Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Encapsulates different case studies where technology can be used as assistive technology for the physically challenged, visually and hearing impaired.
Audience Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering
Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
The importance of socially assistive robots was presented, which entertained the patients socially whenever they required [63]. For motivating, monitoring, and reminding stroke patients, an assistive robotic system was described, which also tracked the arm activity of the patient [64]. The cognitive strategy was extended with rehabilitation robotics by testing the Active Learning Program for Stroke (ALPS) [65]. Socially assistive robotics (SAR) was tested, and their kinematic and temporal features, which were related to fatigue, were determined [66].
1.2.8 Limb Injury
Importance of development of rehabilitation robotics for the patients who suffered from upper limbs impairment was highlighted [67]. An application of wireless sensing technology in rehabilitation robotics was presented for patients who had upper limb injury due to stroke [68]. For the rehabilitation of upper limb injury patients, a task-oriented robotic system ADAPT was designed, and its performance was evaluated [69].
1.2.9 Motion Detection
Patients who suffer from any kind of impairment are not able to produce proper movement. The robotic systems may help in determining their intention of motion and aid it by helping them to move. Production of torque in the desired direction and compensation of kinetic and breakaway friction was presented [70]. Investigation of support vector machine (SVM) identified the sEMG signals from the muscles and produced motion in that direction [71]. A method enhancing the degree of freedom of the patient and supporting the motion was developed. It was tested on ARM in III robotic system [72]. Based on the EMG signals produced by muscles, the torque and intention of motion were determined [73]. The visualization for the intention estimation algorithm is denoted by Figure 1.2for inquisitive readers.
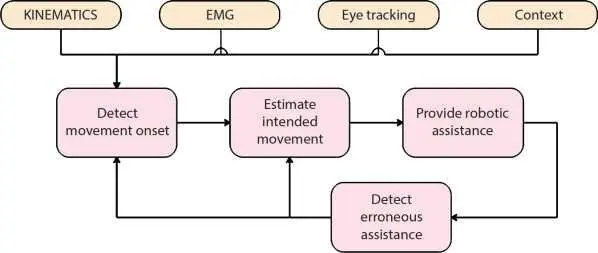
Figure 1.2 Block diagram representation of the intention estimation algorithm.
The intended motion of hand for hemiparetic hand patients was done using sEMG signals. It was introduced in the form of a soft glove [74].
1.3 Discussions and Future Scope of Work
The research focusing on workstation adaptations of rehabilitation robotics is mentioned in [75]. Rehabilitation game was integrated with robotics based on reinforcement learning method and depending on the skills of the player. The difficulty level of the game was increased gradually as per the skills of player [76]. A system was designed for adjusting the difficulty of game based on the score produced by the player [77]. A diagrammatic representation of the difficulty adjustment in games as per the flow model is provided with the help of Figure 1.3.
The works carried out then in Europe on rehabilitation robotics were summarized, and historical aspects and EU’s different funded and active projects were also summarized [78]. The projects that were carried out on rehabilitation robotics in North America were described, and they were judged as success or failure [79]. A summary of the project carried out jointly by VA and Stanford University was examined, and all the pros and cons of the project were listed [80]. Table 1.4showcases a list of certain areas that have the potential future scope as well.
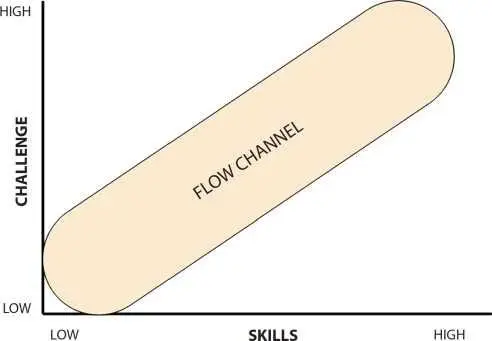
Figure 1.3 The difficulty adjustment in games according to the flow model.
Table 1.4 List of some works done in areas with potential future.
| Ref. number | Area of rehabilitation robotics explored | Remarks |
| [14] | Gentle/G system for patients with brain injury | The design, control, and application of an experimental setup were presented for the rehabilitation. The robot had six active and three passive degrees of freedom. |
| [24] | Virtual Gait Rehabilitation Robotics (ViGRR) | A novel concept for rehabilitation robotics; its insights were based on ViGRR and did not require any therapist. |
| [33] | VR in rehabilitation robotics | Approaches made to cure neurologically disordered patients, and the importance of exercises by clinical robots was presented. |
| [41] | Mechatronic rehabilitation robotics | A systems approach, mobility sensors, cost/benefit ratio, and softness were discussed. The importance of softness was also discussed and was considered as an important factor. |
| [65] | Robotic-assisted therapy | Active Learning Program for Stroke (ALPS) was designed, and testing was done on patients for a while and was found successful in extending cognitive strategies. |
| [66] | Socially assistive robotics (SAR) | SAR was tested, and kinematic and temporal features related to fatigue were determined. The test was done for a sit-to-stand test and concluded that three kinematic features had a relation with fatigue. |
| [71] | Support vector machine (SVM) | The feasibility of SVM for the identification of the locomotion from sEMG signals produced by the muscles for rehabilitation robotics was calculated. |
Application of virtual reality, SVMs, etc. still requires innovative thinking and ingenuity. Robots with multiple degrees of freedom and robotic-assisted therapy have constantly been a subject of research. The readers interested in pursuing this field could consider the above topics for their study.
1.4 Conclusion
This chapter presents a review of the progress of rehabilitation robotics. Robots have found application in neurology, cognitive science, stroke, biomechanical, machine interface, assistive, motion detection, limb injury, etc. They have been used to aid surgeries and therapies, to take care of neurological disorders of patients, assisting patients for movement, etc. Adaptive robotics has been developed catering to patient needs and abilities. Moreover, the application of robots in orthotics, prosthetics, and neuro-rehabilitation has been intriguing. This chapter also presents the scenario of rehabilitation robotics in Europe and the northern part of America. The scope of research lies in the exploration of virtual reality, neural networks, and SVM, and application to robotics. The use of sensing technology in the rehabilitation robots with various degrees of freedom is also worthy of attention. The readers are encouraged to pursue this line of research.
References
1. Speich, J.E. and Rosen, J., Medical robotics, in: Encyclopedia of biomaterials and biomedical engineering , vol. 983 , p. 993, 2004.
2. Loureiro, R.C., Harwin, W.S., Nagai, K., Johnson, M., Advances in upper limb stroke rehabilitation: a technology push. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput ., 49, 10, 1103, 2011.
3. Yue, Z., Zhang, X., Wang, J., Hand rehabilitation robotics on post-stroke motor recovery. Behav. Neurol., 2017 , 2017. 3908135.://doi.org/ 10.1155/2017/3908135
4. Tefertiller, C., Pharo, B., Evans, N., Winchester, P., Efficacy of rehabilitation robotics for walking training in neurological disorders: A review. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev., 48 , 4, 387–416, 2011.
5. Nef, T., Guidali, M., Klamroth-Marganska, V., Riener, R., ARM in-exoskeleton robot for stroke rehabilitation, in: World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering , Munich, Germany, September 7-12, 2009, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 127–130, 2009.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Intelligent Systems for Rehabilitation Engineering» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












