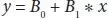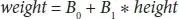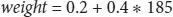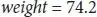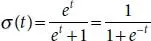
Figure 1.1Linear regression [3].
1 1] Simple linear regression: Single input is used to estimate the coefficients. This involves statistical calculations such as mean, standard deviations (SD), correlations, and covariance.
2 2] OLS: This technique is used when there is more than one input, to calculate the coefficients. This OLS method looks for minimizing the summation of the squared residuals. That is, for a given regression line through the input, the distance is calculated from every data point concerning the regression line then square it, and all together sum the squared errors. Assuming the data as a matrix, this approach uses linear algebra to calculate the coefficient values. Sufficient memory and data should be available to fit the data and to complete matrix operation [6].
3 3] Gradient descent: For more than one input value, the process of optimizing the coefficient values can be achieved by iteratively minimizing the errors on training data. This procedure is termed gradient descent and works for random values for every coefficient. For every couple of input data and output, the summation of the squared errors is estimated. The coefficient values are updated in the path of diminishing the error. This procedure is repetitive up to a minimum sum-squared error is attained or no added progress is possible [6].
4 4] Regularization: This method looks for minimizing the sum-squared error on the training data (using OLS) and also to decrease the complexity in the model. These approaches are said to be operative when the input values are collinear and OLS overfits the training dataset [6].
1.4.2 Predictions With Linear Regression
Predicting values are more like solving an equation for the specified input. Consider an example where weight (y) is predicted from height (x). The LR equation is represented as [6]
(1.1) 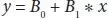
or
(1.2) 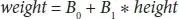
These equations can be conspired as a line in 2-dimension as shown in Figure 1.2.
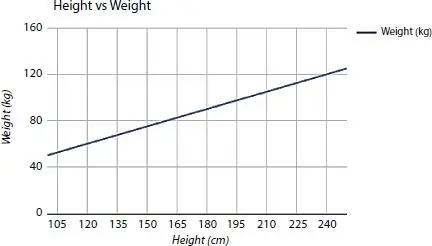
Figure 1.2Height vs. weight graph [6].
Let B 0be the bias coefficient and B 1be the height column coefficient. To find the coefficients, the above learning techniques are used. Later, different height values are used to calculate the weight. For example, let B 0= 0.2 and B 1= 0.4, for an individual of height of 185 cm, the weight is calculated as follows [6]:
(1.3) 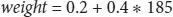
(1.4) 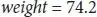
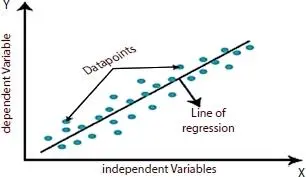
Logistic regression is well-known ML algorithms, which is under the SML technique. It is utilized for anticipating the dependent factor by making use of a given set independent factor, it is used for the classification problems, and it is dependent on the idea of probability. Logistic regression calculates the yield of a dependent variable. Thus, the outcome is a discrete value. It may be either yes or no, zero or one, and valid or invalid [3, 7]. However, instead of giving the definite value as 0 and 1, it provides the probabilistic values which lie in the range of 0 and 1. For instance, consider that you are being given a wide scope of riddles/tests trying to comprehend which concept you are acceptable at. The result of this investigation would be considered a geometry-based issue that is 70% prone to unravel. Next is the history quiz, the chance of finding a solution is just 30%. Consider an event of detecting the spam email. LR is utilized for this event; there is a constraint of setting a limit depending on which classification is possible. Stating if the class is spam, predicted consistently is 0.4 and the limit is 0.5, the information is categorized as not a spam mail, which can prompt the outcome progressively. Logistic regression is classified as binary, multinomial, and ordinal binary can have only two possible values either yes or no or true or false where multinomial can have three or more possible values and Ordinal it manages target factors with classifications. For instance, a grade can be arranged as “very poor”, “poor”, “great”, and “excellent”.
Logistic regression is well defined as [16].
(1.5) 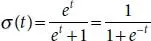
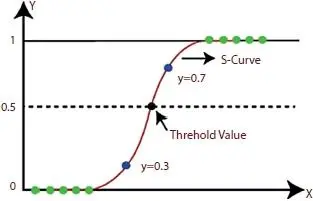
Figure 1.3Logistic regression [3].
Figure 1.3 shows the function curve between the values 0 and 1.
1.6 Support Vector Machine (SVM)
SVMs are an influential yet adaptable type of SML which are utilized both for classification and regression. They are mainly utilized for classification problems. They use a Kernel capacity which is an essential idea for the greater part of the learning process. These algorithms make a hyperplane that is utilized to group the different classes. The hyperplane is produced iteratively, by the SVM with the target to minimize the error. The objective of SVM is to split the datasets into different classes to locate a maximum marginal hyperplane (MMH). MMH can be located using the following steps [10].
• SVM creates hyperplanes iteratively that separates the classes in a most ideal manner.
• Then, it picks the hyperplane that splits the classes accurately.
For example, let us consider two tags that are blue and black with data features p and q . The classifier is specified with a pair of coordinates ( p , q ) which outputs either blue or black. SVM considers the data points which yield the hyperplane that separates the labels. This line is termed as a decision boundary. Whatever tumbles aside of the line, will arrange as blue, and anything that tumbles to the next as black.
The major terms in SVM are as follows:
• Support Vectors: Datapoints that are nearby to the hyperplane are called support vectors. With the help of the data points, the separating line can be defined.
• Hyperplane: Concerning Figure 1.4, it is a decision plane that is parted among a set of entities having several classes.
• Margin: It might be categorized as the gap between two lines on data points of various classes. The distance between the line and support vector, the margin can be calculated as the perpendicular distance.
There are two types of SVMs:
• Simple SVM: Normally used in linear regression and classification issues.
• Kernel SVM: Has more elasticity for non-linear data as more features can be added to fit a hyperplane as an alternative to a 2D space.
Читать дальше