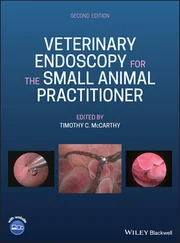
Figure 6.23 Alpha‐loop. One of the most common types of sigmoid loop formation is the alpha‐loop. This can be reduced with clockwise torque of the scope shaft as it is slowly pulled back. Once the loop is reduced, the scope shaft is again straight and can be readily advanced again.
(Copyrighted and used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.)
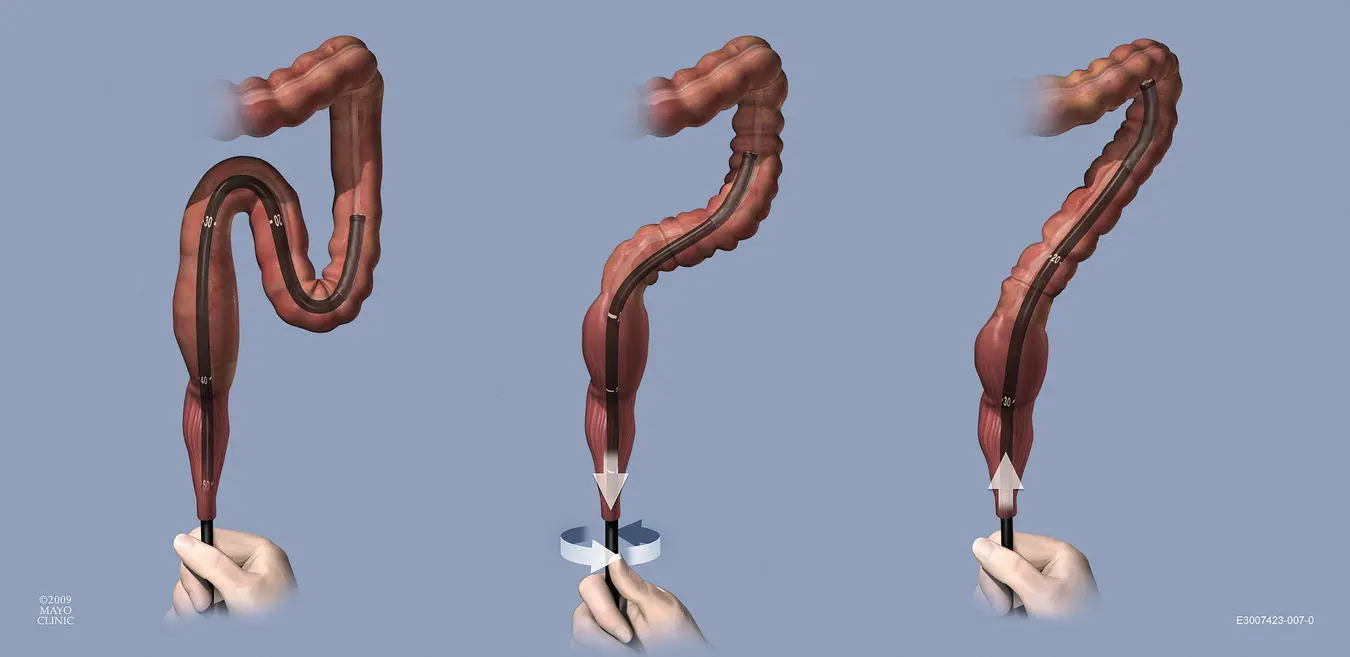
Figure 6.24 N‐loop. The N‐loop is also a common type of loop formation in the sigmoid and can also be reduced with clockwise torque and slow withdrawal like the alpha‐loop.
(Copyrighted and used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.)
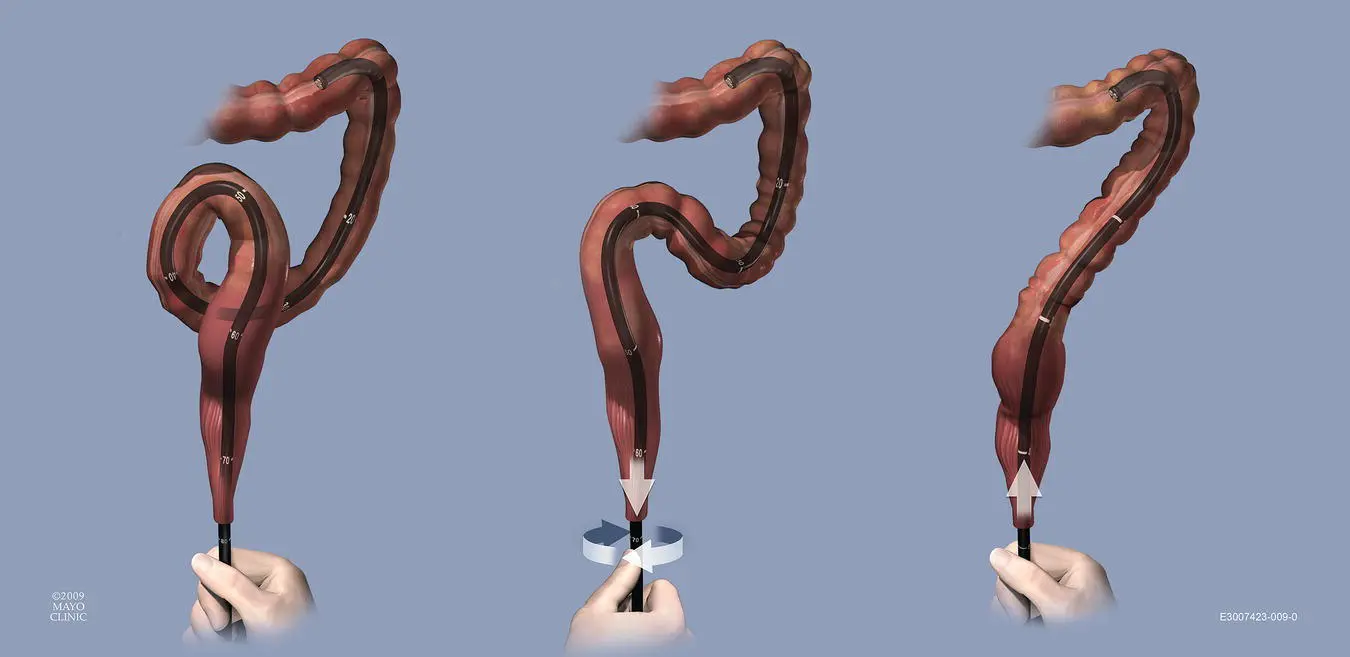
Figure 6.25 Reverse alpha‐loop. A reverse alpha‐loop follows a similar configuration as an alpha‐loop; however, the loop passes posteriorly to the scope shaft. Attempts at clockwise torque of the scope shaft will typically result in tightening of this loop and a sensation of increasing resistance to torque attempts by the endoscopists. Instead, counterclockwise torque and withdrawal is needed to reduce this type of loop.
(Copyrighted and used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.)
In cases such as this, attempts at counterclockwise torque during scope withdrawal may result in successful loop reduction. Other clues that the direction of required torque should be reversed are if one experiences increasing resistance to scope shaft rotation during torque attempts, or if the tip of the scope moves backward with the torque maneuver. In general, the correct direction of torque should result in a sensation of decreasing resistance to shaft rotation and modest scope tip advancement. Once a loop is reduced and the scope is straight, the torque that was used in the reduction can be undone. If the scope is straight, this should not result in any reproduction of the spiral but rather simply rotate the entire shaft of the scope back to a comfortable position. Some scopes are equipped with a variable stiffness feature that is controlled by a dial at the base of the handle. If this feature is available, increasing the stiffness of the scope, now that the loops are removed, can help prevent the reformation of these loops as the scope is advanced. This increased stiffness should be removed during subsequent attempts at loop reduction and reengaged when pushing forward. External pressure can also help prevent the reformation of loops and will be discussed below.
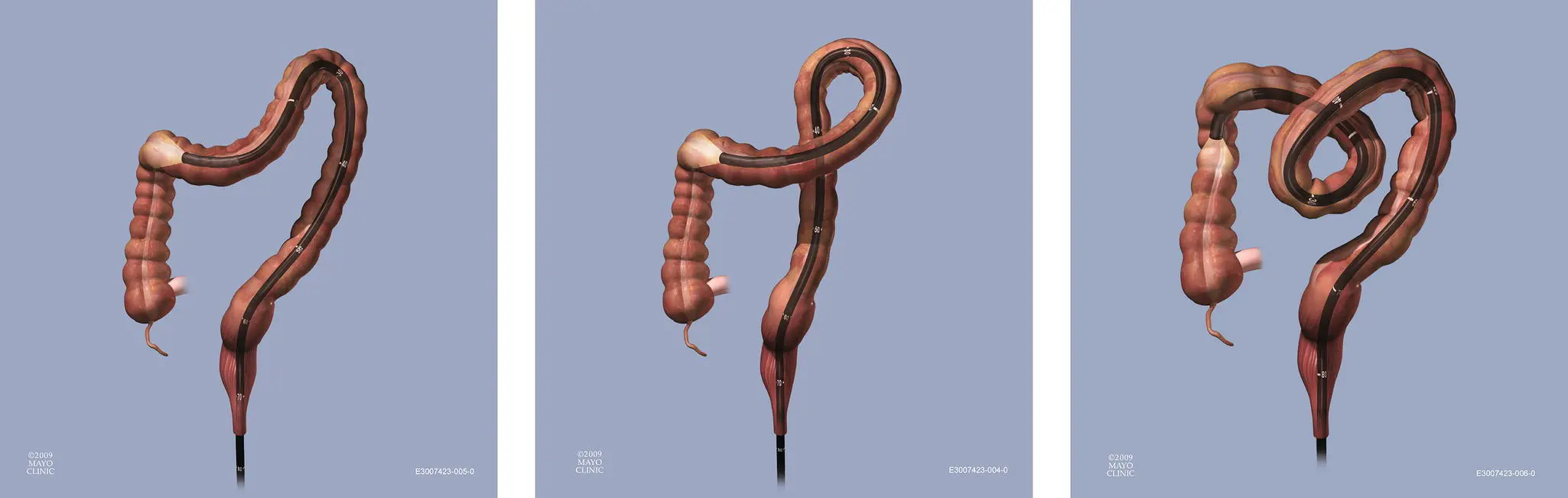
Figure 6.26 Transverse colon loop. Like the sigmoid, the transverse colon is also typically very mobile and can result in an assortment of loops. Reduction techniques vary but often require a combination of torque with slow shaft withdrawal. The direction of torque required will depend on the nature of the loop.
(Copyrighted and used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.)
 The other mobile section of the colon, the transverse colon, also frequently requires loop reduction. Looping here is mainly caused by redundancy of this section of the colon looping down, resulting in multiple changes in the force vector of the scope. The reduction technique is similar to loop reduction in the sigmoid. If possible, the flexible tip of the scope should be advanced around the hepatic flexure and hooked around this turn by holding the scope dials in place. With appropriate torque and withdrawal, the transverse colon will be straightened out. The scope tip may advance considerably down the right colon during this maneuver ( Figure 6.26) (Video 6.8). The direction of torque here can vary, however, like the sigmoid; the correct direction of torque should result in a sensation of decreasing resistance and modest scope tip advancement.
The other mobile section of the colon, the transverse colon, also frequently requires loop reduction. Looping here is mainly caused by redundancy of this section of the colon looping down, resulting in multiple changes in the force vector of the scope. The reduction technique is similar to loop reduction in the sigmoid. If possible, the flexible tip of the scope should be advanced around the hepatic flexure and hooked around this turn by holding the scope dials in place. With appropriate torque and withdrawal, the transverse colon will be straightened out. The scope tip may advance considerably down the right colon during this maneuver ( Figure 6.26) (Video 6.8). The direction of torque here can vary, however, like the sigmoid; the correct direction of torque should result in a sensation of decreasing resistance and modest scope tip advancement.
 Acute turns can be encountered predominately in the sigmoid colon and flexures but can occur in any colon segment. These pose a significant problem to early trainees because they often cause the fellow to develop significant loops of the scope shaft as well as overinflation of the colon as they struggle to round the turn. This overinflation can lead to increasing the acuity of the angulation. The difficulty by trainees is predominately due to incorrect technique of overusing the dials to accomplish these turns. Attempting to use the dials to steer around turns results in acute angulation of the scope shaft at the junction between the steerable tip and the less flexible scope shaft. With this acute bend in the scope, the force vector with advancement will be directed along the scope shaft at the outside wall of the turn rather than where the scope tip is pointing ( Figure 6.27a). This resistance to scope advancement will be transmitted back along the scope shaft to the endoscopist's hand or to an area of mobile colon where a loop will develop. In acute turns such as these, the one‐handed technique of using torque as the primary means of opening up the fold of a turn often results in less acute angulation of the scope tip and avoidance of this problem. This is accomplished by advancing the scope tip just beyond the fold on the inside portion of the acute turn. Up or down defection is used just enough to begin hooking the turn. The scope is then gently pulled back just keeping the scope tip off of the wall of the outside turn while just enough deflection or torque is used to keep the scope hooked around the fold on the inside of the turn ( Figure 6.27b) (Video 6.9) . This hooking and slight withdrawal maneuver pulls this first (inside turn) fold out of the way until the lumen beyond the turn can be visualized ( Figure 6.27c). Now with scope shaft still relatively straight, the force vector from pushing will translate directly into scope tip advancement.
Acute turns can be encountered predominately in the sigmoid colon and flexures but can occur in any colon segment. These pose a significant problem to early trainees because they often cause the fellow to develop significant loops of the scope shaft as well as overinflation of the colon as they struggle to round the turn. This overinflation can lead to increasing the acuity of the angulation. The difficulty by trainees is predominately due to incorrect technique of overusing the dials to accomplish these turns. Attempting to use the dials to steer around turns results in acute angulation of the scope shaft at the junction between the steerable tip and the less flexible scope shaft. With this acute bend in the scope, the force vector with advancement will be directed along the scope shaft at the outside wall of the turn rather than where the scope tip is pointing ( Figure 6.27a). This resistance to scope advancement will be transmitted back along the scope shaft to the endoscopist's hand or to an area of mobile colon where a loop will develop. In acute turns such as these, the one‐handed technique of using torque as the primary means of opening up the fold of a turn often results in less acute angulation of the scope tip and avoidance of this problem. This is accomplished by advancing the scope tip just beyond the fold on the inside portion of the acute turn. Up or down defection is used just enough to begin hooking the turn. The scope is then gently pulled back just keeping the scope tip off of the wall of the outside turn while just enough deflection or torque is used to keep the scope hooked around the fold on the inside of the turn ( Figure 6.27b) (Video 6.9) . This hooking and slight withdrawal maneuver pulls this first (inside turn) fold out of the way until the lumen beyond the turn can be visualized ( Figure 6.27c). Now with scope shaft still relatively straight, the force vector from pushing will translate directly into scope tip advancement.
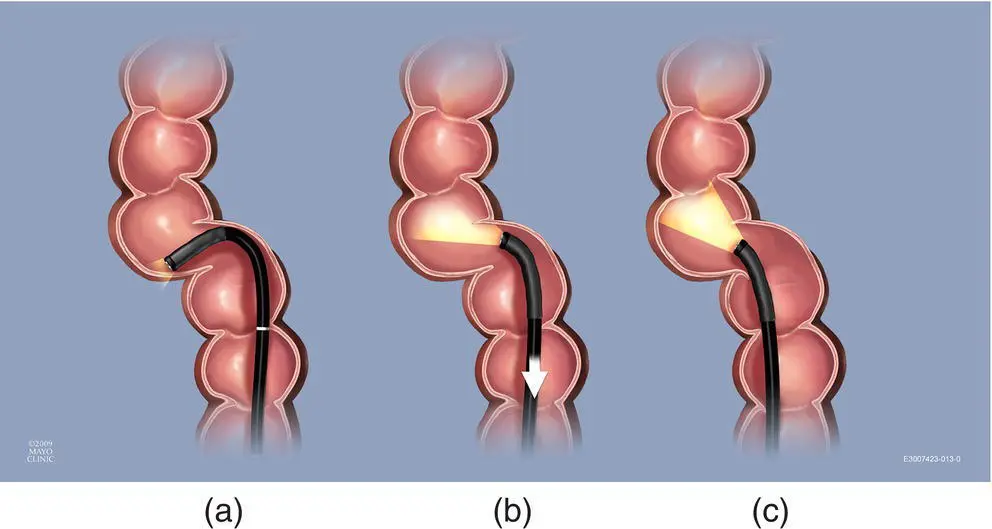
Figure 6.27 Acute turn. When attempting to navigate an acute turn, novices will often rely on excessive use of the dials, resulting in the scope tip flexing greater than 90° around the turn and in poor position to be advanced (a). Correct technique involves passing the fold on the inside of the turn and gently flexing the scope tip just enough to hook the fold (b). The scope shaft is then slowly pulled back, pulling the inside fold back until the lumen can be seen past the next fold (c). This leaves the scope in better position to be advanced once the turn is opened.
(Copyrighted and used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.)
With less acute turns, torque alone, without hooking and pulling, can often push the inside fold out of the way. Again the scope tip is advanced beyond the first fold and the scope is then torqued into the turn while keeping the scope tip straight. This torque pushes the fold aside until lumen beyond it is seen and the straight scope can then be readily advanced ( Figure 6.28). Often these techniques are done over and over in opposite directions in the sigmoid colon until the descending colon is reached. An adult colonoscope is preferable with this technique as the added stiffness allows greater ability to push folds aside with torque. This technique is difficult when the sigmoid or area of acute turn is fixed in position due to adhesions. In instances like this, a pediatric scope and two‐handed dial technique may be a more effective method to pass a turn. Endoscopists tend to favor one technique or scope type over another, but experienced endoscopists must master all techniques and equipment to accommodate any type of colonic anatomy.
Читать дальше





 The other mobile section of the colon, the transverse colon, also frequently requires loop reduction. Looping here is mainly caused by redundancy of this section of the colon looping down, resulting in multiple changes in the force vector of the scope. The reduction technique is similar to loop reduction in the sigmoid. If possible, the flexible tip of the scope should be advanced around the hepatic flexure and hooked around this turn by holding the scope dials in place. With appropriate torque and withdrawal, the transverse colon will be straightened out. The scope tip may advance considerably down the right colon during this maneuver ( Figure 6.26) (Video 6.8). The direction of torque here can vary, however, like the sigmoid; the correct direction of torque should result in a sensation of decreasing resistance and modest scope tip advancement.
The other mobile section of the colon, the transverse colon, also frequently requires loop reduction. Looping here is mainly caused by redundancy of this section of the colon looping down, resulting in multiple changes in the force vector of the scope. The reduction technique is similar to loop reduction in the sigmoid. If possible, the flexible tip of the scope should be advanced around the hepatic flexure and hooked around this turn by holding the scope dials in place. With appropriate torque and withdrawal, the transverse colon will be straightened out. The scope tip may advance considerably down the right colon during this maneuver ( Figure 6.26) (Video 6.8). The direction of torque here can vary, however, like the sigmoid; the correct direction of torque should result in a sensation of decreasing resistance and modest scope tip advancement.