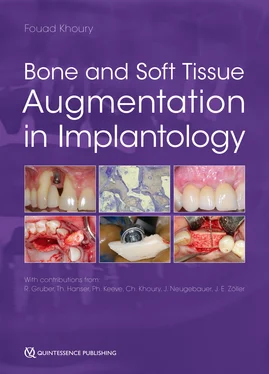
Fig 2-6Intensive hematoma after surgery in patient under regular aspirin medication.
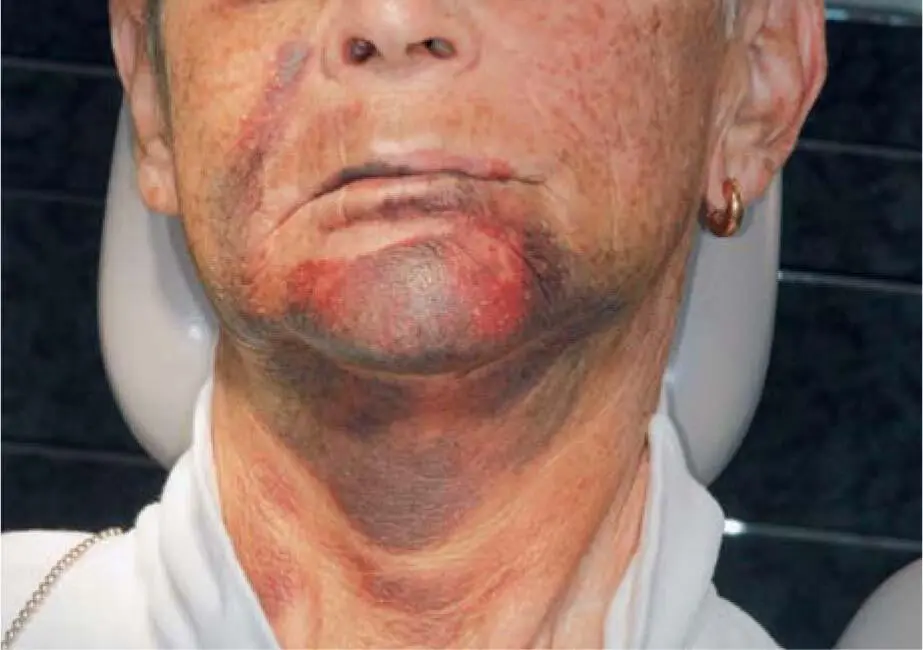
A distinction should be made between antiplatelet agents such as ASS or P2Y12-antagonists or plasma disorders (coumarins, heparin). While platelet aggregation inhibitors are essentially prophylactically formulated to prevent arterial thrombi in the event of heart attack risk, the plasmatic drugs, in addition to the prophylactic indication, are primarily used therapeutically in cardiac arrhythmias, heart valve replacement, and deep venous thrombosis. The latest developments are direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC/NOAC), which are classified as thrombin or factor-Xa inhibitors. The extent of anticoagulant therapy can also be partially recognized during the patient examination. If old hematomas are already recognizable on the legs or hands, this indicates that the anticoagulant therapy is very heavily adjusted or uncontrolled.
The relatively rare congenital disorders of blood clotting are known mostly as hemophilia A and B and von Willebrand-Jürgens syndrome. When this disease is present, important factors in the coagulation cascade (mostly factors 8 and 9) are almost absent or ineffective and can have reduced activity that can reach a severe level until < 1%. Depending on the remaining activity of the factor, surgery can be performed by substituting the appropriate factors. 41,51
Consultation with the treating physician is recommended in all patients with hemorrhagic diathesis, as unauthorized conversion might present the risk of the complication of lethal thromboembolic. Therefore, it is important to decide with the responsible physician whether a change to subcutaneous heparin injections (‘bridging’) or intermittent paralysis of anticoagulant therapy is necessary. In the case of replacement medication, an uncontrolled change of the medication with the reduction of the dose of the previous therapy can already lead to serious complications. To reduce the risk of a lethal thrombosis, the general opinion today in cases of oral surgery is not to stop any kind of antithrombotic treatment and not to perform any bridging with heparin, even with platelet aggregation inhibitors such as clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor or ticlopidine. Heavy postoperative bleeding should be controlled with local surgical possibilities such as an atraumatic approach, avoiding cutting important blood vessels, the use of local hemostatic, and good wound closure with the use of compression plates (see Chapter 8on complications).
2.3.2.8 Diabetes mellitus
While diabetes mellitus type 1, which is caused by absolute insulin deficiency, only shows a prevalence of 0.02% worldwide, the incidence of diabetes mellitus type 2 is rapidly increasing, especially in the social underclasses of industrialized countries. In a few years, a morbidity rate of 10% in these societies is expected.
In these patients, in addition to the risk of a wound-healing disorder after grafting procedures or implant placement, the risk of peri-implantitis also increases. 30,70In the area of the oral cavity, diabetic microangiopathy reduces the regenerative capacity of the oral mucosa, since the nutrition of the tissue is reduced due to damage to the capillaries. This often leads to extensive tissue necrosis with exposure of the augmented area, with partial or complete loss of the augmentation. 85
Table 2-2 Different anticoagulant medications and their doses
Since the circulation is restricted, the soft tissue seal of the osseointegrated implants, which is otherwise well accepted in endosseous implants, can already be disturbed during superficial bacterial colonization, so that the peri-implant bone is subject to infection. The medical treatment of the disease takes place according to the long-term blood sugar value of the glycohemoglobin or HbA1c, the value of which should be below 6%, which corresponds to a value of 120 mg/dl for the acute blood glucose value. From a value of 8%, the risk of healing complications and periodontal disease increases, 80so that the indication should be carefully checked. 54If, in the further course of the disease there are no signs of any disruption of the long-term blood glucose value, the prognosis for implant restorations is good. 29Some studies show no increased failure rates in patients with diabetes in a two-step approach in case of bone augmentation, with appropriate patient guidance and a good maintenance program. 14, 22
2.3.2.9 Other metabolic diseases
The possibilities of implant therapy are limited by other metabolic diseases that directly or indirectly influence bone regeneration. Here, the diseases of the parathyroid gland should be mentioned because, through hyperparathyroidism, a reduced calcium storage in the bone occurs, which leads to osteoporosis. 48
The administration of glucocorticoids has become established in several autoimmune diseases today. Cortisone therapy may lead to increased calcium excretion and thus to osteoporosis or a diabetic metabolic condition. This means per se that there are some risks involved in implant treatment in the case of a disturbance of secondary cortical activity (Addison’s disease), but also in long-term treated bronchial asthma, neurodermatitis, autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. 4,12However, the decision to undergo implant treatment should be made according to the individual risk profile, taking into consideration the duration and intensity of the cortisone therapy.
For implant planning, the extra- and intraoral assessment is carried out to best determine the relevant factors for the necessary prosthetic rehabilitation. Not only should the missing teeth and the patient’s desire to restore them be in the foreground of the treatment, but also the functional and esthetic outcome of the entire functioning of the oral system.
Current development in the field of human genetics is providing an increasing amount of information about genetic developmental disorders. For the development of teeth and the periodontal ligament, ectodermal disorders are mainly relevant. 17In ectodermal dysplasia, disorders occur on multiple structures that develop from the outer cotyledon. In addition to the hair, nails, and skin, the teeth are also affected. Only very few teeth are present (oligodontia or hypodontia) in the first and the second dentition (mostly canines), in combination with some rudimentary teeth ( Fig 2-7ato c). In oligodontia, the existing teeth are often microdontic, so that the prosthetic value is limited. Due to the development-related lack of teeth, the alveolar ridge is also underdeveloped in volume ( Fig 2-7d), but the existing structures compensate for the missing bone supply with a dense bone quality. When planning a restoration, special attention must be paid to the existing available space and the growth pattern, so that pretreatment often requires many years of cooperation with the attending orthodontist ( Fig 2-7eto n). 64
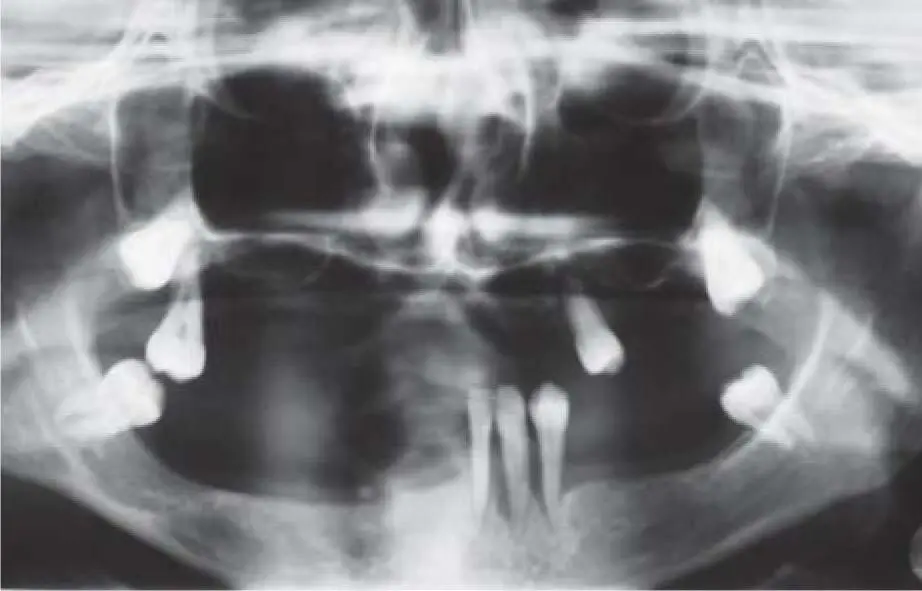
Fig 2-7aPanoramic view of a 28-year-old female patient with a mild form of ectodermal dysplasia.
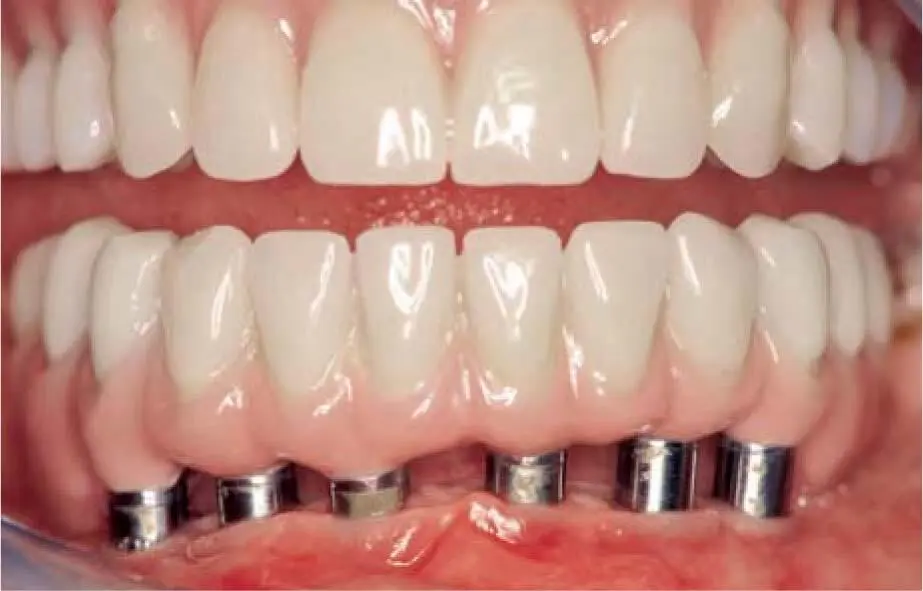
Fig 2-7bClinical situation 12 years after bone grafting and implant restoration in the mandible.
Читать дальше