6.2.6.5.2 V2I/I2V Forwarding
It is designed for urban areas; data is transferred within vehicles and with the road side units. It is used in dense areas or populated areas. Nodes are highly available and node mobility is high [23–26].
6.2.6.5.3 V2V Forwarding Flooding
It is used to communicate between the vehicles. In this scenario, vehicle sends the data to the other for transmission of data for many uses/application regarding to the traffic problems such as traffic jam and bomb blast.
6.2.6.5.4 Geographical Forwarding
Here, forwarding scheme is location-based. Information is stored in nodes and forward it to the kneeboard hops. Geocaching is used to convey the message.
6.2.6.5.5 Opportunistic Forwarding
It uses opportunistic approach for storing and forwarding scheme. It is information driven device which do not merge the information.
6.2.6.5.6 Cluster-Based Forwarding
In cluster-based forward, network considers a node as a midhub before delivering the data to the destination node. To perform this arrangement, we have to arrange the node in such a manner that nodes other than destination node carry the information as the midhub or middle node of network.
6.2.6.5.7 Peer-to Peer Forwarding
In peer-to-peer forwarding, source store data in storage and not send again to nodes until another nodes request the data. This technique is designed to make applications delay tolerant.
1 1. Store-carry and forward.
2 2. Greedy forwarding.
3 3. Path discovery.
4 4. Single path.
5 5. Multi path.
6 6. Prediction.
6.2.6.6.1 Store-Carry and Forward
In store-and-carry forwarding, when nodes could not find the next nodes to deliver, the data then they store the data and wait for the node to transmit it. It happens to faint when the node density is very low.
6.2.6.6.2 Greedy Forwarding
This method is used to minimize the number of hops during transmission of data. It is used to observe the close nodes to transfer the data. In the absence of any close node, it will block the data.
To minimize the cost and use of bandwidth during a transmission, we use this path. This follows RREQ method. First of all, we will observe all the possible paths and then select a suitable path to deliver the data.
In this technique, we establish a single path for transmission from source to target, and it simplifies the handling of table. But if transmission will be stop, there will be no way to start it again.
It is a multipath communication between two nodes. But there is complex table for routing of data. In case of any problem there will be an alternate path.
In this FANET, nodes use to predict the next nodes by using the parameters of location, node size, and its communication model technique. In the case of data loss, there will be information for the node, and for recovery structure, we use store and forward technique to active the paths for communication.
6.2.7 Mobility Model
6.2.7.1 MANETs
MANETs have two mobility models according to the domain of the mobile whether it is in the same or different. First one is Macro while the latter is Micro mobility model.
6.2.7.1.1 IP Macro-Mobility Protocols
It is mobility of nodes between two domains. It separate out the static and moving nodes to support IP Macro mobile IP is best there are version of Ipv4 and Ipv4. It contains three functions. First is to allow the access of home IP to other cell. Second is mobile router. Third is to allow the connection to the foreign through the internet.
6.2.7.1.2 IP Micro-Mobility Protocols
It defines the movement of nodes within the same domain. It is fast, high connected. A gateway is used to connect Cellular IP with internet. Cellular IP maintains two types of distributed cache for 1) location management and 2) routing purposes.
6.2.7.2 VANETs
6.2.7.2.1 RWP
RWP is the node movement in any random direction and speed. Each node assigns the initial value, destination value with the speed, and time interval. After the simulation, again transmission is created and node moves in the new path.
It is map-based city site model. It consist of the vertical and horizontal lanes, and before simulation, nodes are randomly placed and according to the security distance and point of view they can turn right, left and straight. The probability is 0.5, 0.25, and 0.25, respectively.
It is used for simulation of group movement behaviors in practical life. It is used in the form the groups and coordinate each other for transmission of data. MANETs and VANETs work in group model.
It is type of model which consists of maps having freeways and many lanes. There is no city path is present. It is imaginary. At first, nodes are placed randomly in lines but there are security distances between two nodes. If there is less distance between two nodes, adjust the distance. Node moves in the lane and it is not possible to change the lane.
Figure 6.4shows mobility model of flying adhoc networks. Details of these models are presented in next section.
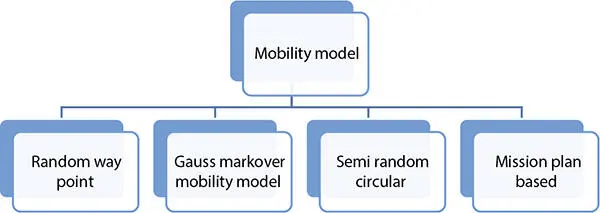
Figure 6.4 Mobility model.
6.2.7.3.1 Random Way Point Mobility Model
RWP is the movement of nodes randomly within the specific area. This model contain three steps turn right, turn left and going. It calculates the time pause from speed changing and direction. But it is difficult to change the aircraft. It is not suitable for the aircraft. As shown in Figure 6.5.
GMM model uses the mobility of nodes by setting the directions and speed of a data packet which is constantly updated by the specific interval of time. Speed and data is constantly by the neighbor nodes shown in Figure 6.6.
6.2.7.3.3 Semi Random Model
This model is used for monitoring purpose. These UAV have curving flight manners. They will fly over the specific area to capture the information. UAV is using for monitoring and spying purpose over the specific area presented in Figure 6.7.
Figure 6.5 Random way model.
Figure 6.6 GMM model.
Figure 6.7 Semi-random model.
Figure 6.8 Mission model.
Читать дальше

















