
FIG 3-7Belotero Balance is formulated with a lower viscosity than many of the other HAs, making it suitable for perioral rhytids, tear troughs, and atrophic scars. It is FDA approved for the correction of moderate to severe facial wrinkles and folds.
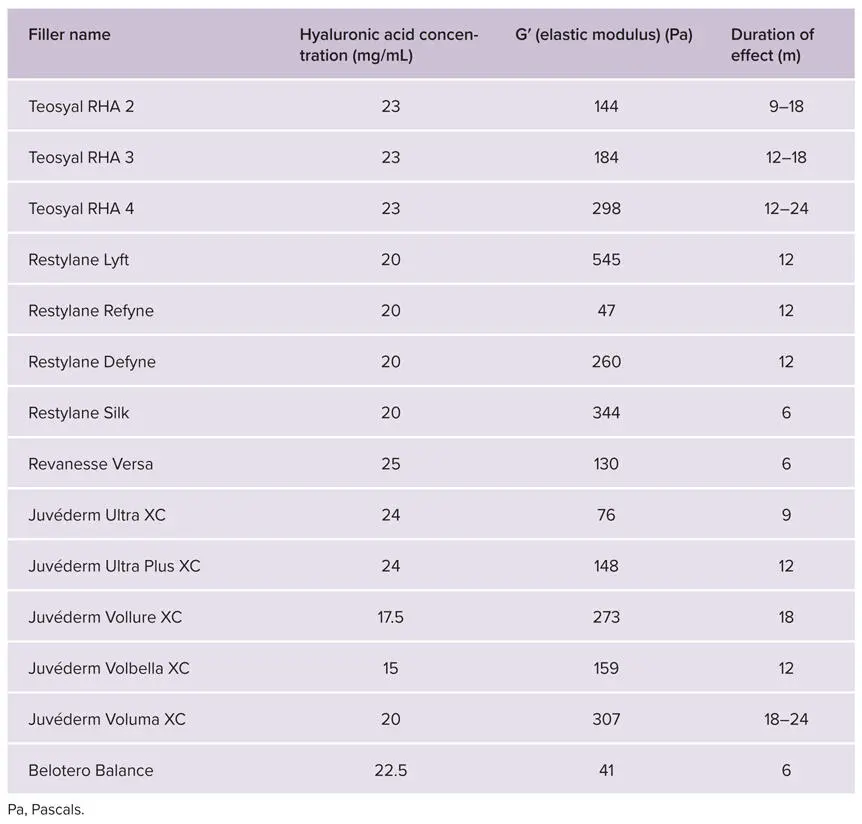
TABLE 3-2Concentration of hyaluronic acid in commercial HA dermal filler products 12,13
Long-Acting Fillers
This category includes commercial products made of poly-l-lactic acid (Fig 3-8) and calcium hydroxyapatite (Fig 3-9) as well as cells harvested from the patient’s own fat and blood tissues.

FIG 3-8Sculptra Aesthetic is the only dermal filler made of poly-l-lactic acid (PLLA), a synthetic polymer, that has been cleared by the FDA and is sold in the United States. It is intended for soft tissue augmentation and correction of shallow to deep skin depressions and contour deficiencies. Unlike most of the other dermal fillers, the effects of Sculptra are not apparent until about 4 weeks after the initial injection.

FIG 3-9Radiesse and Radiesse (+) are the first and only FDA-cleared calcium hydroxyapatite dermal fillers sold in the United States. Radiesse is indicated for midface and lower face wrinkles and folds and lasts for about 1 year.
Calcium hydroxyapatite
Commonly employed in dentistry as a bone grafting substitute, calcium hydroxyapatite (CaHA) was FDA cleared as a dermal filler agent in 2006. Unlike its predecessors, CaHA fillers provide immediate volume replacement while also stimulating a response in the body to produce its own collagen, resulting in a longer-lasting effect. CaHA is nonallergenic and inherently biocompatible, and it has a well-established safety profile. When used as a dermal filler, CaHA usually lasts for a minimum of 1 year before it is fully resorbed by the body.
Currently, only one CaHA dermal filler product is FDA cleared for use in the United States. Radiesse (Merz North America) consists of 30% synthetic CaHA microspheres suspended in a 70% aqueous carboxymethylcellulose gel carrier. The soluble carrier distributes the CaHA microspheres and gradually dissipates, while the microspheres induce neocollagenesis via fibroblast activation. Radiesse has a high G’ and is highly viscous compared to other dermal fillers, a property that allows it to remain in place when it is injected and not migrate. 6 In 2009, a protocol for mixing Radiesse with lidocaine was approved by the FDA. This formulation significantly increases patient comfort during the injection process.
Poly-l-lactic acid
Poly-l-lactic acid (PLLA) is a synthetic polymer that is probably familiar to most readers as a key component of Vicryl sutures (Ethicon). Indeed, polylactides have a long history of safe use in a number of biomedical pins, plates, and screws, in addition to sutures. First FDA cleared as a dermal filler in 2009, PLLA is unique among commercially available fillers in a number of ways. 15 First, PLLA is not a volumizer in the technical sense because it does not achieve its effect by taking up space. Its singular mechanism of action is the stimulation of neocollagenesis, which means that it restores but does not replace lost volume. Consequently, its full effects are gradual, requiring 3 to 4 injections at least 4 to 6 weeks apart. However, many patients continue to see improvement 2 years after the initial injection.
Second, the injection protocol is less convenient and more technique-sensitive than that of other fillers. The freeze-dried PLLA powder must be reconstituted in sterile water at least 24 hours before the scheduled injection in order to form a suspension. To ensure a uniform concentration, PLLA should be injected at room temperature to avoid the risk of an uneven response. Also, because the effects of the filler are delayed, it is essential not to overcorrect, which puts patients at increased risk of developing minute palpable nodules at the injection site that can last as long as 1 year. 16 Over time, the PLLA microparticles are metabolized by the body and expelled as carbon dioxide.
Sculptra Aesthetic (Galderma) is the only PLLA dermal filler available in the United States. It is primarily indicated for broad dermal correction rather than smoothing individual rhytids and is contraindicated in and around the lips. With regard to the procedures described in this text, Sculptra is ideal for augmentation of the malar areas and the chin.
Autologous fat
Encouraged by publicity of the broad versatility of stem cells, more patients are choosing fat harvested from their own body as a dermal filler over commercial options. Autologous fat transfer (AFT), also known as lipofilling , is a low-risk procedure that offers a number of advantages that many patients find attractive. First, fat grafts not only have an immediate volumizing effect on grooves and wrinkles, but stem cells that exist in the fat tissue are a rich source of growth factors that stimulate new collagen production. Second, most patients are delighted to be relieved of the extra fat around their abdomen or thighs. Third, because the filler consists of the patient’s own cells, the risk of an allergic reaction is nonexistent. So far, however, most studies report disappointing long-term outcomes, mostly because of unpredictable resorption of up to 70% of the volume of the fat graft. 17,18Furthermore, there is strong disagreement among clinicians as to the ideal method for harvesting and handling the fat grafts. 18 Therefore, its long-term results are variable and unpredictable.
Allofill (Biologica Technologies) is an off-the-shelf fat allograft that is available for patients who wish to avoid the pain, cost, and recovery time associated with the harvesting of autologous fat through liposuction. It offers all the benefits of AFT minus the guarantee of nonimmunogenicity, as it is sourced from donated tissue.
Platelet-rich plasma
Another autologous dermal filler option, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) offers all the benefits of lipofilling but without the drawbacks associated with fat graft harvesting. 19 Commonly used in dental (and other) surgical procedures to promote healing, PRP is inherently biocompatible and delivers an abundance of stem cells and other growth factors. Because it requires only a simple venipuncture procedure, it is significantly less painful, less invasive, and less expensive to harvest than autologous fat (Figs 3-10 and 3-11). Adding PRP to facial lipofilling can reduce recovery time and improve the overall esthetic outcome.
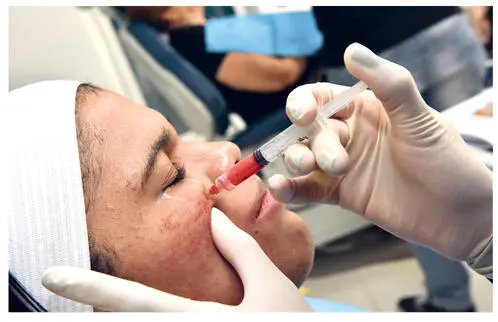
FIG 3-10Application of PRP through a needleless syringe following microneedling therapy.
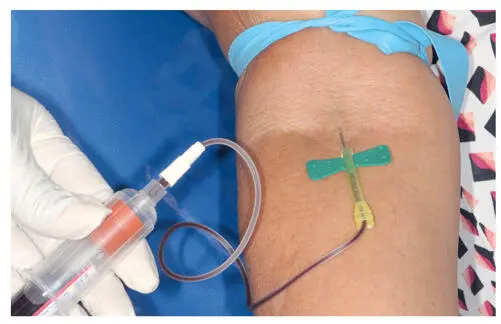
FIG 3-11PRP requires a venipuncture to draw the patient’s blood but eliminates the cost of using a commercial product.
Читать дальше


















