Umashankar Subramaniam - Smart Grids and Micro-Grids
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Umashankar Subramaniam - Smart Grids and Micro-Grids» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Smart Grids and Micro-Grids
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Smart Grids and Micro-Grids: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Smart Grids and Micro-Grids»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Written and edited by a team of experts in the field, this is the most comprehensive and up-to-date study of smart grids and microgrids for engineers, scientists, students, and other professionals.
Audience:
Smart Grids and Micro-Grids — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Smart Grids and Micro-Grids», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
In general, the performance of a PV panel highly depends on solar irradiance and conversion efficiency. The specification of PV panel data is obtained from the manufacturer datasheet. However, it is given only for standard test condition (STC) of solar irradiance (1000 W/m 2) and operating temperature (25 °C). Indeed, the data available are insufficient even at STC. Hence, it is essential to design a predictive performance tool that can estimate the unknown parameters of SPV with which economic feasibility of PV panel at any location characterized by particular operating environmental conditions can be investigated [9]. Practically, the SPV panel operates far from the STC. Therefore, the intrinsic parameters of the PV panel are obtained by solving the transcendental equation of the SPV module using analytical and numerical approaches for estimating its performance efficiency. As analytical approaches are problem-specific and complex to solve the non-linear equations, the deterministic based numerical approaches are used for solving the transcendental equation of the SPV module [10, 11]. In various studies, researchers neglect the series or shunt resistance to estimate the parameters of SPV module which result in mismatch error in V-I characteristics between the simulated and experimental results [12]. Further, to reduce the mismatch error the shunt and series resistance are considered in addition with ideality factor, light generated current and diode saturation current to estimate the five parameters of SPV. But in some cases, the value of shunt or series resistance is maintained constant to estimate the MPP which decreases the maximum power accuracy of SPV. The work in [5], presents the parameter estimation using NR and Levenberg-Marquardt method. In which, the author estimates the maximum power by modifying the characteristic equations for change in irradiance and temperature separately. The study fails to consider the variation in parameters under dynamic conditions and also the combined effect of change in temperature and irradiance is not considered simultaneously. The work reported in [13], uses the particle swarm optimization (PSO) to deduce the parameters and the results obtained are compared with NR. The result reveals that the NR method gives best results for monocrystalline type of SPV panel compared to PSO. However, this study neglects the shunt resistance for estimating the maximum power at MPP. Similarly, the study in [14] considers the series resistance and diode thermal voltage for estimation of maximum power. Nonetheless, in the literature the variation in shunt resistance, series resistance and thermal voltage are considered for estimation of maximum power using NR technique. However, the authors in [15] accounted the variation in parameters of R se, R sh, and V tto estimate the maximum voltage and current using GS technique. Therefore, attempt has been made in this chapter to estimate the five parameters of the PV panel for deducing the maximum voltage and current under variations in solar irradiance and operating temperature by considering change in R se, R sh, and V t. Then, the results obtained are compared with literature work using GS technique to determine the equivalent parameters of the PV module of a single diode model (SDM) and to estimate the maximum power from the PV system. The main contributions of this chapter are as follows:
The parameters of series resistance (Rse), shunt resistance (Rsh) and diode thermal voltage (Vt) are estimated by solving three non-linear equations using NR method under STC for SDM of solar PV. Then, the derived solution from NR were used to extract the light generated current (ILG), and diode reverse saturation current (Isat).
The variation in shunt, series, and thermal voltage are calculated under dynamic conditions using the data given in the manufacturer data sheet by using appropriate equations. Then, these values are used to evaluate the maximum voltage and current at MPP by solving the two non-linear equations using NR technique.
The unknown parameters and MPP are evaluated for different PV modules of KD245GX, U5-80 and Shell SP70 using Matlab simulation. The I-V and P-V characteristics of HST60FXXXP solar PV panel obtained during simulation are validated with experimental results.
1.2 Mathematical Model of Solar PV
The mathematical modeling and analysis of SPV panel is more significant to study the operation of the PV system and to forecast the influence of various factors on the PV module’s performance particularly under dynamic environmental situations. To study the operation of SPV cell under given operating conditions of solar irradiance and temperature, a SDM is considered for analysis. As in most of the studies, SDM has been considered for the estimation of electrical parameters due to its simplicity and accuracy [14, 16]. The equivalent circuit of SDM is represented using a current source with an inverted diode, series (R se), and shunt resistance (R sh) as shown in Figure 1.1.
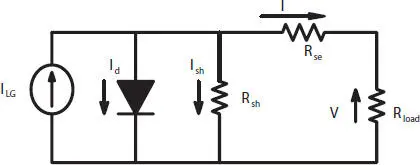
Figure 1.1 Equivalent circuit of SDM.
On applying Kirchhoff ’s current law (KCL) to the equivalent circuit of SDM, the relationship obtained among the output voltage (V) and current (I) of PV cell can be described as follows:
(1.1) 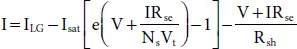
Where, I -Output current of PV panel terminals in Amps, V-output voltage of PV panel terminals in Volts, I LG - Light generated current of PV panel in Amps, N s-Number of series connected solar cells, I sat- Reverse saturation current of diode in Amps, R se , and R sh–Series and shunt resistance of solar PV module in Ohms. The thermal voltage ( V t) of a diode for one individual cell is represented as,
(1.2) 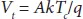
Where, A depicts the ideality factor of diode, k represent the Boltzmann constant (1.3806 × 10 -23J/K), T cis the SPV module temperature (STC) in K, and q is the Electronic charge (1.602 × 10 19C). The unknown parameters of PV panel namely I LG, Isat , A , Rse and Rsh can be calculated by numerical and analytical approaches using the information of datasheet given by the manufacturer for the PV module at STCs [15]. From (1.1), it is observed that the I-V characteristics curve greatly depends on five unknown parameters of the SPV cell. Therefore, the accurate estimation of electrical parameters is very important to achieve the characteristics closer to real time. The equations used to determine these five parameters such as I LG, Isat , A , Rse and Rsh using numerical techniques are as follows:
Step-1: Short Circuit Condition (SCC) - During this condition, the output voltage across the panel becomes zero (V=0) resulting in maximum short circuit current (I sc). This can be obtained by substituting V=0 in (1.1)resulting,
(1.3) 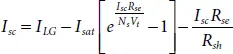
By substituting the short circuit conditions in (1.1)and after few simplifications, the light generated current (I LG) can be expressed as [17, 18]:
(1.4) 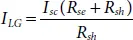
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Smart Grids and Micro-Grids»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Smart Grids and Micro-Grids» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Smart Grids and Micro-Grids» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.