e-h pairs in semiconductors [50]. For example, deposition of Au, Ag, or Cu metal nanoparticle array in Si/SiO 2device increases 20 times more photocurrent in plasmonic solar cell. The various solar cell technologies such as conventional silicon, GaAs, CIGS, CdTe, and CZTS have been demonstrated using plasmonic nanostructures with improved efficiency. By making stacks of thin film PV cell, the multi-wavelength light can be absorbed in plasmonic solar cells through enhanced scattering [51–53].
2.4.3 Plasmonic Thin Film Solar Cells
Plasmonic thin film designs in solar cells improve the absorption using SPR. This enhancement is mainly because of the manipulation of light for getting desired circulation, absorption, and scattering. The very thin photo active layer upto 100 nm has been proved theoretically. They can use cheaper substrate than silicon such as plastic, steel, or glass [54].
The arrays of metal nanostructures at top of GaAs solar cell have been demonstrated and achieved enhanced performance in near-IR region [55]. The silver metal nanoparticle based plasmonic GaAs solar cells have shown 8% increment in short circuit current and achieved 5.9% efficiency. The plasmonic nanoparticles have the potential to make thinner PV layers with enhanced performance.
Integrating plasmonic nanostructures with silicon solar cells can significantly enhance the absorption in visible as well as near-IR spectrum. Green et al . have demonstrated the enhanced absorption in silicon thin film PV cells using Ag plasmonic nanoparticles [52]. Yang et al . have demonstrated monocrystalline silicon solar cells with effect of plasmon resonance on silicon nanowire decorated with Ag metal nanoparticles [53]. Yue et al . have demonstrated 15% enhancement in absorption by using plasmonic core-shell (the dielectric as core and metal as shell) insulators for a-Si solar cells [54]. Atwater et al . have demonstrated amorphous Si PV device with about 26% efficiency by usage of plasmonic nanostructure [59]. This device configuration has improved the electrical properties of the PV cells. Zhang et al . have fabricated plasmonic solar cell with about 18.2% efficiency using advanced light trapping approach in a proper device design, which has reduced the wafer thickness without loss in energy conversion [53]. Derkacs et al . have demonstrated 8.3% energy conversion efficiency with gold nanoparticles on thin film silicon [57]. Stuart and Hall et al. have achieved enhanced photocurrent by a factor of 18- at 800-nm wavelength in 165 nm thick Si/insulator with silver metal nanoparticles at the top surface of PV cell [56]. Schaadt et al . have shown the improvements in silicon solar cells by 80% at 500-nm wavelength using gold nanoparticles at top of surface [58]. Pillai et al . have shown the increment in photocurrent by 19%–33% using Ag plasmonic nanoparticles [52]. Singh and Verma et al . have used fabricated silicon plasmonic solar cell using copper plasmonic nanoparticles [65]. The mc-Si PV devices also have been shown using Al metal nanoparticles as antireflection coating (ARC) on top surface. This configuration has achieved the solar cell parameters such as 34.0 mA/ cm 2short circuit current (I sc) and efficiency of 14.5% [66]. Lian et al . have reported on the loss of hot electrons [59]. There is a need of quality research to develop plasmonic silicon solar cells for commercial applications.
CIGS and CdTe PV cells have fabricated using Ag and Au plasmonic nanoparticles and achieved conversion efficiencies of about 10.34% and 9%, respectively [68, 69]. The research interest in CZTS has been increased due to its low cost, non-toxic and earth abundant elements. These results could open a new way of integrating plasmonic nanostructure with existing PV devices for higher efficiency. A layer of Au plasmonic nanostructure in CZTS has shown enhancement in light trapping and efficiency. CZTS solar cells with integration of plasmonic nanostructures as ARC coatings are promising to decrease reflection and for increasing absorption for increasing its efficiency at commercial scale applications [70, 71].
2.4.4 Plasmonic Dye Sensitized Solar Cells (PDSSCs)
PDSSC with plasmonic Au nanoparticles embedded in TiO 2has shown 26% efficiency [73]. There are interesting mechanisms that are responsible for enhancing conversion of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS)–based solar cells using metal nanostructures. These mechanisms include the increment in photocurrent by local electric field enhancement and amplification of the electric field near semiconductor surfaces by surface plasmons [74]. The plasmonic DSSC with hematite coated on Au nanopillars and N719 dye has shown enhanced absorption in visible range and efficiency of 10.2% [75]. Chander et al . have developed plasmonic DSSC with Au nanoparticle embedded with TiO 2thin film with enhanced absorption in visible range and energy conversion efficiency of 4.46% [73].
Читать дальше













