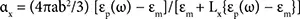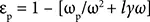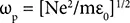The specific wavelengths of light spectrum make the conductive electrons to oscillate collectively in the metal. This phenomenon is known as plasmonic resonance or surface plasmon resonance (SPR), which is schematically shown in Figure 2.2. Plasmon resonance of free electrons in metal nanoparticle is basis of the plasmonic effect. SPR wavelength is depending on the medium, size and shape of metal nanoparticles. SPR excitations increase more absorption and scattering of light compared to nonplasmonic nanoparticles [18, 19]. The optical properties can be tuned to absorb wide range of light spectrum of the electromagnetic radiation by tuning the thickness, size, shape, and composition of nanostructure. The reflecting color also can also be tuned by shifting the scattering and absorption, for example, solutions of gold and silver nanoparticles have ruby red and yellow color due to strong scattering, respectively [20, 21]. The resonance wavelength of plasmonic nanostructure is influenced by the refractive index (n) of material, for example, peak resonance of Ag nanoparticles (80 nm in size) in water (n = 1.33) is at 445 nm and in air is about 380 nm. This theory was explored by Mie theory that can be used to analyze the scattering from spherical particle at any wavelength of light [22, 23]. The coupling effect in plasmonic nanoparticles is responsible for the shifting in absorption and color of particles. The scattering by the metal nanoparticles is more important than the absorption of light in plasmonic solar cells and hence plasmonic nanostructures have emerged as promising candidate to enhance the characteristics in solar cells, detectors, and sensors. The plasmonic nanoparticles of silver (Ag) and gold (Au) are mostly used at the top of the surface of PV device because of their SPR exist in the visible range. Al nanoparticles show SPR in UV range but they are unable increase the efficiency in plasmonic solar cells [24].
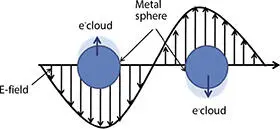
Figure 2.2 Schematic representation of surface plasmon resonance.
2.1.2 Classification of Plasmonic Nanostructures
SPR are sensitive to the geometry of device, material, and light-matter interaction. The shapes of nanostructure can be classified as sphere, thin film, star, core-shell, disk, cavity, cage, etc. [25]. The plasmonic metal nanoparticles or thin films are used to get maximum absorption of light in absorbing layer. SPRs can be tuned to obtain desired frequency by using specific grating. The plasmonic nanostructures such as metal nanoparticle or thin film are mainly used in plasmonic solar cells that depend on the design and method. The most frequent and widely used design is the deposition plasmonic nanoparticle at the top surface of PV device. The light is scattered by the SPR in all directions. This increases the overall absorption in solar cells. The core (metal)–shell (dielectric) designs are also used to absorb more light. The other design of plasmonic nanostructure is depositing a nano-sized thin film of metal on or below the semiconductor layer. The sunlight generates electric fields inside the absorber layer and electrons can be collected as a flow of current [26–28]. The schematic representation of plasmonic solar cell with nanoparticle and thin film configuration is shown in Figure 2.3.
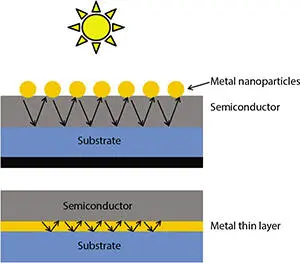
Figure 2.3 The utilization of plasmonic nanoparticle (upper) and thin film (lower) for solar cells.
2.2 Principles and Working Mechanism of Plasmonic Solar Cells
2.2.1 Working Principle
A plasmonic nanostructure can be used as direct and indirect applications such as active PV material and plasmon modified active semiconductor, respectively [29]. The fundamental operational principle of plasmonic solar cell is scattering through SPR in metallic nanoparticles on semiconductor and surface plasmon polaritons at the metal/semiconductor interface.
Solar cell performance mostly depends on photon energy and active PV layers. When a photon falls on the surface of semiconductor, the photons will pass through material (if photons have energy lower than the semiconductor band gap, E photons< E g) and photons will reflect from the surface or they will be absorbed by the semiconductor layer (if photons have energy higher than the band gap of semiconductor, E photons> E g). The unused sunlight produces heat in the solar cell through lattice vibrations and decreases the performance. An electron is excited into conduction band from the valance band due to the illumination of light and creates hole in semiconductor. Thus, absorbed photon generates e-h pair in the semiconductor. The electrons and holes have tendency to recombine due to their opposite charge, so they can be separated and the electrons can be collected as a flow of current. The fast collection of electrons would produce more electricity. Plasmonic nanostructures decrease the loss of incident photons by increasing optical path length in PV devices [30]. The very thin semiconducting layer absorbs less sunlight and hence the plasmonic nanostructures are used to enhance the absorption through scattering at resonance wavelengths in solar cell. The thinner conducting material will make quick collection of electrons but thin surface absorbs less photons. Hence, the thickness of photoactive material needs to be tuned for achieving maximum absorption of light, which will help to improve the efficiency of solar cell [31–33]. The overall absorption increases due to the surface plasmons in plasmonic solar cells. The plasmonic effect can be understood using polarizability of particles [34]. The polarizability α of the particle is given by Equation (2.1):
(2.1) 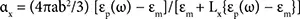
where ε pand ε mcorrespond to dielectric function of metal nanoparticle and medium, respectively. L xstands for depolarization factor and depends on shape of nanoparticle. The polarizability of spherical metal nanoparticle becomes maximum when resonance occurs. ε pcan be defined as Equation (2.2):
(2.2) 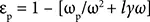
Plasmon frequency (ω p) is defined as Equation (2.3). It depends on free electrons in spherical particles. For example, gold, silver, copper, and aluminum show the resonance frequency in visible, UV, visible and UV, respectively. A gold show broader resonance peak than silver and it is highly stable where as silver is highly unstable [35]:
(2.3) 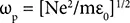
where N, e, m e, and ε 0correspond to free electron density, charge of electron, electron’s effective mass, and dielectric constant in free space, respectively.
A resonance frequency in free space can be given as Equation (2.4).
(2.4) 
2.2.2 Mechanism of Plasmonic Solar Cells
Plasmonic nanostructures are used as light harvesting antennas in thin film solar cells. Plasmonic nanostructures such as metallic nanoparticles or thin films are used to trap or concentrate light. They can be introduced at top or back surface as antireflecting coating in solar cells. Various fabrication techniques can be used to deposit metal nanoparticles. A simple technique is the evaporation followed by heat treatment for making arrays of metal nanoparticles. The lithography is also used for making metal nanoparticles [36, 37].
Читать дальше