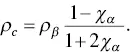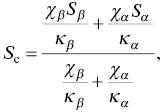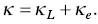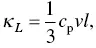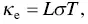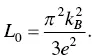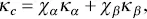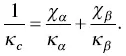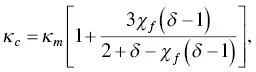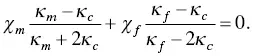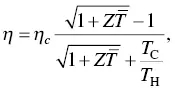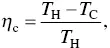If the α phase is less resistive than the β phase, ρ α< (1/10) ρ β, the resistivity of the composite is given by
(1.21) 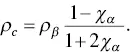
The Seebeck coefficient of the composites is also related to the microstructure of the two phases. When the α and β phases are in series, the Seebeck coefficient ( S c) of the composite is given by,
(1.22) 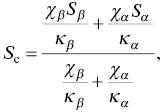
where S αand S βare the Seebeck coefficients of the α and β phases, respectively, and κ αand κ βare the thermal conductivities of the two phases, respectively. When the two phases are in parallel, the Seebeck coefficient of the composite is given by
(1.23) 
1.1.6 Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity ( κ ) of an electronic material include the lattice thermal conductivity ( κ L) and the electronic thermal conductivity ( κ e),
(1.24) 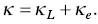
The lattice thermal conductivity is given by the Debye equation,
(1.25) 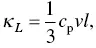
where c p, v , and l are the specific heat capacity, the phonon velocity, and the phonon mean free path, respectively. The phonon mean free path of polymers is usually extremely small due to the scattering by other phonons, defects, and grain boundaries. Thus, polymers usually have a thermal conductivity much lower than metals and semiconductors. For example, the values of c p, v , and l are 1.8 × 10 6J (K −1m −3), 1.58 × 10 3m s −1, and 0. nm, respectively, for PEDOT:PSS. The κ Lvalue of PEDOT:PSS is thus ~0.3 W (m −1K −1). The lattice thermal conductivity is related to the crystallinity of polymers. The higher the crystallinity, the higher the thermal conductivity.
The electronic thermal conductivity is related to the electrical conductivity by the Wiedemann–Franz law,
(1.26) 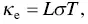
where L is the Lorentz number. The Sommerfeld value of the Lorenz number at T → 0 K is given by
(1.27) 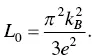
One important reason for the thermoelectric application of polymer nanocomposites is their low thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of a composite with polymer matrix and fillers depends on its microstructure [30]. A composite has the highest thermal conductivity when its structure is modeled with two components in parallel and the lowest thermal conductivity when it is modeled with the two components in series.
The thermal conductivity ( κ c) of a composite by the parallel model is given by
(1.28) 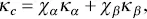
where χ αand χ βare the volume fractions of the two phases, respectively, and κ αand κ βare the thermal conductivities of the two phases, respectively. The parallel model usually overestimates the contribution of the fillers to the overall thermal conductivity of the composites.
The thermal conductivity of a composite by the series model is given by
(1.29) 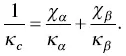
The thermal conductivity of composites with nano‐fillers dispersed in polymers is between that by the parallel model and series model, and it is usually close to the value by the series model.
A more precise equation for the thermal conductivity of composites with fillers in matrix is given by the Maxwell–Garnett equation,
(1.30) 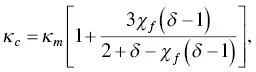
where κ mand κ fare the thermal conductivities of the matrix and fillers, respectively, and δ = κ f/ κ m. The thermal conductivity of nanofillers like carbon nanotubes and graphene is usually much larger than that of the polymer matrix. Assuming that the values for a composite are δ = 1 and χ f= 0.05, we can obtain κ c= 1.1 κ min terms of the Eq. (1.32), that is, the thermal conductivity of the composite is almost the same as the polymer matrix. Thus, the composite may have high electrical conductivity and high Seebeck coefficient but thermal conductivity is low. In terms of the Maxwell‐Garnett equation, the thermal conductivity of a composite linearly increases with the filler loading when the filler loading is low.
When the fillers form percolation for thermal conduction, the thermal conductivity of composites is underestimated by the Maxwell–Garnet equation. At the filler concentration higher than the percolation threshold, the thermal conductivity is given by the Bruggeman equation,
(1.31) 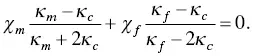
There is an interface between the polymer matrix and fillers in composites. Phonons can be scattered at this interface if the interfacial coupling between the matrix and fillers is weak. If the fillers are small and the separation between the fillers is large, the thermal conductivity of the composites is low.
1.2 Thermoelectric Generators
1.2.1 Dependence of Thermoelectric Efficiency on ZT
The most important application for thermoelectric materials is the energy conversion between heat and electricity. It is important to understand the heat transfer, drift electrical current and thermoelectric current in thermoelectric generators. The Seebeck effect is exploited to convert heat into electricity in thermoelectric generator. Assume that the p ‐type and n ‐type thermoelectric materials have the same ZT value, the thermoelectric conversion efficiency depends on the ZT value of the thermoelectric materials,
(1.32) 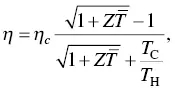
where η cis the Carnot efficiency for the temperature difference at the hot ( T H) and cold ends ( T C),
(1.33) 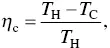
Читать дальше