Die im Cluster verfügbaren Bereiche sind:
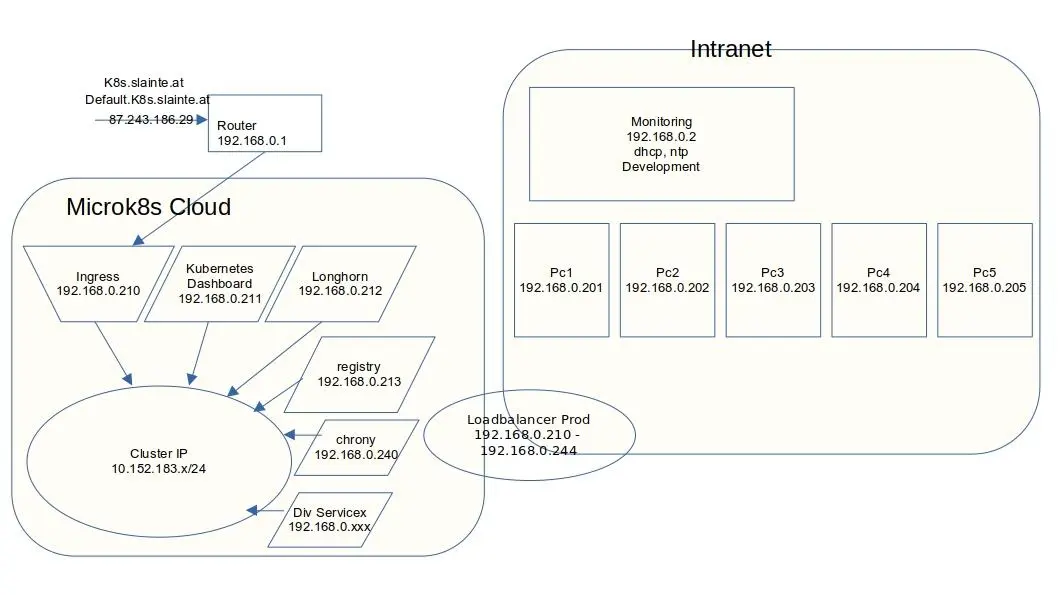
Im Konkreten:
k8s.slainte.at 87.243.186.29
default.k8s.slainte.at 87.243.186.29
Aus dem Cluster selbst:
alfred@pc1:~/yaml$ k get svc --all-namespaces | grep -v ''
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ingress ingress LoadBalancer 10.152.183.126 192.168.0.210 443:31287/TCP,80:31681/TCP 22h
kube-system kubernetes-dashboard LoadBalancer 10.152.183.150 192.168.0.211 443:31449/TCP 22h
longhorn-system longhorn-frontend LoadBalancer 10.152.183.199 192.168.0.212 80:31444/TCP 22h
container-registry registry LoadBalancer 10.152.183.207 192.168.0.213 5000:32000/TCP 22h
admin chrony-udp-svc LoadBalancer 10.152.183.77 192.168.0.240 123:32658/UDP 40m
admin pgadmin-svc LoadBalancer 10.152.183.201 192.168.0.241 5432:30954/TCP,80:30675/TCP,443:30676/TCP 19m
Source Repository
Inspiration:
https://microk8s.io/docs/registry-built-in
Eine Software-Registry wird benötigt, wenn man selbst entwickelte Anwendungen lokal speicher und verwenden möchte. Prinzipiell könnte man auch öffentliche Registrys nehmen, aber wir haben ja einen k8s-cluster.
alfred@pc1:~$ microk8s enable registry:size=40Gi
Addon storage is already enabled.
Enabling the private registry
Applying registry manifest
namespace/container-registry created
persistentvolumeclaim/registry-claim created
deployment.apps/registry created
service/registry created
configmap/local-registry-hosting configured
The registry is enabled
The size of the persistent volume is 40Gi
alfred@pc1:~$
Nun ist die Registry vorhanden. Das Cluster-Setup ist wie folgt:
alfred@pc1:~$ microk8s status
microk8s is running
high-availability: yes
datastore master nodes: 192.168.0.202:19001 192.168.0.203:19001 192.168.0.204:19001
datastore standby nodes: 192.168.0.201:19001 192.168.0.205:19001
addons:
enabled:
dashboard # The Kubernetes dashboard
dns # CoreDNS
ha-clusalfred@pc1:~$ microk8s status
microk8s is running
high-availability: yes
datastore master nodes: 192.168.0.202:19001 192.168.0.203:19001 192.168.0.204:19001
datastore standby nodes: 192.168.0.201:19001 192.168.0.205:19001
addons:
enabled:
dashboard # The Kubernetes dashboard
dns # CoreDNS
ha-cluster # Configure high availability on the current node
helm3 # Helm 3 - Kubernetes package manager
ingress # Ingress controller for external access
metallb # Loadbalancer for your Kubernetes cluster
metrics-server # K8s Metrics Server for API access to service metrics
prometheus # Prometheus operator for monitoring and logging
rbac # Role-Based Access Control for authorisation
registry # Private image registry exposed on localhost:5000
storage # Storage class; allocates storage from host directory
disabled:
helm # Helm 2 - the package manager for Kubernetes
host-access # Allow Pods connecting to Host services smoothly
linkerd # Linkerd is a service mesh for Kubernetes and other frameworks
portainer # Portainer UI for your Kubernetes cluster
traefik # traefik Ingress controller for external access
alfred@pc1:~$
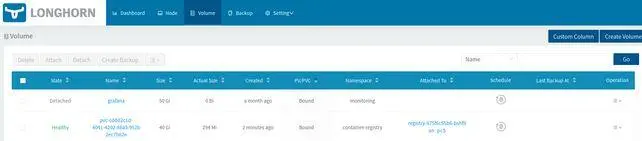 Abbildung 7: Registry Clusterdisk
Abbildung 7: Registry Clusterdisk
Das Volume wurde als ClusterDisk angelegt. Die Storageclass longhorn ist als default eingerichtet.
Das Skript zum Einrichten der Registry ist wie folgt:
#!/bin/bash
############################################################################################
# $Date: 2021-11-23 21:37:19 +0100 (Di, 23. Nov 2021) $
# $Revision: 1285 $
# $Author: alfred $
# $HeadURL: https://monitoring.slainte.at/svn/slainte/trunk/k8s/k8s/K13_registry.sh $
# $Id: K13_registry.sh 1285 2021-11-23 20:37:19Z alfred $
#
# Schnell-Installation microk8s - Installation praktischer AddOns
#
############################################################################################
#shopt -o -s errexit #—Terminates the shell script if a command returns an error code.
shopt -o -s xtrace #—Displays each command before it’s executed.
shopt -o -s nounset #-No Variables without definition
# Voraussetzung: Sauber installierte Nodes, Verbundener Cluster
sname=$(basename "$0")
app="mikrok8s/install/${sname}"
pf=\$"Revision: "
sf=" "\$
fr="\$Revision: 1285 $"
revision=${fr#*"$pf"}
revision=${revision%"$sf"*}
xd=(`date '+%Y-%m-%d'`)
wd="${HOME}/copy/${app}/${xd}/r${revision}"
id="/opt/cluster/${app}/${xd}/r${revision}"
rm -f -R ${wd}
mkdir -p ${wd}
#
# Zu diesem Zeitpunkt sollte es eine Default-Storage-Class geben, wo das abgelegt wird.
ansible pc1 -m shell -a 'microk8s enable registry:size=40Gi'
ansible pc -m shell -a 'microk8s status --wait-ready'
#
# Adaptieren der Services
#
cat < ${wd}/do_registry.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
# \$Date: 2021-11-23 21:37:19 +0100 (Di, 23. Nov 2021) $
# \$Revision: 1285 $
# \$Author: alfred $
# \$HeadURL: https://monitoring.slainte.at/svn/slainte/trunk/k8s/k8s/K13_registry.sh $
# \$Id: K13_registry.sh 1285 2021-11-23 20:37:19Z alfred $
#
# Ändern des Services auf Loadbalancer
#
#shopt -o -s errexit #—Terminates the shell script if a command returns an error code.
shopt -o -s xtrace #—Displays each command before it’s executed.
shopt -o -s nounset #-No Variables without definition
# registry - 192.168.0.213
microk8s kubectl -n container-registry get service registry -o yaml > ${id}/registry-svc.yaml
sed 's/NodePort/LoadBalancer/' ${id}/registry-svc.yaml > ${id}/new-registry-svc.yaml
microk8s kubectl apply -f ${id}/new-registry-svc.yaml --validate=false
EOF
#
chmod 755 ${wd}/do_registry.sh
ansible pc1 -m shell -a ${id}'/do_registry.sh ' > ${wd}'/do_registry.log'
#
cat < ${wd}/do_nodes.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
# \$Date: 2021-11-23 21:37:19 +0100 (Di, 23. Nov 2021) $
# \$Revision: 1285 $
# \$Author: alfred $
# \$HeadURL: https://monitoring.slainte.at/svn/slainte/trunk/k8s/k8s/K13_registry.sh $
# \$Id: K13_registry.sh 1285 2021-11-23 20:37:19Z alfred $
#
# Eintragen der Nodes in die hosts-Datei
#
#shopt -o -s errexit #—Terminates the shell script if a command returns an error code.
shopt -o -s xtrace #—Displays each command before it’s executed.
shopt -o -s nounset #-No Variables without definition
sudo sed --in-place '/docker.registry/d' /etc/hosts
microk8s kubectl -n container-registry get service registry -o yaml > ${id}/nodes-registry-svc.yaml
ip=\$(cat ${id}/nodes-registry-svc.yaml | grep -i " ip: " | awk '{print \$3 }')
text="\${ip} docker.registry"
sudo sed -i "$ a \${text}" /etc/hosts
#
EOF
#
chmod 755 ${wd}/do_nodes.sh
ansible pc -m shell -a ${id}'/do_nodes.sh '
#
# Und jetzt die Repository-Info
#
cat < ${wd}/do_docker.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
# \$Date: 2021-11-23 21:37:19 +0100 (Di, 23. Nov 2021) $
# \$Revision: 1285 $
# \$Author: alfred $
# \$HeadURL: https://monitoring.slainte.at/svn/slainte/trunk/k8s/k8s/K13_registry.sh $
# \$Id: K13_registry.sh 1285 2021-11-23 20:37:19Z alfred $
Читать дальше


 Abbildung 7: Registry Clusterdisk
Abbildung 7: Registry Clusterdisk