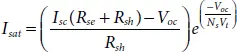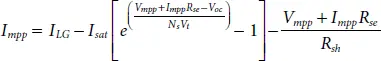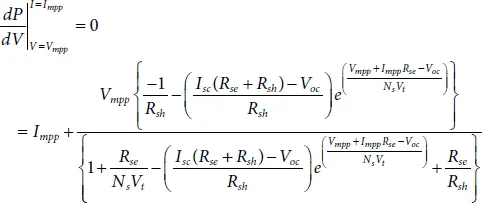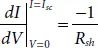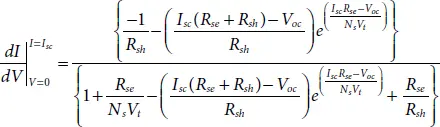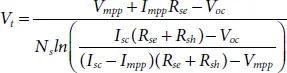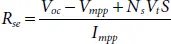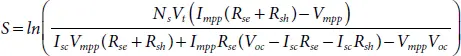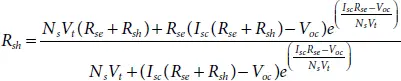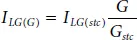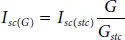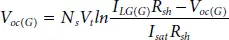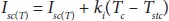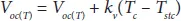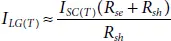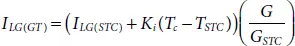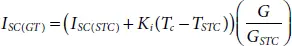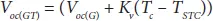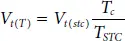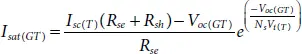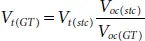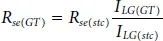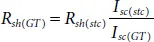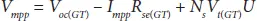Step-2: Open Circuit Condition (OCC) – During OCC, the panel output current is zero (I=0) and substituting this condition in (1.1)becomes [17, 18]:
(1.5) 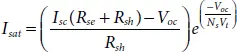
Step-3: Maximum Power Point condition (MPP)- The maximum point voltage V mppand current I mppof PV panel is available in manufacturer datasheet. By substituting these parameters in (1.1)we get,
(1.6) 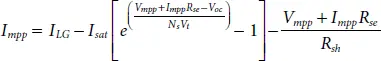
The derivative at the maximum power point (MPP) is zero as the tangent at MPP is parallel to voltage axis [19]. Therefore,
(1.7) 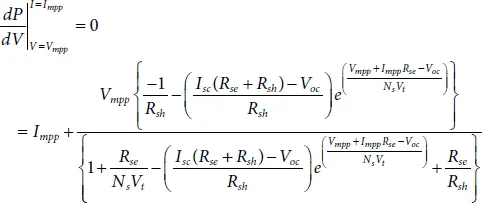
The derivative of current with respect to voltage at SCC is mainly determined using the shunt resistance as [15],
(1.8) 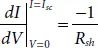
From above equation, the dI/dV can be illustrated as,
(1.9) 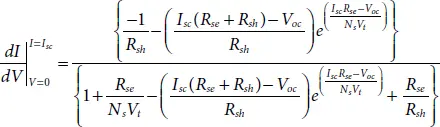
1.2.1 Calculation of Vt, Rse and Rsh
As numerical methods are sensitive to initial conditions assumed for solving the non-linear transcendental equations, improper selection of initial values may lead to failure of convergence. Therefore, proper initial values are need to be selected for achieving good convergence and it is discussed [15]. By rearranging equations (1.6), (1.7)and (1.9), the expressions for determining V t, R seand R shcan be obtained as given in (1.10), (1.11)and (1.13), respectively.
(1.10) 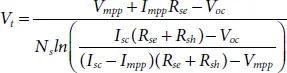
(1.11) 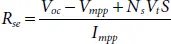
Where
(1.12) 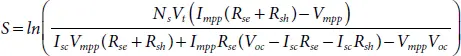
(1.13) 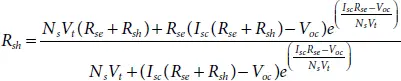
The above transcendental equations of V t, R seand R shneed to be solved using either analytical or numerical approaches. Using the derived results, the parameters of I LGand I satcan be obtained from equations (1.4)and (1.5).
1.2.2 Effect of Irradiance and Temperature
The I LGand I scare directly proportional to solar irradiance and temperature which can be expressed as below [15],
(1.14) 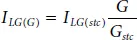
(1.15) 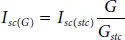
where, G stcand G are the standard and actual irradiance in W/m 2. Similarly, the open-circuit voltage is also varying as function of irradiance which can be expressed as,
(1.16) 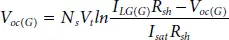
The V ocequation is a non-linear transcendental equation and also need to be solved using numerical methods for determining the parameters under dynamic condition. The procedure for obtaining this value using GS or NR technique is similar as that of five parameter estimation of SDM of SPV. For a given operating temperature, the I scand V occan be evaluated using the following expressions:
(1.17) 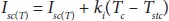
(1.18) 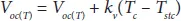
Where T stcand T denotes the standard and actual operating cell temperature in K. On the other hand, the light generated current as a function of temperature can be determined using (1.4)and is rewritten as,
(1.19) 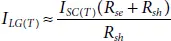
For any operating temperature and irradiance, the value of I LG, I SCand V occan be estimated using the equations (1.20)to (1.22)as below,
(1.20) 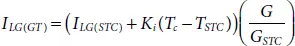
(1.21) 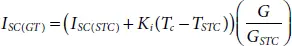
(1.22) 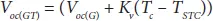
The thermal voltage (V t) as function of cell temperature can be represented as,
(1.23) 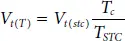
The diode dark current also called reverse saturation current as a function of cell operating temperature and irradiance can be represented using (1.6)and (1.23)as,
(1.24) 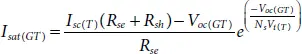
1.2.3 Estimation of Maximum Power Point
For accurate evaluation of maximum power point of SPV panel, the initial values of V mppand I mppshould be selected properly using the known values of V ocand I scunder STC. The variation of parameters like V t(GT), R se(GT), and R sh(GT)with respect to operating temperature and irradiance can be deduced using equations shown below [15],
(1.25) 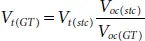
(1.26) 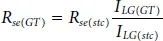
(1.27) 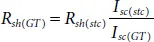
To determine the voltage at MPP, (1.6)has been modified as a function of irradiance and temperature as represented below,
(1.28) 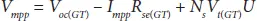
Читать дальше