Georgi Popov - Risk Assessment
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Georgi Popov - Risk Assessment» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Risk Assessment
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Risk Assessment: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Risk Assessment»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Explore the fundamentals of risk assessment with references to the latest standards, methodologies, and approaches Risk Assessment: A Practical Guide to Assessing Operational Risks
Risk Assessment: A Practical Guide to Assessing Operational Risks
Risk Assessment — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Risk Assessment», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
This standard specifies general safety requirements for the design, construction, operation and maintenance (including installation, dismantling and transport) of machinery and machinery systems. This standard also applies to devices that are integral to these machines. (p. 8)
This author believes that every safety professional who is involved in machinery safety should have a copy of this standard. It is supported by the standard known as ANSI B11.19‐2019, the title of which is “Performance Requirements for Risk Reduction Measures: Safeguarding and other Means of Reducing Risk.” This is a 231‐page document that is devoted to means of risk reduction. This is the stated Purpose of B11.0‐2020:
This standard describes procedures for identifying hazards, assessing risks, and reducing risks to an acceptable level over the life cycle of machinery. (p. 9)
The objective of the B11 series of standards:
Is to eliminate injuries to personnel from machinery or machinery systems by establishing requirements for the design, construction, reconstruction, modification, installation, set‐up, operation and maintenance of machinery or machine systems. This standard should be used by suppliers and users, as well as by the appropriate authority having jurisdiction. (p. 9)
The standard includes an explicit requirement that machinery suppliers, reconstructors, modifiers, and users achieve acceptable risk levels.
ANSI B11.0 is the most comprehensive standard outlining the risk assessment process currently applicable to machinery for all of the operational categories just previously mentioned. Recognition is given to the Prevention through Design concept in the Forward.
Prevention Through Design or PtD is a recent term in the industry; the objectives of risk assessment, risk reduction and elimination of hazards as early as possible are integral and not new to this standard. The phrase “Prevention Through Design” is used within the standard, as are other equivalent terms such as “elimination by design,” “design out,” and “substitution” to thoroughly address risk assessment and applying it to the lifecycle and operations of the machine. (p. 8)
Because many American makers of machinery sell their goods to other countries, there was a need for harmonization with other applicable standards. This sentence follows the caption Harmonization.
This standard has been harmonized with international (ISO) and European (EN) standards by the introduction of hazard identification and risk assessment as the principal method for analyzing hazards to personnel to achieve a level of acceptable risk.
That statement presents an interesting and weighty concept. If all safety professionals accept that hazard identification and analysis and risk assessment are the first steps in preventing injuries to personnel, a major concept change in the practice of safety will have been achieved.
This is how acceptable risk is defined in the standard – Definitions (p. 18):
Acceptable risk: A risk level achieved after risk reduction measures have been applied. It is a risk level that is accepted for a given task (hazardous situation) or hazard. For the purpose of this standard, the terms “acceptable risk” and “tolerable risk” are considered to be synonymous.
Informative Note 1: The expression “acceptable risk” usually, but not always, refers to the level at which further technologically, functionally and financially feasible risk reduction measures or additional expenditure(s) of resources will not result in significant reduction in risk. The decision to accept (tolerate) a risk is influenced by many factors including the culture, technological and economic feasibility of installing additional risk reduction measures, the degree of protection achieved through the use of additional risk reduction measures, and the regulatory requirements or best industry practice.
Informative Note 2: The user and supplier may have different level(s) of acceptable risk.
Informative Note 3: A similar phraseology used in some ISO standards is as follows: “the risk has been adequately reduced.”
A particularly outlined risk assessment process is included on B11.0‐2020. It is duplicated here to emphasize several purposes: it is illustrative although it differs from other outlines, it indicates that people involved in the process should be qualified, the scope of the risk assessment exercise is to be defined, hazards are to be identified and analyzed, initial risks are to be assesses, risks are to be reduced if necessary, and acceptable risk levels are to be achieved.
6 The Risk Assessment Process (p. 4)6.1 General6.1.1 Quality personnel6.1.2 Goal6.1.2 Fundamental steps in the risk assessment process6.2 Prepare for and set scope (limits) of the assessment6.3 Identify tasks and hazards6.3.1 Identify affected persons6.3.2 Identify tasks6.3.3 Identify hazards and hazardous situations6.3.4 Similar machines6.4 Assess initial risk6.4.1 Select a risk scoring system6.4.2 Assess risk6.4.3 Check for new hazards6.6 Assess residual risk6.7 Achieve acceptable risk6.8 Validate and verify risk reduction measures6.9 Document the process6.9.1 Content6.9.2 Document retention
“General Risk Assessment Requirements” are outlined in the following section of the standard. (p. 4)
ANSI B11.0‐2020 is available for purchase at www.b11standards.orgor www.ansi.org
1.6 Risk Scoring Systems
Note that 6.4.1 in The Risk Assessment Process is “Select a risk scoring system.” Why do so? It is necessary in the management of risks to establish priorities for action. That can be done through a risk scoring system – risk levels being Low, Moderate, Serious or High, or a variation thereof. And it is important that the people involved in the risk assessment process understand what those terms mean and what action levels are implied by the terms used.
The risk assessment matrix shown in Figure 1.3is a composite of matrices that include numerical values for likelihood and severity levels that are transposed into qualitative risk gradings. It was originally developed for people who prefer to deal with numbers rather than qualitative indicators. To provide a one‐page tool that could be used by safety professionals who wanted to get shop floor personnel involved in risk assessments, extensions were made to include severity and likelihood descriptions and action levels.
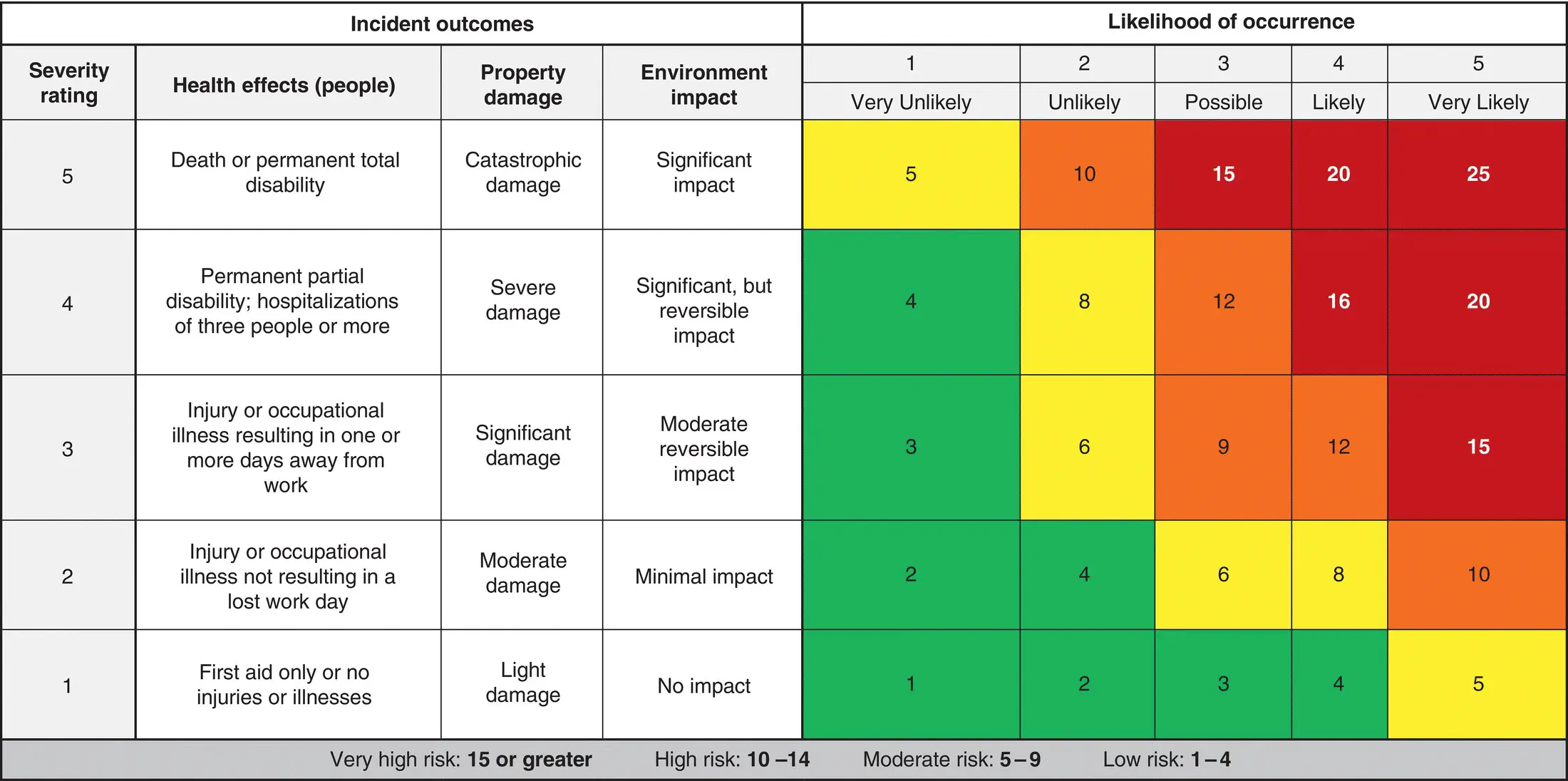
Figure 1.3 Risk matrix example.
In two instances, shop floor personnel said to safety professionals that relating numbers to each other first – such as 6–12 – was a big help in understanding whether the risk category was moderate or high‐risk. If using a risk assessment matrix in which numbers are used to begin with to establish risk levels makes the process more understandable and acceptable for operating personnel, that should be encouraged.
It is important to understand that the numbers in Figure 1.3were intuitively derived: they are semi‐quantitative. Thus, the numbers have value only in relation to each other. And that is the case for all risk scoring systems that are not based on hard probability and severity numbers, which are rarely available.
Note that this Risk Assessment Matrix pertains to personal injury and illness, system loss or down time (from any source), and environmental release. Others may not be as inclusive.
1.7 European Union – Risk Assessment
In August 2008, The European Union launched a two‐year health and safety campaign focusing on risk assessment. Their bulletin said:
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Risk Assessment»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Risk Assessment» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Risk Assessment» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












