Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
An updated and comprehensive reference to pathology in every organ system in genetically modified mice Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice
Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice
Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
| Advantages Provides a unique identifierStandardizes spelling for accurate retrievalConveys the maker and technology used to create mutations and strainsCan communicate detailed genetic background information |
| Disadvantages Sometimes complexSometimes incomplete information |
| Uses Publications (most journals require use of official standardized symbols)Accurate ordering (to make sure that you get what you think you really ordered!)Correct breeding (facilities management)Maintain master pedigree and records |
In the early development of the Mouse Genome Database and MGI (see Chapter 2), italics and Greek letters could not always be used online and be retrieved by different computers, browsers, or software versions. Thus, in many databases, gene symbols are not italicized, and Greek letters are replaced by the modern English alphabet. Periods and commas could not always be visualized on computer screens so commas were replaced by semi‐colons, a critical problem when dealing with congenic strains, as discussed below. Gene names and symbols also changed over time to reflect new discoveries and to more accurately place them in molecular pathways or with genes of similar structure and function. In spite of all of this, MGI constantly maintains the most up‐to‐date nomenclature that can be searched using all previously assigned or published symbols ( Figure 3.2). It is important to look for and use the most current symbol as, over time, the same symbol may have been used by different laboratories for many different genes. For example, p38 currently is the synonym for 13 different genes on 10 different chromosomes ( Figure 3.3).
Standardized strain names inform readers of the specific strain type (inbred, hybrid, outbred, etc.), genetic background, source (vendor or research laboratory), and the mutation(s) carried by the mice used in a study. This information is critical for accurate reporting and scientific reproducibility. But where to start and how to understand and use this information? This chapter will discuss basic mouse genetics as it relates to the nomenclature used at the time of writing.
Inbred Mice
Inbreeding is well known to concentrate deleterious mutations. Most commonly inbreeding depression is due to the creation of homozygous recessive pathogenic or maladaptive genotypes but also loss of the fitness advantage of heterozygosity due to overdominance.
Most people are familiar with the “Royal disease,” hemophilia B, that affected males of European royalty (https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2009/10/case‐closed‐famous‐royals‐suffered‐hemophilia#:~:text=Now%2C%20new%20DNA%20analysis%20on,subtype%20known%20as%20hemophilia%20B.&text=Such%20was%20the%20case%20with,heir%20to%20the%20Russian%20throne). The same thing happens with laboratory mice. However, with a uniform genetic background combined with strict environmental controls and pathogen free status it is possible to minimize variables to test very specific parameters in a statistically efficient way. It is easier to identify a genetic component to a trait when the population under investigation is effectively one of 150 identical twins rather than 150 unrelated individuals. This comes at a cost ( Table 3.3); many lines are lost during inbreeding as they can be hard to maintain due to poor breeding efficiency and impacted by strain‐specific genetic diseases, all of which lead to increased expense compared to use of outbred mice. For example, the commonly used C3H/HeJ inbred strain has a short breeding time (around five months of age) due to the females having a high frequency of ovarian cysts and tumors [6]. There are, however, some advantages of specifically outbred populations such as the Collaborative Cross discussed below.
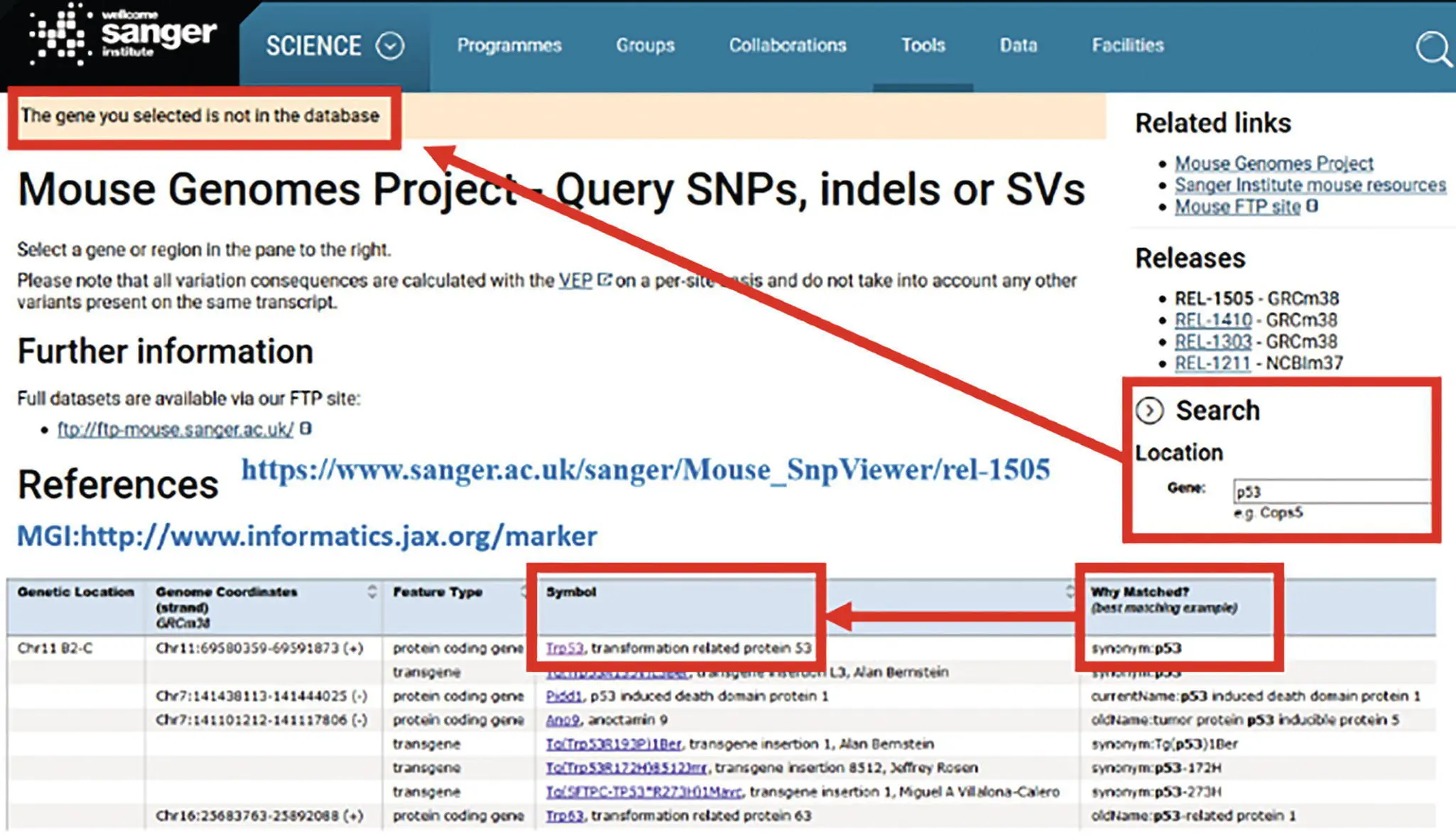
Figure 3.1 Top, searching p53 SNPs reveals “The gene you selected is not in the database.”An MGI search (bottom) reveals the current, correct symbol is Trp53 which does yield data in the Sanger database. Source: Wellcome Sanger Institute.
Inbred strains are developed by first mating a female (note that in mouse genetics, the female information is usually listed first) and male of disparate or even unknown backgrounds. From their progeny, one breeding pair is selected for breeding, and again one breeding pair is selected from their offspring. This is repeated for 20 generations (written F20 for filial generation 20) at which point the genome is mathematically about 99% homogeneous at all loci. At this point, the mice produced are considered to be an incipient inbred strain, and at F60, a fully inbred strain. In the process, many sublines will not reproduce, produce nonviable progeny, or develop other phenotypic problems making them difficult to maintain.
The first inbred strain, the DBA, was begun in 1909 by C.C. Little, the founder of The Jackson Laboratory ( http://www.informatics.jax.org/morsebook/chapters/russell.shtml). These mice were produced by crosses with a stock of mice that carried three different coat colors, dilute ( d ), brown ( b ), and non‐agouti ( a ), the letters of which designated the genes for these different colors [7]. This provides insight into the inbred strain names. The names are always in capital letters and not italicized and can represent coat color (C57BL where BL stands for black), origin of the strain or the person who created it (SJL: Swiss, Jim Lambert), or the phenotype (NOD: non‐obese diabetic or NON: non‐obese non‐diabetic). The line numbers were designated by the creator of the line. For example, C.C. Little mated female 57 and female 58 to male 52 (line C descended from Lathrop's stock) resulting in the C57 and C58 lines ( http://www.informatics.jax.org/morsebook/chapters/russell.shtml). A laboratory (lab) code is a 1–5 letters long symbol representing an investigator or institution that is registered with the Institute for Laboratory Animal Research (ILAR). Lab codes are assigned to alleles and strains to designate who made them ( Table 3.4).
While the full‐inbred strain designation is important, many of the most commonly used inbred strain names have been assigned official abbreviations ( Figure 3.4), to incorporate in derivative strains as described below. Many investigators use abbreviations, often incorrectly, in their publications. Some of the most common mistakes are to use B for BALB/cJ (correct is C) or B6 for any undefined C57BL substrain. Thus, it is often best for investigators to use official strain designations in the methods section of a publication.
Hybrid Mice (F1 and F2)
A cross of two unrelated inbred mice (for example, A/J × BALB/cByJ) produces pups that are all identically 50% maternal genome and 50% paternal genome with no recombination between any of the chromosomes. This is called the first filial or F1 hybrid generation and is named by putting the maternal then paternal parental strain names in parentheses separated by a lower case x, to represent cross, and followed by F1, (A/J x BALB/cByJ)F1 ( Figure 3.4). This can be abbreviated using the strain abbreviations ( Table 3.5) and dropping the parentheses and x, ACByJF1 in this case ( Figure 3.4). Aside from spontaneous mutations arising in that single generation, all pups from all litters of such a cross should be genetically identical and have hybrid vigor, which is increased fecundity and overall health resulting, in part, from the loss of homozygosity of detrimental recessive alleles. Additionally, F1 hybrid mice can generally accept tissue transplants from either parent ( Table 3.6). Unlike inbred strains, F1 hybrid mice are not self‐perpetuating because at meiosis each germ cell will have a unique set of recombinations between each of the two parental chromosomes, except for the sex chromosomes outside of the pseudoautosomal region.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Pathology of Genetically Engineered and Other Mutant Mice» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












