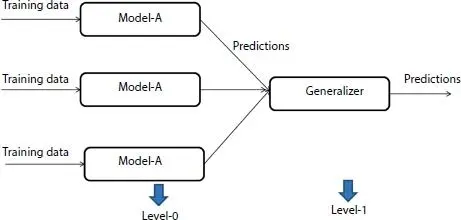
Figure 2.6A high-level representation of stacking.
The efficiency achieved by the considered ensemble machine learning techniques, i.e., Bayes optimal classifier, bagging, boosting, BMA, bucket of models, and tacking, is compared toward the performance metrics, i.e., accuracy, throughput, execution time, response time, error rate, and learning rate [30]. From the analysis, it is observed that the efficiency achieved by Bayesian model combination, stacking, and Bayesian model combination are high compared to other ensemble models considered for identification of zonotic diseases.
| Technique |
Accuracy |
Throughput |
Execution time |
Response time |
Error rate |
Learning rate |
| Bayes optimal classifier |
Low |
Low |
High |
Medium |
Medium |
Low |
| Bagging |
Low |
Medium |
Medium |
High |
Low |
Low |
| Boosting |
Low |
Medium |
High |
High |
High |
Low |
| Bayesian model averaging |
High |
High |
Medium |
Medium |
Low |
Low |
| Bayesian model combination |
High |
High |
Low |
Low |
Low |
High |
| Bucket of models |
Low |
Low |
High |
Medium |
Medium |
Low |
| Stacking |
High |
High |
Low |
Low |
low |
Medium |
This chapter provides introduction to zonotic diseases, symptoms, challenges, and causes. Ensemble machine learning uses multiple machine learning algorithms to identify the zonotic diseases in early stage itself. Detailed analysis of some of the potential ensemble machine learning algorithms, i.e., Bayes optimal classifier, bootstrap aggregating (bagging), boosting, BMA, Bayesian model combination, bucket of models, and stacking are discussed with respective architecture, advantages, and application areas. From the analysis, it is observed that the efficiency achieved by Bayesian model combination, stacking, and Bayesian model combination are high compared to other ensemble models considered for identification of zonotic diseases.
1. Allen, T., Murray, K.A., Zambrana-Torrelio, C., Morse, S.S., Rondinini, C., Di Marco, M., Daszak, P., Global hotspots and correlates of emerging zoo-notic diseases. Nat. Commun ., 8 , 1, 1–10, 2017.
2. Han, B.A., Schmidt, J.P., Bowden, S.E., Drake, J.M., Rodent reservoirs of future zoonotic diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci ., 112 , 22, 7039–7044, 2015.
3. Salata, C., Calistri, A., Parolin, C., Palu, G., Coronaviruses: a paradigm of new emerging zoonotic diseases. Pathog. Dis ., 77 , 9, ftaa006, 2019.
4. Mills, J.N., Gage, K.L., Khan, A.S., Potential influence of climate change on vector-borne and zoonotic diseases: a review and proposed research plan. Environ. Health Perspect ., 118 , 11, 1507–1514, 2010.
5. Ardabili, S., Mosavi, A., Várkonyi-Kóczy, A.R., Advances in machine learning modeling reviewing hybrid and ensemble methods, in: International Conference on Global Research and Education , 2019, September, Springer, Cham, pp. 215–227.
6. Gao, X., Shan, C., Hu, C., Niu, Z., Liu, Z., An adaptive ensemble machine learning model for intrusion detection. IEEE Access , 7 , 82512–82521, 2019.
7. Yacchirema, D., de Puga, J.S., Palau, C., Esteve, M., Fall detection system for elderly people using IoT and ensemble machine learning algorithm. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput ., 23 , 5–6, 801–817, 2019.
8. Zewdie, G.K., Lary, D.J., Levetin, E., Garuma, G.F., Applying deep neural networks and ensemble machine learning methods to forecast airborne ambrosia pollen. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health , 16 , 11, 1992, 2019.
9. Dang, Y., A Comparative Study of Bagging and Boosting of Supervised and Unsupervised Classifiers For Outliers Detection (Doctoral dissertation), Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio, United States, 2017.
10. Wiens, J. and Shenoy, E.S., Machine learning for healthcare: on the verge of a major shift in healthcare epidemiology. Clin. Infect. Dis ., 66 , 1, 149–153, 2018.
11. Bollig, N., Clarke, L., Elsmo, E., Craven, M., Machine learning for syndromic surveillance using veterinary necropsy reports. PLoS One , 15 , 2, e0228105, 2020.
12. Shen, X., Zhang, J., Zhang, X., Meng, J., Ke, C., Sea ice classification using Cryosat-2 altimeter data by optimal classifier–feature assembly. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett ., 14 , 11, 1948–1952, 2017.
13. Dalton, L.A. and Dougherty, E.R., Optimal classifiers with minimum expected error within a Bayesian framework—Part II: properties and performance analysis. Pattern Recognit ., 46 , 5, 1288–1300, 2013.
14. Boughorbel, S., Jarray, F., El-Anbari, M., Optimal classifier for imbalanced data using Matthews Correlation Coefficient metric. PLoS One , 12 , 6, e0177678, 2017.
15. Hassan, A.R., Siuly, S., Zhang, Y., Epileptic seizure detection in EEG signals using tunable-Q factor wavelet transform and bootstrap aggregating. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed ., 137 , 247–259, 2016.
16. Hassan, A.R. and Bhuiyan, M.I.H., Computer-aided sleep staging using complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise and bootstrap aggregating. Biomed. Signal Process. Control , 24 , 1–10, 2016.
17. Pino-Mejías, R., Jiménez-Gamero, M.D., Cubiles-de-la-Vega, M.D., Pascual-Acosta, A., Reduced bootstrap aggregating of learning algorithms. Pattern Recognit. Lett ., 29 , 3, 265–271, 2008.
18. Hinne, M., Gronau, Q.F., van den Bergh, D., Wagenmakers, E.J., A conceptual introduction to Bayesian model averaging. Adv. Methods Pract. Psychol. Sci ., 3 , 2, 200–215, 2020.
19. Ji, L., Zhi, X., Zhu, S., Fraedrich, K., Probabilistic precipitation forecasting over East Asia using Bayesian model averaging. Weather Forecasting , 34 , 2, 377–392, 2019.
20. Liu, Z. and Merwade, V., Separation and prioritization of uncertainty sources in a raster based flood inundation model using hierarchical Bayesian model averaging. J. Hydrol ., 578 , 124100, 2019.
21. Isupova, O., Li, Y., Kuzin, D., Roberts, S.J., Willis, K., Reece, S., Computer Science, Mathematics, BCCNet: Bayesian classifier combination neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.12258 , 8, 1–5, 2018.
22. Yang, J., Wang, J., Tay, W.P., Using social network information in community-based Bayesian truth discovery. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Networks , 5 , 3, 525–537, 2019.
23. Yang, J., Wang, J., Tay, W.P., IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, Using Social Network Information in Bayesian Truth Discovery. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.02954 , 5, 525–537, 2018.
24. Dadhich, S., Sandin, F., Bodin, U., Andersson, U., Martinsson, T., Field test of neural-network based automatic bucket-filling algorithm for wheel-loaders. Autom. Constr ., 97 , 1–12, 2019.
Читать дальше













