1 ...7 8 9 11 12 13 ...21 Question: What is the appropriate treatment for this patient?
Answer:Primary surgical therapy is generally considered the standard of care for lip cancers as with oral cavity cancers. While the resection of lip cancer is relatively straightforward, the complex functional and aesthetic roles of the lip present major reconstructive challenges.
Due to the challenges of achieving acceptable functional and aesthetic outcomes with surgery for extensive lip cancer, radiotherapy is considered an acceptable alternative. In particular, extensive lower lip cancers that extend over a significant proportion of the surface of the lip are particularly amenable to this approach.
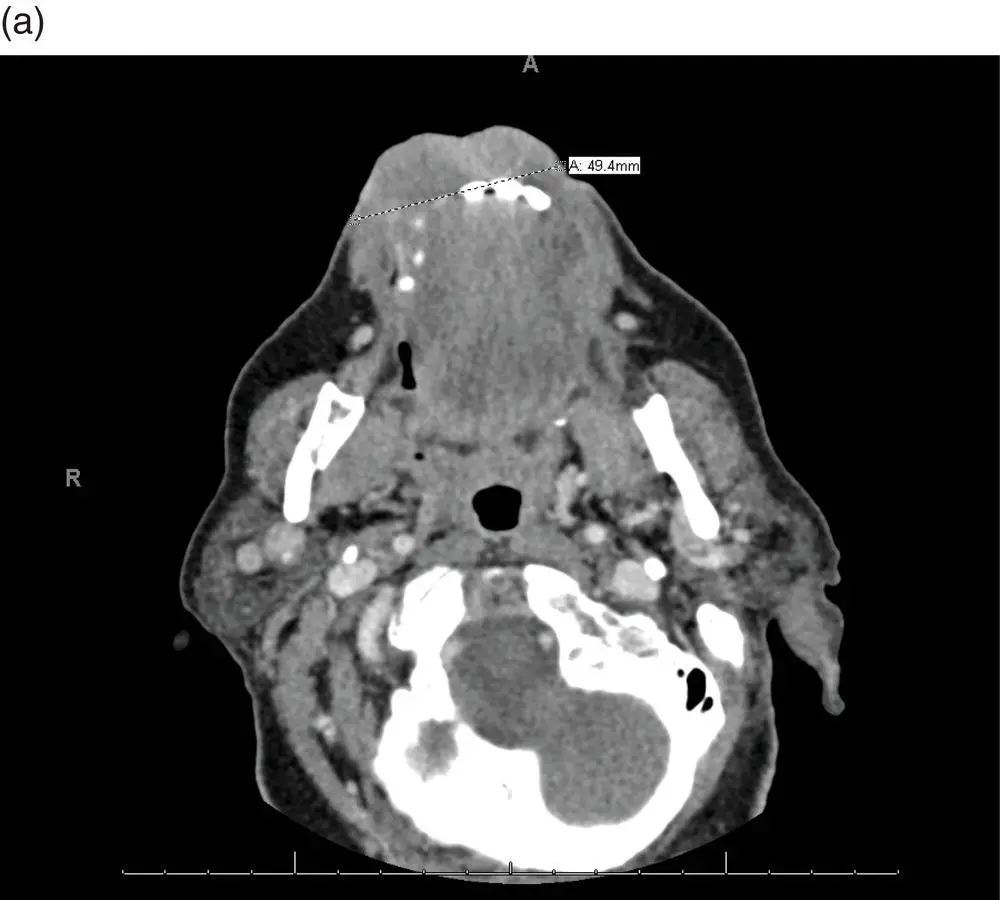
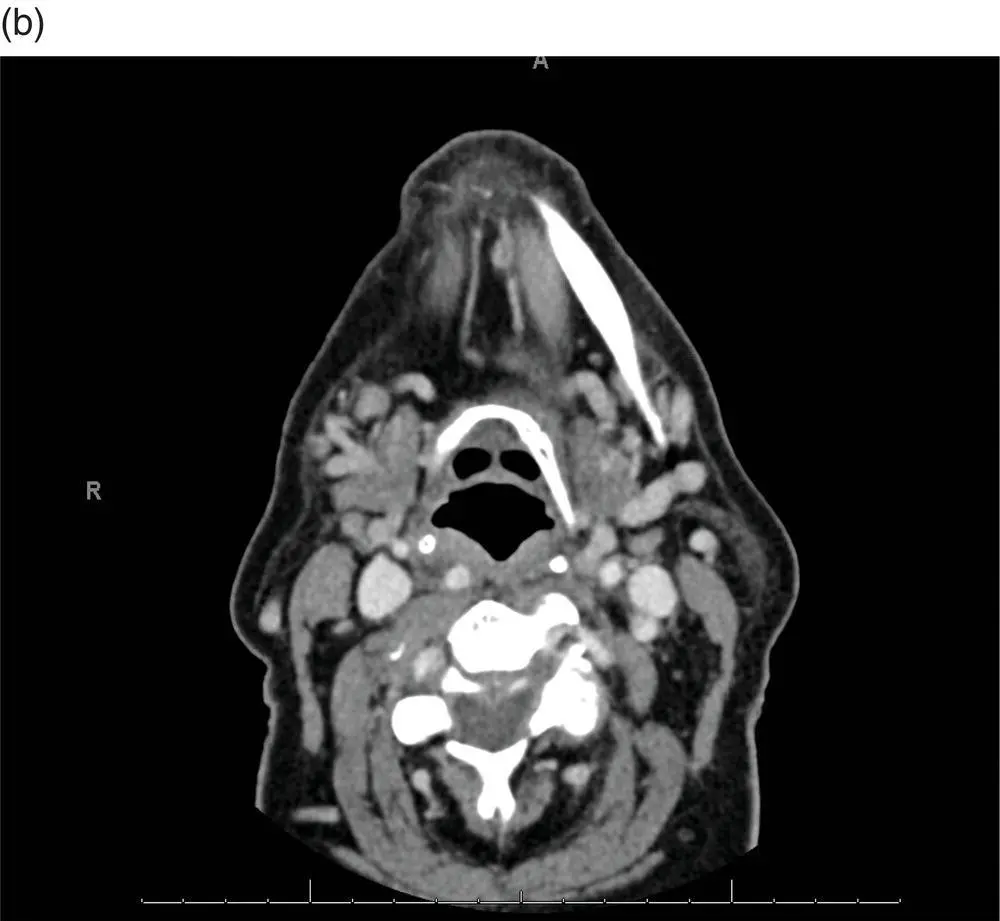
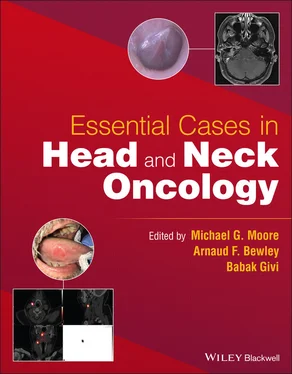
FIGURE 5.2 These representative axial cuts for the patient's neck CT with IV contrast demonstrate a large ill‐defined soft tissue tumor of the lower lip (a) with rounded level Ia and (b) Ib lymph nodes without obvious necrosis.
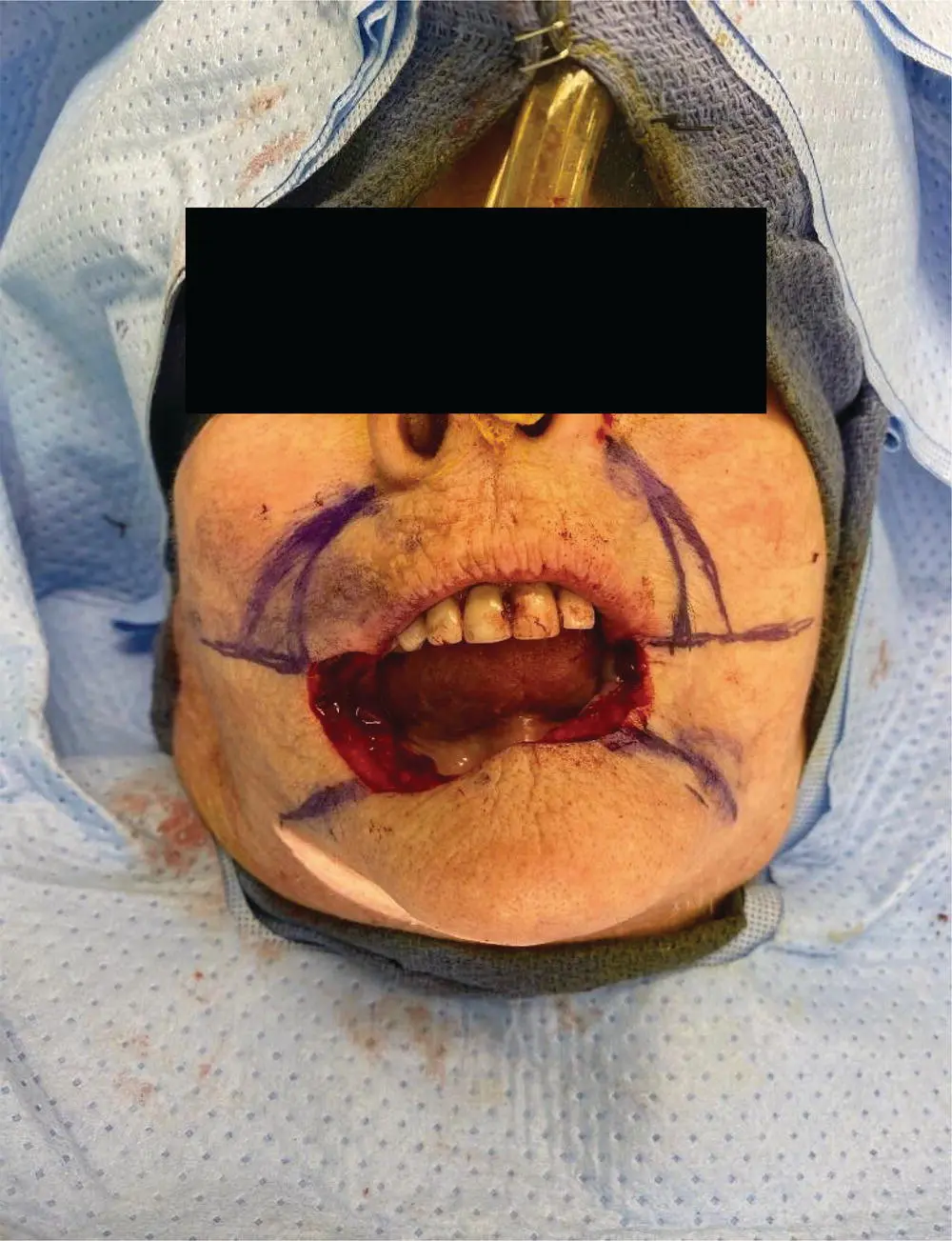
FIGURE 5.3 This intraoperative photo shows the patient's total lower lip defect.
In this patient's case, given the thickness of the tumor and soft tissue extension, she elected for definitive surgical resection, yielding the defect pictured below (see Figure 5.3).
Final pathology report showed SCC, 4.1 cm in greatest dimension, with a depth of invasion of 13 mm. Perineural invasion is present, but no lymphovascular invasion. The closest margin is 3 mm.
Question: How would you reconstruct the primary defect depicted in Figure 5.3?
Answer:While a Karapandzic flap is an excellent option for large lower lip defects, it relies entirely on the existing lip. As a result, some amount of preserved lower lip is needed to prevent severe microstomia. With a total lower lip defect, a Karapandzic flap would result in an unacceptable degree of microstomia.
Abbe/Estlander flaps are ideal for small lateral defects of the lip where sufficient lip can be recruited from the uninvolved lip to achieve a functional reconstruction. This defect is clearly too extensive to be amenable to these types of flaps.
Bernard/Webster flap could be used as an option. Total lower lip defects require the recruitment of additional tissue to recreate the lip, thereby minimizing the degree of microstomia. The Bernard and Webster flaps recruit tissue from the cheek and buccal mucosa to reconstruct the lower lip and are therefore ideal for total or subtotal lip defects. The reconstructed tissue is not contractile but maintains sensation with good skin match.
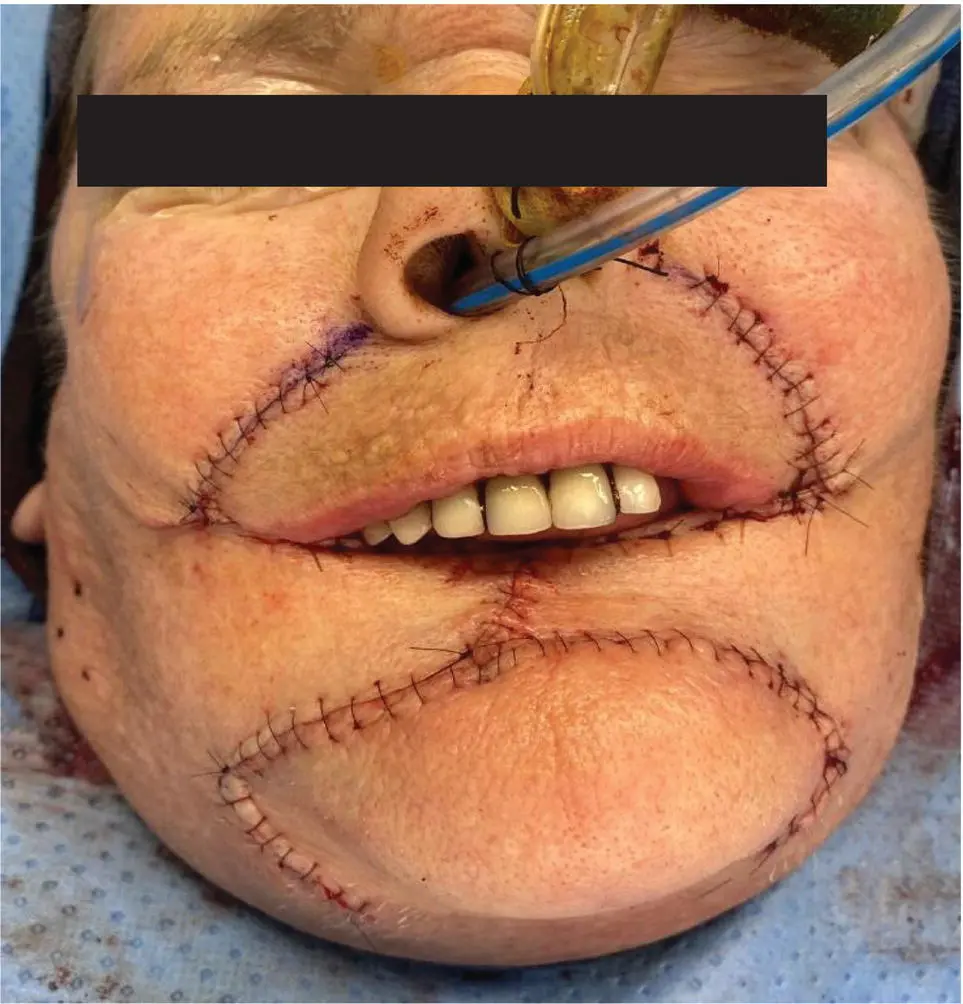
FIGURE 5.4 Bernard-Webster bilateral advancement flap reconstruction.
The radial forearm free flap is another method of creating a new lip and is best for mitigating microstomia. This is often performed with a palmaris longus tendon sling to aid with oral competence. Disadvantages are lack of contractility, lack of sensation, and poor skin match.
This patient was reconstructed with a Bernard‐Webster bilateral advancement flap as pictured below (see Figure 5.4).
Question: How would you manage the patient's regional lymph node basin?
Answer:Bilateral supra‐omohyoid neck dissection is an acceptable way to address the high risk for occult regional disease in locally advanced lower lip cancer. This is a particularly appealing approach in patients who may be able to avoid adjuvant RT. Given the tumor involvement of the bilateral lower lip, any elective nodal dissection should address both sides of the neck.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy ( SLNB) has been shown to be feasible and effective in patients who may be at high risk of metastases based on tumor size and depth. However, given the extensive nature of this primary tumor, the specificity of a sentinel node identification may be lower as four‐quadrant injection of the radiotracer would likely trace to a variety of nodes. This would, therefore, not be an ideal case for SLNB. In general, sentinel node biopsy is recommended in T1, T2 tumors.
Given the locally advanced nature of this patient's tumor (T3) and the presence of PNI, she would benefit from adjuvant radiation therapy to the tumor bed. The regional lymphatics could likewise be irradiated to an adjuvant dose without the need for elective neck dissection.
Cancers of the lip mucosa continue to be staged as cancers of the oral cavity, while cancers of the external vermillion lip are now staged as cutaneous carcinomas.
Primary radiotherapy can offer equivalent oncologic outcomes to surgical resection for early stage tumors.
Extensive, superficial lower lip cancers are good candidates for primary radiotherapy as they avoid the potential high morbidity of surgical resection.
Total lower lip defects require the recruitment of additional tissue to recreate the lip, thereby minimizing the degree of microstomia.
The Bernard and Webster flaps recruit tissue from the cheek and buccal mucosa to reconstruct the lower lip and are therefore ideal for total or subtotal lip defects.
SLNB has been shown to be feasible and effective in patients with lip tumors who may be at high risk of metastases based on tumor size and depth.
Due to extensive lymphatic drainage from the upper lip and commissure, tumors of these subsites have a higher incidence of lymph node metastases at the time of diagnosis.
Ian Ganly
A 45‐year‐old man presents with a soft tissue swelling of the left hard palate and soft palate. He denies pain. The patient had previously been seen by his dentist, who initiated a course of antibiotics with no effect. The patient was referred for further investigation. Examination showed a diffuse swelling of the hard palate as shown in Figure 6.1.
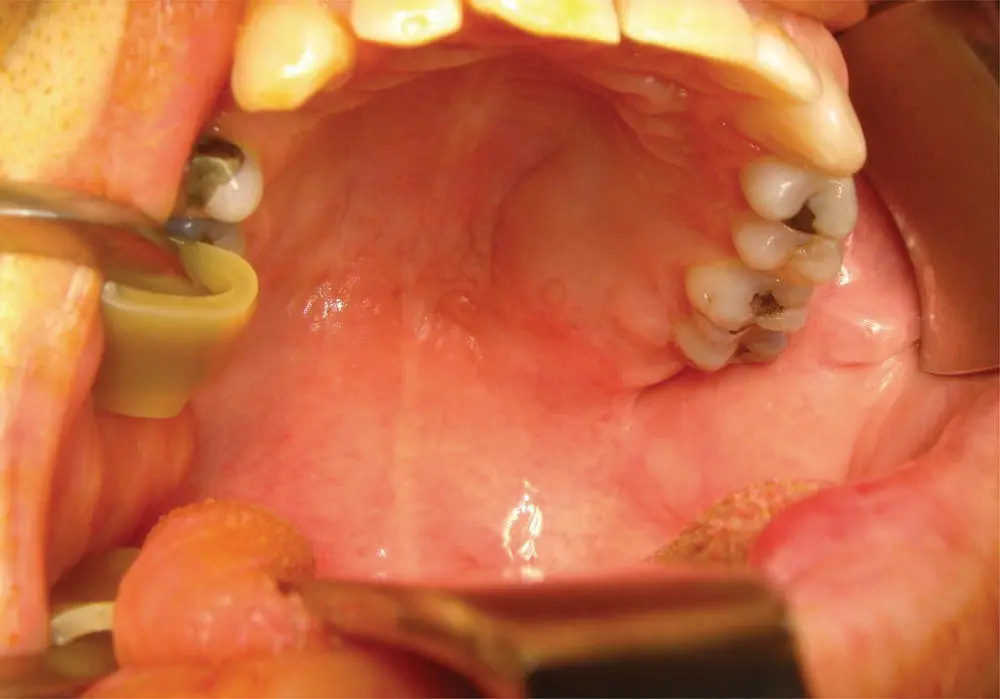
FIGURE 6.1 This transoral photograph shows mild submucosal fullness of the left aspect of the hard palate.
Question: What are the differential diagnoses for this mass?
Answer:Hard palate tumors are rare. The differential includes ameloblastoma, odontogenic keratocyst, and lymphoma, among others. However, the most common pathologies are minor salivary gland tumors.
Question: What is the most common minor salivary tumor in the oral cavity?
Answer:The most common minor salivary tumor of the oral cavity is mucoepidermoid carcinoma, followed by adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Question: What would you recommend next? What further investigations should be done for this patient?
Answer:Tissue diagnosis is the next step. Fine needle aspirate will most likely determine if this is a malignant versus benign tumor. However, core needle biopsy is often needed due to the heterogeneity in salivary gland pathology to establish the exact pathological diagnosis.
Читать дальше