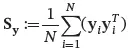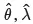Random effects, as the name implies, refer to the underlying random factors in an industrial process or system that impact on the outcome of the process. In diagnosis and prognosis applications, random effects can be used to model the sources of variation in a process and the variation among individual characteristics of multiple heterogeneous units. Some excellent books are available in the industrial statistics area. However, these existing books mainly focus on population level behavior and fixed effects models. The goal of this book is to adapt and bring the theory and techniques of random effects to the application area of industrial system diagnosis and prognosis.
The book contains two main parts. The first part covers general statistical concepts and theory useful for describing and modeling variation, fixed effects, and random effects for both univariate and multivariate data, which provides the necessary background for the second part of the book. The second part covers advanced statistical methods for variation source diagnosis and system failure prognosis based on the random effects modeling approach. An appendix summarizing the basic results in linear spaces and matrix theory is also included at the end of the book for the sake of completeness.
This book is intended for students, engineers, and researchers who are interested in using modern statistical methods for variation modeling, analysis, and prediction in industrial systems. It can be used as a textbook for a graduate level or advanced undergraduate level course on industrial data analytics and/or quality and reliability engineering. We also include “Bibliographic Notes” at the end of each chapter that highlight relevant additional reading materials for interested readers. These bibliographic notes are not intended to provide a complete review of the topic. We apologize for missing literature that is relevant but not included in these notes.
Many of the materials of this book come from the authors’ recent research works in variation modeling and analysis, variation source diagnosis, and system condition and failure prognosis for manufacturing systems and beyond. We hope this book can stimulate some new research and serve as a reference book for researchers in this area.
Shiyu Zhou Madison, Wisconsin, USA Yong Chen Iowa City, Iowa, USA
We would like to thank the many people we collaborated with that have led up to the writing of this book. In particular, we would like to thank Jianjun Shi, our Ph.D. advisor at the University of Michigan (now at Georgia Tech.), for his continuous advice and encouragement. We are grateful for our colleagues Daniel Apley, Darek Ceglarek, Yu Ding, Jionghua Jin, Dharmaraj Veeramani, Yilu Zhang for their collaborations with us on the related research topics. Grateful thanks also go to Raed Kontar, Junbo Son, and Chao Wang who have helped with the book including computational code to create some of the illustrations and designing the exercise problems. Many students including Akash Deep, Salman Jahani, Jaesung Lee, and Congfang Huang read parts of the manuscript and helped with the exercise problems. We thank the National Science Foundation for the support of our research work related to the book.
Finally, a very special note of appreciation is extended to our families who have provided continuous support over the past years.
S.Z. and Y.C.
We will follow the custom of notations listed below throughout the book.
| Item |
Notation |
Examples |
| Covariance matrix (variance–covariance matrix) |
cov(⋅), Σ |
cov( Y), Σy |
| Cumulative distribution function |
F ( y), F ( y; θ ), Fθ ( y) |
|
| Defined as |
:= |
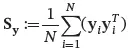 |
| Density function |
f ( y), f ( y; θ ), f ( y) |
|
| Estimated/predicted value |
accent ^ |
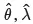 |
| Expectation operation |
E (⋅) |
E ( Y ), E ( Y) |
| Identity matrix |
I, I n( n by n identity matrix) |
|
| Indicator function |
I (⋅) |
I ( y > a ) |
| Likelihood function |
L (⋅) |
L ( θ | y) |
| Matrix |
boldface uppercase |
X, Y |
| Matrix or vector transpose |
superscript T |
X T , Y T |
| Mean of a random variable (vector) |
μ , μ |
μy |
| Model parameter |
lowercase Greek letter |
θ, λ |
| Negative log likelihood function |
− l (⋅) |
− l ( θ | y) = −ln L ( θ | y) |
| Normal distribution function |
N (⋅,⋅) |
N ( μ ,σ 2), N ( μ, Σ) |
| Parameter space |
uppercase script Greek letters |
Θ, Ω |
| Probability of |
Pr(⋅) |
Pr( t 1≤ T ≤ t 2 |
| Trace of a matrix |
tr(⋅) |
tr( Σy) |
| Variance of a r.v. |
var(⋅), σ 2 |
var( Y ), var( ϵ ), σ bi 2, σ ϵ 2 |
| Vector |
boldface lowercase |
x, y |
| Vector or matrix of zeros |
0, 0 n , 0 n×m |
|
| Vector of ones |
1, 1 n( n by 1 vector of ones) |
|
1 Introduction
1.1 Background and Motivation
Today, we are facing a data rich world that is changing faster than ever before. The ubiquitous availability of data provides great opportunities for industrial enterprises to improve their process quality and productivity. Indeed, the fast development of sensing, communication, and information technology has turned modern industrial systems into a data rich environment. For example, in a modern manufacturing process, it is now common to conduct a 100% inspection of product quality through automatic inspection stations. In addition, many modern manufacturing machines are numerically-controlled and equipped with many sensors and can provide various sensing data of the working conditions to the outside world.
One particularly important enabling technology in this trend is the Internet of Things (IoT) technology. IoT represents a network of physical devices, which enables ubiquitous data collection, communication, and sharing. One typical application of the IoT technology is the remote condition monitoring, diagnosis, and failure prognosis system for after-sales services. Such a system typically consists of three major components as shown in Figure 1.1: (i) the in-field units (e.g., cars on the road), (ii) the communication network, and (iii) the back-office/cloud data processing center. The sensors embedded in the in-field unit continuously generate data, which are transmitted through the communication network to the back office. The aggregated data are then processed and analyzed at the back-office to assess system status and produce prognosis. The analytics results and the service alerts are passed individually to the in-field unit. Such a remote monitoring system can effectively improve the user experience, enhance the product safety, lower the ownership cost, and eventually gain competitive advantage for the manufacturer. Driven by the rapid development of information technology and the critical needs of providing fast and effective after-sales services to the products in a globalized market, the remote monitoring systems are becoming increasingly available.
Читать дальше