ZRP [13–18] is comprises of different zones and after division we note the position of sender and receiver mobile node is observed. If sender and receiver mobile nodes are present in one zone, then proactive routing protocol used for data delivery between them, and if sender and receiver mobile nodes are present in various zones, then reactive routing is used to transmit the data packets between them.
6.2.6.2 VANET
6.2.6.2.1 Transmission Base
• Unicast: MANET is topology base routing protocol. There is a table of link storage information by which data is transferred from one node to other.
• Multicast: In MANETs, information is delivered from source to destination through the multiple ways. If there is any path breaker for one way, then packet is delivered through the other ways. It is classified into the following categories:1) Geo-Cast–Based Routing Protocol: To deliver data from one node to other via multicasting approach. It works on the basis of GPS system. In VANETs, if all nodes are in the same zone, then one vehicle can send data from one node to many nodes. If one of the node moves out the zone, then nodes changes the position of the sender node according to the GPS location.2) Robust Vehicular Routing (ROVER): ROVER works same as AODV protocol. Sender node sends request to the destination node. Each node has ID, location, and table for routing. If the destination node accepts the request from sender, then it will reply back to the sender. If sender node is out of the zone, then there is no possibility of reply. After the acceptance of the data packet and reply, there will be transmission of data packet.3) Mobile Just In Time Multicasting Protocol (MOBICAST): When packet is transferred from sender to receiver through ZRP. Communication breaks down when the node slow down and faster. ZRP solves this issue by considering time into the transmission of data packet delivery and calculate the time by location of vehicle through GPS. It is flexible than ZRP and result of throughput is higher.
6.2.6.2.2 Routing Information
6.2.6.2.2.1 Cluster-Based Routing Protocol
In this routing scheme, there are number of nodes which combine to form clusters. In every cluster group, there is a cluster head that transfer information from one node to other. The main drawback is it increases the delay during the transmission.
6.2.6.2.2.2 COIN: Clustering for Open Network
To improve network scalability, this mechanism is introduced. It separates the zones into clusters. To select the cluster, there are three following QOS:
1 1) Nodes mobility.
2 2) Location of nodes.
3 3) Nodes behavior.
IVC solves issue of different distance between vehicles into the one zone. To find the path, first declare the cluster head into the zone. To remain cluster head for long time, mobility of head should be low as compared to the other cluster nodes.
6.2.6.2.2.3 Cluster-Based Directional Routing Protocol (CBDRP)
CBDRP into clusters and there is cluster heads for the transmission of data from sender to receiver. For transmission, source has to send the request to the destination. Data packet contains ID, location, and address of the node due to which size increases. Delay of the packet also increases which is drawback of this protocol. Due to the overhead, this protocol is also slow [19].
6.2.6.3 FANETs
6.2.6.3.1 Load Carry and Deliver Protocol
In this UAV load, the information/data from ground and deliver it to the destination. It can be used for single source single destination and multipath destination. It is to minimize the throughput with minimum delay and reduction of hops. Its drawback is the coverage of large area. When distance between UAVS is increased delay also increase. Detailed classification is presented in Figure 6.3.
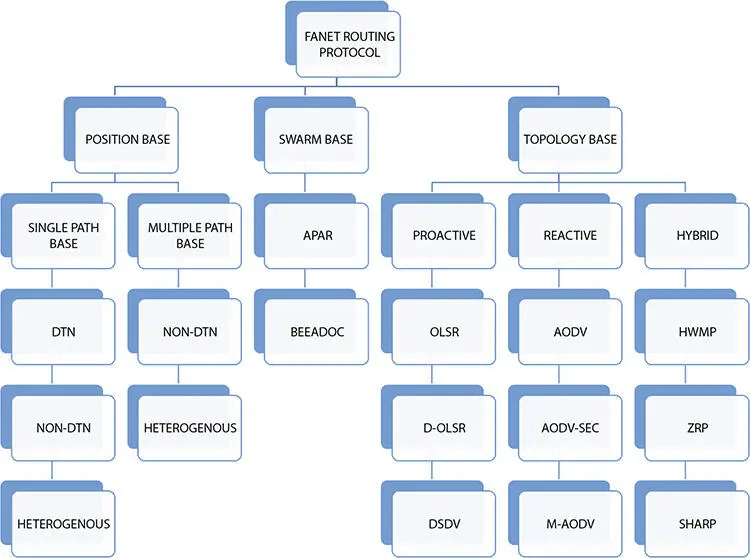
Figure 6.3 FANETs.
6.2.6.3.2 Data Centric Routing (DCR)
This scheme is used to collect the data from different sources and divide it on the bases of on-demand protocol. Three dimensions are present in the DCR: 1) In the space decoupling, no need of node ID; 2) Data is present and can be transferred to online nodes; 3) Asynchronous communication is present for flow decoupling.
6.2.6.3.2.1 Static Routing Protocols
Static protocols contain tables. It is used in the mission in which no requirement of changing table. During mission, UAVS can communicate to the other UAVS and ground stations and can store the information.
6.2.6.3.2.2 Proactive Routing Protocols
Table is already prepared for the network. This table contains all information of the nodes and their location. Every node remembers all information of all the nodes. This is helpful for the data packet transmission.
6.2.6.3.2.2.1 Optimized Link State Routing (DLSR)
In DLSR, there are two types of messages sent to the destination node. First is hello message to check the connectivity of the network nodes with each other. Second is control message to refresh the routes of the transmission of data. Large overhead is present in the network. To reduce overheads, multiple relay is used for forwarding schemes [20].
6.2.6.3.2.2.2 Destination-Sequenced Distance Vector (DSDV)
DSDV contains the UAVs. They all know everything about every other node. Assignment of sequence numbers are the main feature of DSDV. By doing this, loop system is avoided and system becomes simple. Main disadvantage is the overheads [21].
6.2.6.3.3 Reactive Routing Protocols
Reactive protocols are on demand protocols, they find out path during transmission. It consists of two request, send request and reply request. First request is sent to the destination nodes via flooding procedure. Reply request is send from destination to source through unicast method. It delays the transmission due to finding of path.
6.2.6.3.3.1 Dynamic Source Routing (DSR)
It is different in the sense of the ID. Each node has different ID. Route is stored in the in the header of the nodes. It is a multihop system, in the case of hop fail, there is need of another path.
6.2.6.3.3.2 AdHoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV)
It is table-driven protocol. It uses sequence numbers to transfer the data from source to destination. It stores the data of the next hop nodes. It maximizes the bandwidth and decrease the delay in data packet delivery. In the case of path failure, path refreshes again and again due to which congestion occurs. In AODV, time slot is present along with the hop information.
6.2.6.4 MANETs
6.2.6.4.1 Tunneling
In tunneling forward strategy [22], to send the data, we use AODV or searching in tables. Sink is available within the MANET zone and then we can easily send the data. To send outside the network, we encapsulated the data to gateway and then send it to the destination by slandered IP address.
For non-tunneling approach, we used to transfer the data from the sender to the receiver node which is located outside the zone. Gateway approach is used to send the data. IP address is used to forward data.
6.2.6.5 VANETs
6.2.6.5.1 Greedy
Frequent change of topology is the main point of greedy routing protocol. This is the main disadvantage of the previous work of the routing protocols. Weak signal is the drawback of the protocol. It involves near most node and intermediate nodes scheme for transmission. It will approach node. Change of topology and time delay is less and throughput is high.
Читать дальше













