In power condensers, very‐high‐velocity steam may impinge on the tubes, causing excessive vibration. Figure 1-6shows a fatigue failure of a titanium condenser tube. The vibration amplitude was sufficient for the tubes to contact each other at midspan. In this case, the condenser was operated with only four of the six tube bundles, resulting in 150% of design flow velocity. Operation at 100% design flow did not cause any vibration damage.
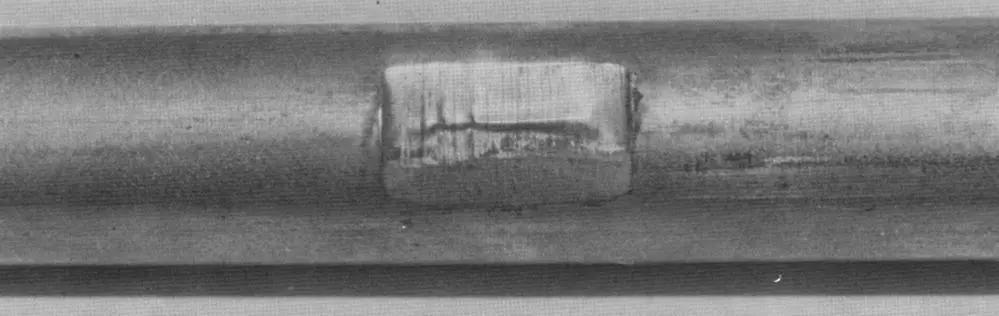
Fig. 1-4 Fretting Wear Through Tube Wall at a Lacing Strip Location in a Process Heat Exchanger (Pettigrew et al, 1977).
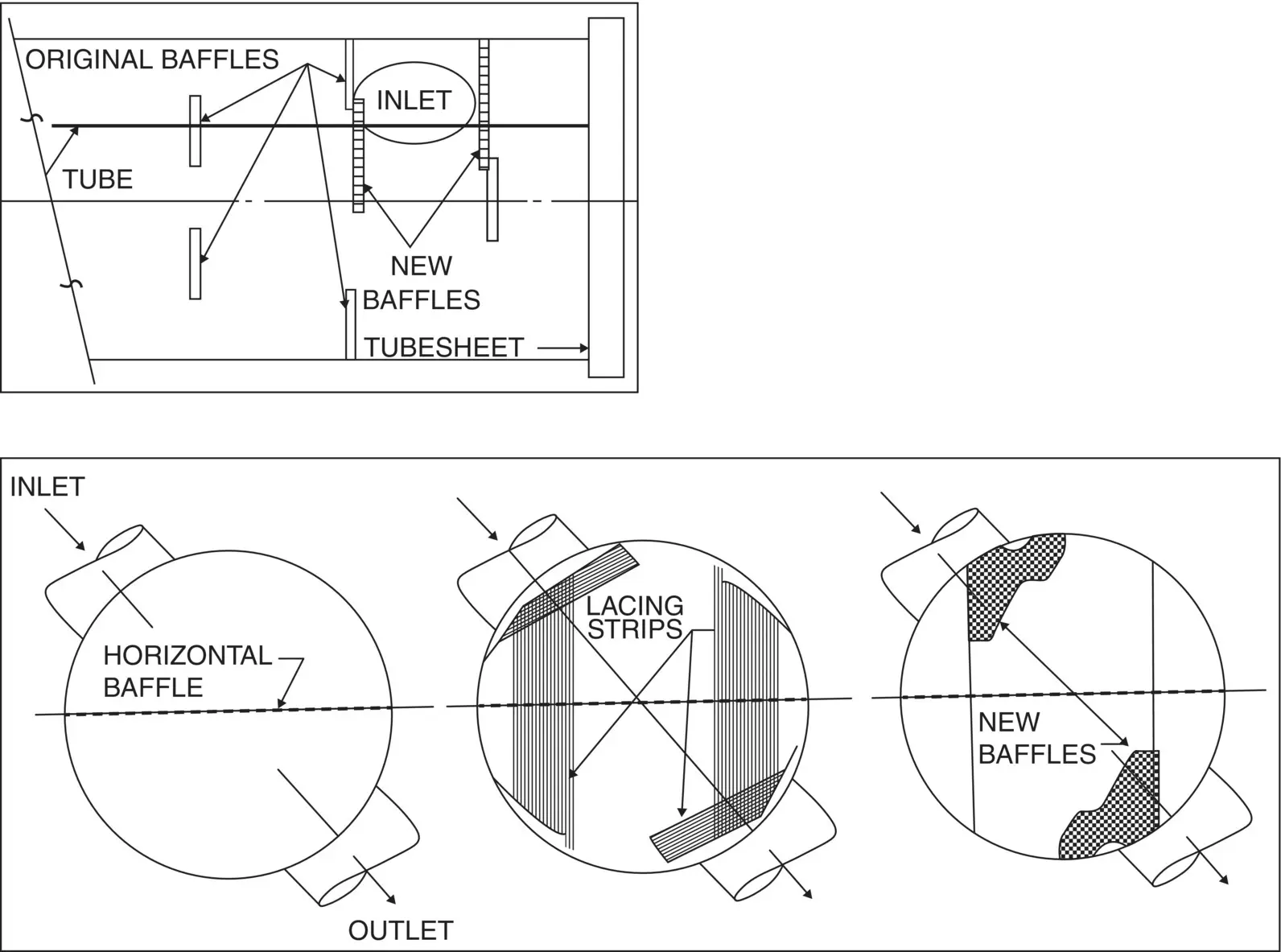
Fig. 1-5 Fretting Wear of Process Heat Exchanger: Repair (Pettigrew and Campagna, 1979 / with permission of Atomic Energy of Canada Limited).
Figure 1-7shows tube‐to‐tube fretting‐wear damage in another power condenser. In this case, the damage was sufficient to wear through the tube wall, causing leakage of sea water into the secondary side of a power plant.
An example of fretting‐wear damage of a tube located just beyond the baffle cut (window tube) vibrating against a baffle edge is shown in Fig. 1-8. This tube came from a gas‐to‐gas heat exchanger, which was inadvertently operated at several times above design flow during a commissioning operation.
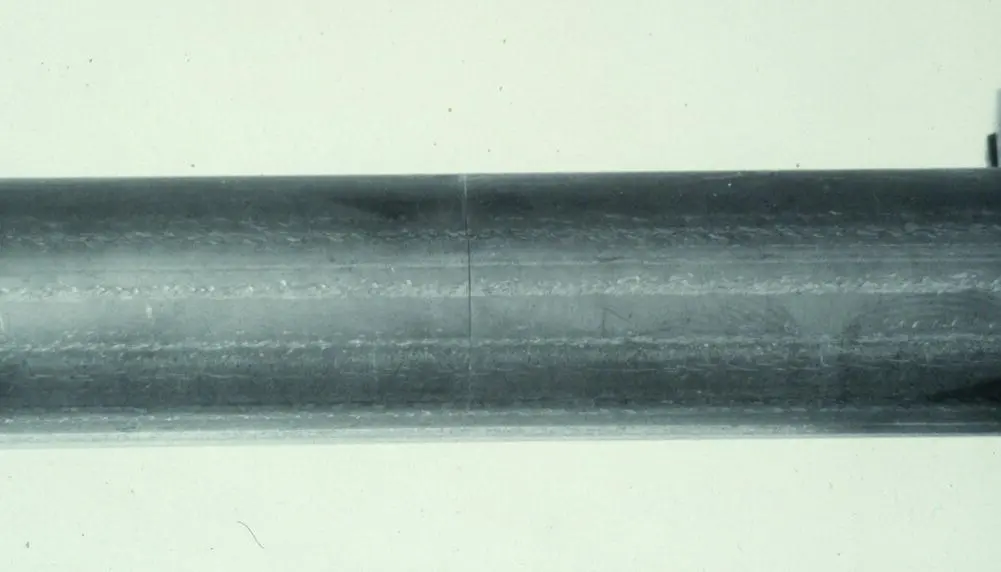
Fig. 1-6 Fatigue Failure of a Titanium Tube in a Nuclear Power Plant Condenser (Pettigrew et al, 1991).
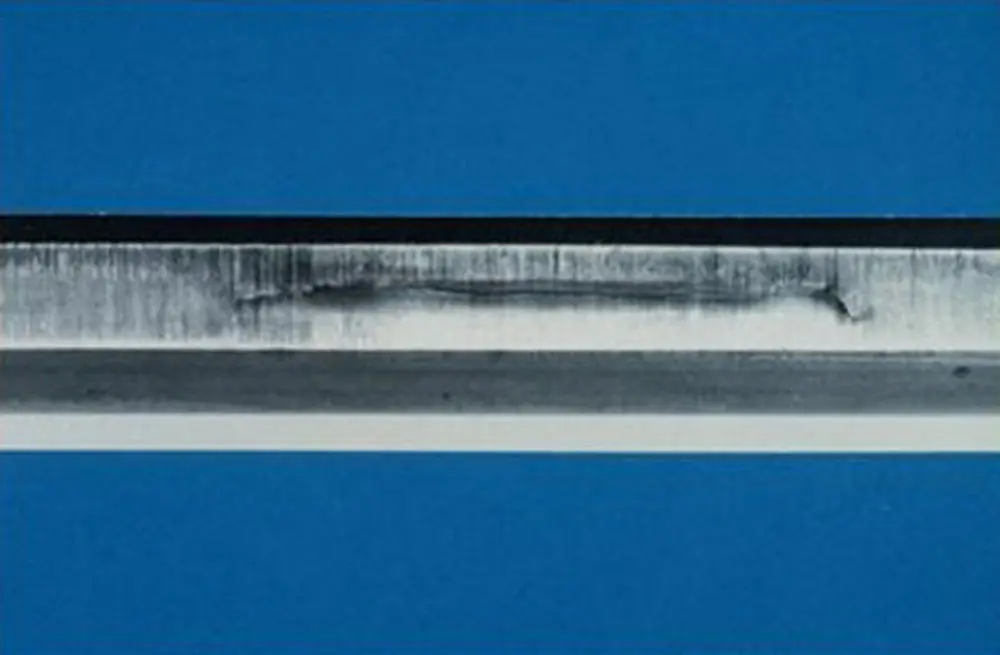
Fig. 1-7 Tube‐to‐Tube Fretting Wear in a Power Plant Condenser.
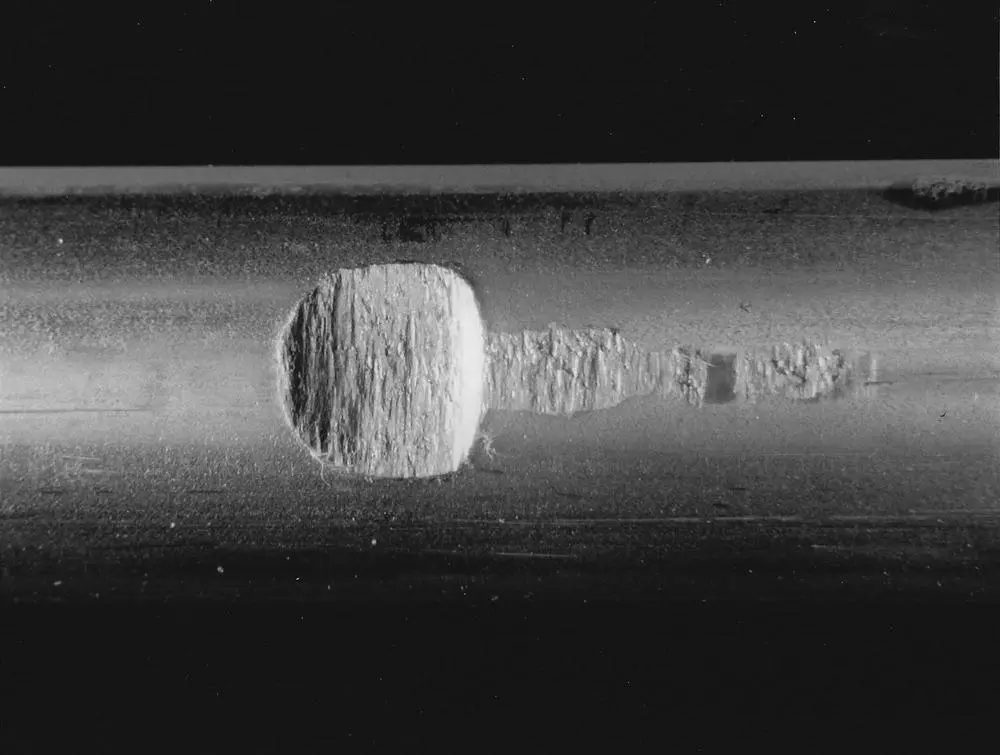

Fig. 1-8 Fretting Wear of a Gas Heat Exchanger Tube at a Baffle Edge Location.
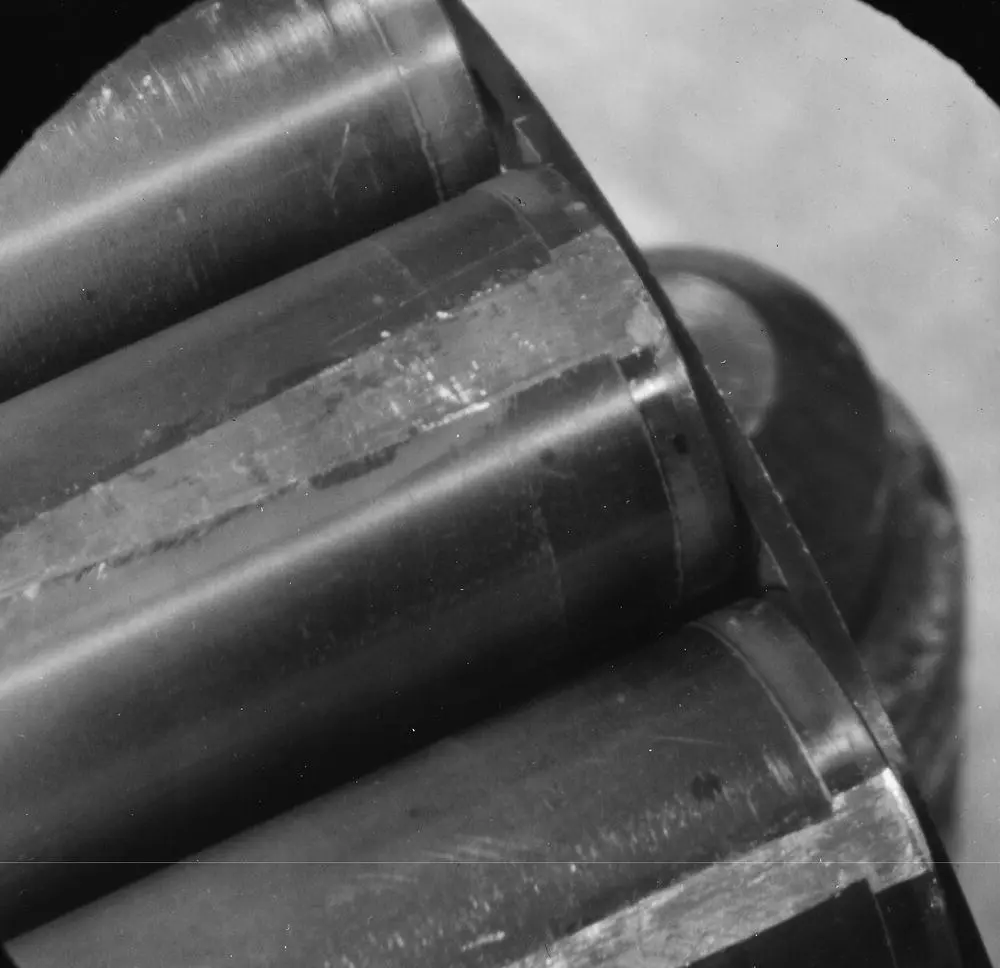

Fig. 1-9 Fretting‐Wear Damage on Nuclear Fuel (Hot Cell Examination) (Pettigrew, 1976).
Figure 1-9is an example of fretting wear of nuclear fuel as seen through an optical magnifier during “hot cell” examination. The damage occurred at the top of fuel string assemblies in 40% of the high flow fuel channels of a prototype CANDU‐BLW® 1 nuclear station. The fuel strings were inserted in upward‐flow vertical fuel channels where they were attached at the bottom and free at the top. The flow in each channel became two‐phase as boiling occurred along the fuel and reached approximately 16% steam quality near the top. The mass flux was typically 4400 kg/m 2 s. The fretting problem was attributed to transverse flow‐induced vibration of the fuel strings. Inadvertently, some of the fuel strings were assembled eccentrically. This caused the strings to be bent and promoted fretting wear. The corrective measures taken were to ensure concentric assembly of the fuel and increase fuel string flexural rigidity to reduce vibration.
One of the most costly vibration related problems took place in the early 1990s at the Darlington Nuclear Power Station, where nuclear fuel bundles were seriously damaged by fatigue and fretting wear ( Fig. 1-10). The cost of investigation, repairs and particularly lost production totalled approximately 1 billion dollars Canadian. The problem was caused by acoustic resonance in the inlet headers due to coincidence of the pump pressure pulsation frequency, (30 Hz x 5 vanes = 150 Hz) and the natural acoustic frequency of the headers. The pressure pulsations were transmitted and amplified in the fuel channels, subjecting the fuel bundles to significant pressure fluctuations causing extensive damage. The problem was solved by simply replacing the five‐vane pump impellers by seven‐vane impellers, thus eliminating the acoustic resonance.
Sometimes vibration problems develop because of changes in operating conditions. For example, pressurized water reactor (PWR) fuel failures occurred in the 1990s due to fretting wear between fuel rods and support grids. The problem was related to longer fuel residence time, which caused increased clearances between the rods and grids due to creep, and deregulation of fuel procurement. The latter allowed fuels from different suppliers at the same time in the reactor core. Differences in design caused slight differences in impedance resulting in increased cross flows and, thus, more flow‐induced vibration excitation. Changes in support grid design solved this problem.
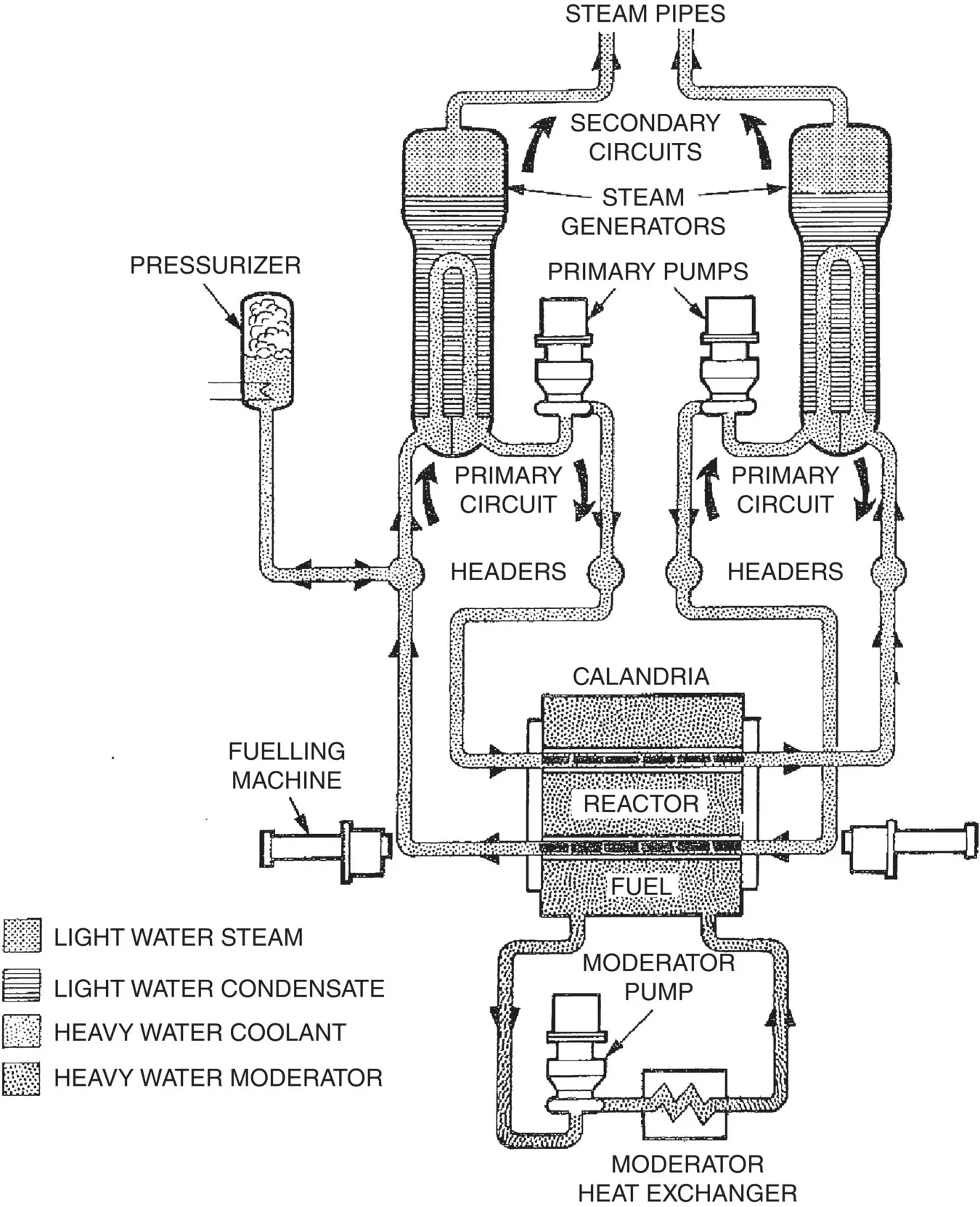
Fig. 1-10 Schematic Drawing of CANDU‐PHW ®Reactor (Pettigrew, 1978 / with permission of Atomic Energy of Canada Limited)
Vibration problems are not limited to material damage such as fatigue and fretting wear. For example, excessive vibration of control absorber guide tubes due to jet impingement could have caused a serious reactor control problem (see Fig. 1-11a). The problem was avoided by shielding the guide tube with a protective shroud, as shown in Fig. 1-11b.
Many other vibration problems have been encountered, such as fatigue failures of PWR core barrel tie rods and in‐core instrumentation nozzles, excessive acoustic noise due to control valve dynamics and mechanical damage resulting from acoustic resonance in gas heat exchangers. Although most vibration problems have very costly consequences, they are usually solved by simple design modifications or changes in operating conditions. After the fact, it is easy to see that most problems could have been avoided by proper understanding of flow‐induced vibration phenomena. Thus, it is important to understand flow‐induced vibration and damage mechanisms to prevent problems at the design stage and assist plant operators in predicting the life of components. It is hoped that this handbook will help in that direction.
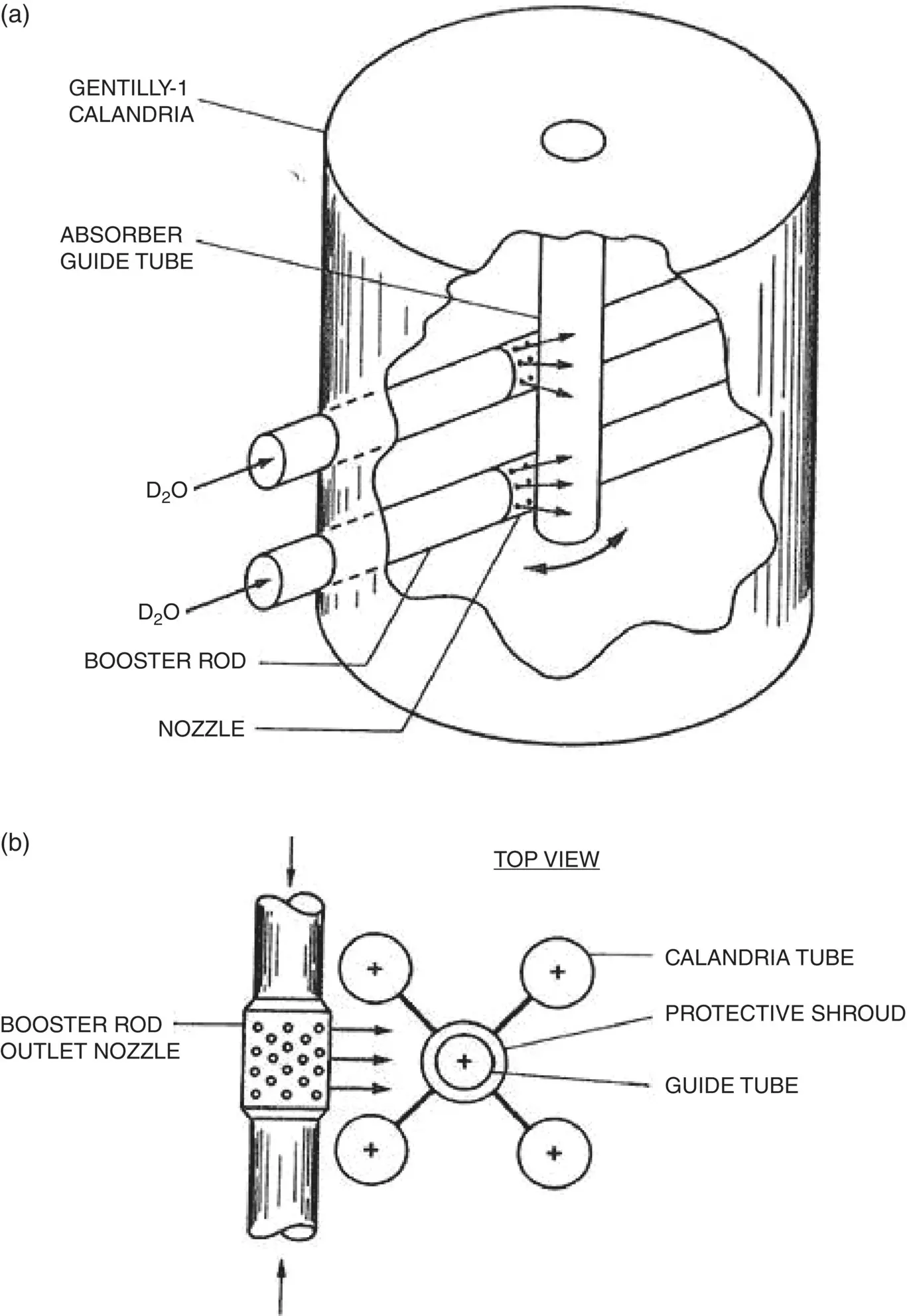
Fig. 1-11 a) Control Absorber Guide Tube Vibration due to Jetting, b) Modification with Protective Shroud (Pettigrew, 1976 / with permission of Atomic Energy of Canada Limited).
1.3 Dynamics of Process System Components
1.3.1 Multi‐Span Heat Exchanger Tubes
From a mechanical dynamics point of view, heat exchanger and steam generator tubes are multi‐span beams clamped at the tubesheet and held at the baffle supports with varying degree of constraint (see Fig. 1-12). The degree of constraint depends on support geometry and, particularly, on tube‐to‐support clearance. Heat exchanger dynamics is inherently a non‐linear phenomenon since it depends largely on the interaction (impacting and sliding) between a particular tube and its supports. This non‐linearity is particularly important since it governs the evaluation of damping at the supports and the prediction of fretting‐wear damage to the tube.
Читать дальше




















