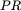9 Chapter 9Figure 9.1 Identify friend or foeFigure 9.2 MiG‐in‐the‐middleFigure 9.3 Too simple authenticationFigure 9.4 Simple replay attackFigure 9.5 Simple authentication with a hashFigure 9.6 Generic authenticationFigure 9.7 Challenge–responseFigure 9.8 Symmetric key authentication protocolFigure 9.9 Mutual authentication?Figure 9.10 Secure mutual authentication?Figure 9.11 Trudy's attackFigure 9.12 Strong mutual authentication protocolFigure 9.13 Authentication with public key encryptionFigure 9.14 Authentication via digital signatureFigure 9.15 Authentication and a session keyFigure 9.16 Signature‐based authentication and a session keyFigure 9.17 Mutual authentication and a session keyFigure 9.18 Encrypt and sign mutual authenticationFigure 9.19 Naïve attempt at PFSFigure 9.20 Diffie–HellmanFigure 9.21 Ephemeral Diffie–Hellman for PFSFigure 9.22 Mutual authentication, session key, and PFSFigure 9.23 Authentication using a timestampFigure 9.24 Encrypt and sign using a timestampFigure 9.25 Trudy's attack on encrypt and signFigure 9.26 Secure encrypt and sign with a timestampFigure 9.27 TCP 3‐way handshakeFigure 9.28 TCP “authentication” attackFigure 9.29 Initial SEQ numbers [139]Figure 9.30 Bob's caveFigure 9.31 Bob's cave protocolFigure 9.32 Fiat–Shamir protocolFigure 9.33 Protocol subject to replacement attack
10 Chapter 10Figure 10.1 Simplified SSHFigure 10.2 Man‐in‐the‐middle “attack” on SSHFigure 10.3 Socket layerFigure 10.4 Too‐simple protocolFigure 10.5 Simplified SSLFigure 10.6 Man‐in‐the‐middle attack on SSLFigure 10.7 SSL connection protocolFigure 10.8 IPsecFigure 10.9 IPsec digital signature main modeFigure 10.10 IPsec digital signature aggressive modeFigure 10.11 IPsec public key encryption main modeFigure 10.12 IPsec public key encryption aggressive modeFigure 10.13 Trudy making mischiefFigure 10.14 IKE phase 2Figure 10.15 IP datagramFigure 10.16 IPsec transport modeFigure 10.17 IPsec from host‐to‐hostFigure 10.18 IPsec tunnel modeFigure 10.19 IPsec from firewall‐to‐firewallFigure 10.20 Kerberized loginFigure 10.21 Alice gets TicketToBobFigure 10.22 Alice contacts BobFigure 10.23 WEP authenticationFigure 10.24 WEP encryptionFigure 10.25 GSM overviewFigure 10.26 GSM authentication and encryption keyFigure 10.27 GSM fake base station
11 Chapter 11Figure 11.1 Buffer and a boolean flagFigure 11.2 Simple buffer overflowFigure 11.3 Memory organizationFigure 11.4 Stack exampleFigure 11.5 Buffer overflow causes a problemFigure 11.6 Evil buffer overflowFigure 11.7 Improved evil buffer overflowFigure 11.8 Incorrect serial numberFigure 11.9 Buffer overflow in serial number programFigure 11.10 Failed buffer overflow attackFigure 11.11 Successful buffer overflow attackFigure 11.12 CanaryFigure 11.13 How mkdiris supposed to workFigure 11.14 Attack on mkdirrace conditionFigure 11.15 Slammer and Internet trafficFigure 11.16 Icon for freeMusic.mp3Figure 11.17 Unexpected effect of freeMusic.mp3TrojanFigure 11.18 Trojan revealed
12 Chapter 12Figure 12.1 Serial number programFigure 12.2 Correct serial numberFigure 12.3 Patched executableFigure 12.4 False disassemblyFigure 12.5 Anti‐debugging example
13 AppendixFigure A‐1 Number “line” mod 6Figure A‐2 DES expansion permutationFigure A‐3 DES P‐box permutationFigure A‐4 Initial 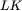 permutationFigure A‐5 Initial
permutationFigure A‐5 Initial 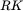 permutationFigure A‐6 Permutation
permutationFigure A‐6 Permutation 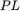 Figure A‐7 Permutation
Figure A‐7 Permutation 
1 Cover Page
2 Title Page Information Security Principles and Practice Third Edition Mark Stamp San Jose State University San Joe, California
3 Copyright
4 Dedication
5 Preface
6 About the Author
7 Acknowledgments
8 Table of Contents
9 Begin Reading
10 Appendix
11 Bibliography
12 Index
13 WILEY END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
1 v
2 xiii
3 xiv
4 xv
5 xvi
6 xvii
7 xviii
8 1
9 2
10 3
11 4
12 5
13 6
14 7
15 8
16 9
17 10
18 11
19 12
20 13
21 15
22 16
23 17
24 18
25 19
26 20
27 21
28 22
29 23
30 24
31 25
32 26
33 27
34 28
35 29
36 30
37 31
38 32
39 33
40 34
41 35
42 36
43 37
44 38
45 39
46 40
47 41
48 42
49 43
50 44
51 45
52 46
53 47
54 48
55 49
56 50
57 51
58 52
59 53
60 54
61 55
62 56
63 57
64 58
65 59
66 60
67 61
68 62
69 63
70 64
71 65
72 66
73 67
74 68
75 69
76 70
77 71
78 72
79 73
80 74
81 75
82 76
83 77
84 78
85 79
86 80
87 81
88 82
89 83
90 84
91 85
92 86
93 87
94 88
95 89
96 90
97 91
98 92
99 93
100 94
101 95
102 96
103 97
104 98
105 99
106 100
107 101
108 102
109 103
110 104
111 105
112 106
113 107
114 108
115 109
116 110
117 111
118 112
119 113
120 114
121 115
122 116
123 117
124 118
125 119
126 120
127 121
128 122
129 123
130 124
131 125
132 126
133 127
134 128
135 129
136 130
137 131
138 132
139 133
140 134
141 135
142 136
143 137
144 138
145 139
146 140
147 141
148 142
149 143
150 144
151 145
152 146
153 147
154 148
155 149
156 150
157 151
158 152
159 153
160 154
161 155
162 156
163 157
164 159
165 161
166 162
167 163
168 164
169 165
170 166
171 167
172 168
173 169
174 170
175 171
176 172
177 173
178 174
179 175
180 176
181 177
182 178
183 179
184 180
185 181
186 182
187 183
188 184
189 185
190 186
191 187
192 188
193 189
194 190
195 191
196 192
197 193
198 194
199 195
200 196
201 197
202 198
203 199
204 200
205 201
206 202
207 203
208 204
209 205
210 206
211 207
212 208
213 209
214 210
215 211
216 212
217 213
218 214
219 215
220 216
221 217
222 218
223 219
224 221
225 223
226 224
227 225
228 226
229 227
230 228
231 229
232 230
233 231
234 232
235 233
236 234
237 235
238 236
239 237
240 238
241 239
242 240
243 241
244 242
245 243
246 244
247 245
248 246
249 247
250 248
251 249
252 250
253 251
254 252
255 253
256 254
257 255
258 257
259 258
260 259
261 260
262 262
Читать дальше

 permutationFigure A‐5 Initial
permutationFigure A‐5 Initial  permutationFigure A‐6 Permutation
permutationFigure A‐6 Permutation  Figure A‐7 Permutation
Figure A‐7 Permutation