Fermentable, oligosaccharides, disaccharides and monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs) are short-chain carbohydrates (sugars) that can induce abdominal symptoms that are similar to people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Some people’s small intestines poorly absorb this group of carbohydrates.
The FODMAP food list is extensive and includes milk, dairy products, legumes, cruciferous vegetables such as cabbage and cauliflower, some fruits, and grains, especially wheat and rye. Many of these foods are gas-producing foods. Other symptoms of carbohydrate malabsorption are diarrhea, pain, and bloating. In 2005, a low FODMAP diet was introduced as a therapy for IBS. Since then the mechanisms of action, food content of FODMAPs, and efficacy of the diet have been extensively studied. In many parts of the world, the low FODMAP diet is now considered a frontline therapy for IBS. Before you consider the FODMAP diet, consult with your healthcare provider and a registered dietitian nutritionist (RDN).
Discovering How Carbs Affect Your Blood Sugar Levels
The glycemic index measures the effects of equal quantities of different carbohydrates on blood glucose levels. Since introduced more than 40 years ago, the glycemic index challenged traditional thinking about carbohydrate effects on blood sugar; the scientific community was slow to embrace the index. Traditional theory stated that simple carbohydrates, such as orange juice, raised blood glucose levels quickly, whereas complex carbs, such as crackers, raised blood glucose levels more slowly. Researchers now realize the distinction between sugar and starch is largely useless from a biological viewpoint. Research on glycemic index values showed some simple carbohydrates raise blood glucose slowly and some complex carbohydrates raise blood glucose quickly.
 The glycemic load is a measurement that is calculated from the glycemic index and is used to evaluate the glucose response in a normal serving of a particular food. The formula is the glycemic index multiplied by the number of grams of carbohydrate in a serving, divided by 100.
The glycemic load is a measurement that is calculated from the glycemic index and is used to evaluate the glucose response in a normal serving of a particular food. The formula is the glycemic index multiplied by the number of grams of carbohydrate in a serving, divided by 100.
Don’t worry about the mathematical formulas though: Appendix Alists more information on the glycemic index and glycemic load of foods. You can use glycemic load to evaluate the kinds of foods in your diet. If most of your foods are on the high glycemic load level and those foods are low in nutritive factors, then I recommend exchanging some of those high glycemic choices for low glycemic choices. If most of your foods fall into the low glycemic category, then chances are you’re eating a very healthy diet.
Carbohydrate foods that are low in glycemic load seem to increase satiety (feeling of fullness after eating) and maintain consistent blood glucose and insulin levels. Non-starchy vegetables, fruits, legumes, and high-fiber whole-grain products tend to have a low glycemic load. These foods have a proven record of health benefits such as lower risk of heart disease and cancer and less gastrointestinal diseases and are a component of any reasonable diet. Such slowly absorbed carbohydrates can contribute greatly to overall health, satiety, and weight loss.
Understanding Refined and Processed Carbs
A refined food is a food that doesn’t contain all its original nutrients. For example, a grain of wheat to make white flour has 16 essential nutrients refined out of it. Five of those (iron, thiamin, niacin, riboflavin, and folic acid) are added back in by the government enrichment program to prevent nutritional deficiencies. All refined foods are processed foods; you can’t pick a refined food out of your garden and eat it. On the other hand, a healthy whole food is considered processed if it has simply been sliced, chopped, rolled, or ground. That is, it has gone through a process, but its original nutrition content is intact.
Most refined and processed carbs are high in glycemic load and may result in hunger soon after their rapid digestion. Refined and processed carbs such as those found in cookies, crackers, rice cakes, bagels, cakes, doughnuts, croissants, chips, pastries, pretzels, most packaged breakfast cereals, white bread, and white rice have a high glycemic load; their easy digestion causes a rapid elevation in blood glucose and insulin levels. After a couple of hours, the blood glucose levels quickly decline, resulting in cravings for more food in some people. This phenomenon may have led to the coining of the phrase carbohydrate addiction.
You don’t have to totally avoid high-glycemic-load foods. You can eat some high-glycemic foods in the presence of low-glycemic foods and the effect on your blood sugar wouldn’t be as great as it would be with high-glycemic foods alone. What you need to be aware of is the percentage of high-glycemic load foods to low-glycemic-load foods. Try to include more low-glycemic-load foods in your diet than high. See Appendix Afor more information on glycemic load and glycemic index.
Replacing the Food Pyramid with a Healthy Eating Plate
Even though the Food Guide Pyramid was around for many years and increased nutrition knowledge in the United States, it did little to change the eating habits of consumers. The Food Guide Pyramid emphasized lowering fat in the diet and replacing it with bread, cereals, grains, fruits, and vegetables. Fat is a calorie-dense fuel and provides 9 calories per gram, whereas carbohydrate and protein each supply 4 calories per gram.
Current wisdom would say if you cut out something that gives 9 calories and replace it with something that gives 4 calories, you’d reduce your total calorie intake. Sounds reasonable, right? Take away high-fat foods and replace them with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, but that’s not what happened.
Unfortunately, along with the reduced-fat message came fat-free cookies, cakes, chips, snacks, and desserts that displaced the intended healthier choices of fruits, veggies, and whole grains. After all, fat tastes good, so to trick consumers’ taste buds into thinking that fat-free foods tasted good, manufacturers loaded the food with sugar. So, they didn’t just replace a fat gram with a carbohydrate gram in an even swap; they replaced the fat with double, triple, and quadruple the carbohydrate! Many consumers saw a box of fat-free cookies as a free food and ate the whole box rather than just a serving.
Scientists realized a change needed to happen to provide guidance to consumers to help them eat healthier. That’s how the Healthy Eating Plate came about. Designed by experts at Harvard School of Public Health and Harvard Medical School, the Healthy Eating Plate (see Figure 3-1) directs consumers to the healthiest choices in major food groups.
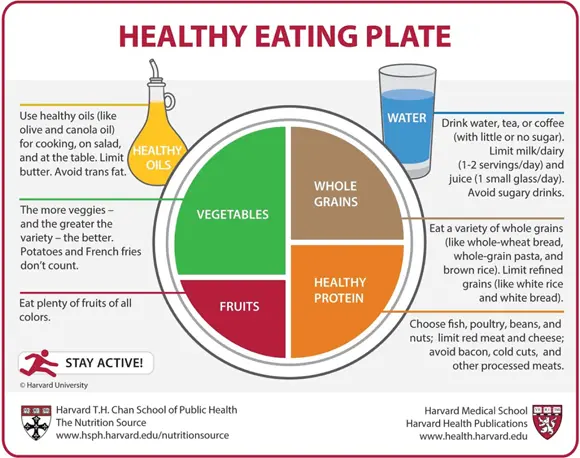
Copyright © 2011 Harvard University.
FIGURE 3-1:The Healthy Eating Plate.
 For more information about The Healthy Eating Plate, see The Nutrition Source, Department of Nutrition, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health,
For more information about The Healthy Eating Plate, see The Nutrition Source, Department of Nutrition, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, www.thenutritionsource.org and health.harvard.edu .
A number of research studies suggest that diets designed to lower the insulin response to ingested carbohydrate (such as a low-glycemic-index diet) may improve utilization of stored energy (body fat), decrease hunger, and promote weight loss. The Healthy Eating Plate demonstrates that such a diet would have as its base abundant quantities of low- to moderate-glycemic vegetables and fruits, moderate amounts of protein, legumes, reduced-fat dairy, and healthy fats (like olive and canola oil), and an emphasis of whole grains over refined-grain products, potatoes, french fries, and concentrated sugars. The Whole Foods Weight Loss Eating Plan closely approximates the recommendations of Harvard’s Healthy Eating Plate (refer to Chapter 2for more about this plan).
Читать дальше

 The glycemic load is a measurement that is calculated from the glycemic index and is used to evaluate the glucose response in a normal serving of a particular food. The formula is the glycemic index multiplied by the number of grams of carbohydrate in a serving, divided by 100.
The glycemic load is a measurement that is calculated from the glycemic index and is used to evaluate the glucose response in a normal serving of a particular food. The formula is the glycemic index multiplied by the number of grams of carbohydrate in a serving, divided by 100.
 For more information about The Healthy Eating Plate, see The Nutrition Source, Department of Nutrition, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health,
For more information about The Healthy Eating Plate, see The Nutrition Source, Department of Nutrition, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, 










