Keywords : Indian agriculture, Artificial Intelligence, farmers
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad field of computer science that focuses on creating intelligent machines that can accomplish activities that would normally need human intelligence. Although AI is a multidisciplinary field with many methodologies, advances in machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) [4] are causing a paradigm shift in nearly every sector of the IT industry.
One of the oldest occupations in the world is farming and agriculture. It has a significant impact on the economy. Climate variations also play an influence in the agriculture lifecycle. Climate change is a result of increasing deforestation and pollution, making it difficult for farmers to make judgments about which crop to harvest. Nutrient insufficiency can also cause crops to be of poor quality [37]. Weed control has a significant impact and can lead to greater production costs. The above traditional farming can be replaced by using modern technology with AI.
1.2 Different Forms of AI
Agriculture is extremely important, and it is the primary source of income for almost 58% of India’s population [2]. However, it lacks support and suffers from a variety of factors, such as groundwater depletion, erratic monsoons, droughts, plant diseases, and so on. To detect the relationship between influencing factors with crop yield and quality, a variety of tools and approaches have been identified. The impact of recent technological advancements in the field of AI is significant. Recently, large investors have begun to capitalize on the promise of these technologies for the benefit of Indian agriculture. Smart farming and precision agriculture (PA) are ground-breaking science and technological applications for agriculture growth. Farmers and other agricultural decision makers are increasingly using AI-based modeling as a decision tool to increase production efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence is silently entering Indian agriculture and impacting society to a greater extent. There are three forms of AI, namely Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), and Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) [3] as shown in Figure 1.1Artificial Narrow Intelligence as the name suggests uses computer programming to do a specific task. Artificial General Intelligence refers to a machine that can think like a human and perform huge tasks. Artificial Super Intelligence is designed to think beyond humans. Artificial Narrow Intelligence is mainly used in agriculture to do some specific tasks, such as identification of diseases in leaf, optimization in irrigation, the optimal moisture content in crops, and so on, using AI techniques. The different forms of AI are shown in Figure 1.1.
Figure 1.1 Different forms of AI [3].
1.3 Different Technologies in AI
There are many subfields, such as ML, Artificial Neural Network (ANN), and DL, as shown in Figure 1.2. The distinguishing features of these subfields are shown in Table 1.1.
Figure 1.2 AI versus ML versus ANN versus DL.
Table 1.1 Distinguishing feature of subfields of AI.
| AI |
AI is a technology that allows us to build intelligent systems that mimic human intelligence. |
| ML |
ML is an AI discipline that allows machines to learn from previous data or experiences without having to be explicitly programmed. |
| ANN |
ANN depends on algorithms resembling the human brain. |
| DL |
DL algorithms automatically build a hierarchy of data representations using the low- and high-level features. |
A subset of AI focuses on algorithm development by learning from experience and helps in the improvement of decision making with greater accuracy. The categories and the corresponding tasks are shown in Figure 1.3. Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement are the three main learning paradigms. Supervised is the most prevalent training paradigm for developing ML models for both classification and regression tasks [27]. It finds the relationship between the input and target variables. Some of the supervised learning algorithms are support vector machine (SVM), logistic regression, Decision Tree (DT), random forest, and so on. Unsupervised learning is often used for clustering and segmentation tasks. This method does not require any target variable to group the input data sets. Some of the examples are K-means, hierarchical, density, grid clustering, and so on. Reinforcement learning corresponds to responding to the environment and deciding the right action to complete the assignment with maximum reward in a given application. It finds its applications in a real-time environment.
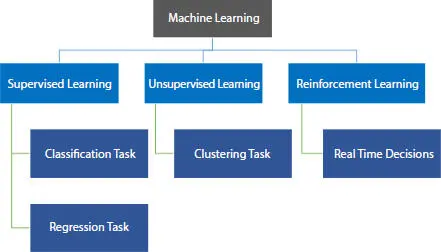
Figure 1.3 Types of machine learning.

Figure 1.4 Generic methodology in building a model using machine learning algorithms.
In ML, training is performed with a huge amount of data to get accurate decisions or predictions. The general steps involved in building an ML model are shown in Figure 1.4.
1.3.1.1 Data Pre-processing
It is a process of converting raw data into a usable and efficient format.
1.3.1.2 Feature Extraction
Before training a model, most applications need first transforming the data into a new representation. Applying pre-processing modifications to input data before presenting it to a network is almost always helpful, and the choice of pre-processing will be one of the most important variables in determining the final system’s performance. The reduction of the dimensionality of the input data is another key method in which network performance can be enhanced, sometimes dramatically. To produce inputs for the network, dimensionality reductions entail creating linear or nonlinear combinations of the original variables. Feature extraction is the process of creating such input combinations, which are frequently referred to as features. The main motivation for dimensionality reduction is to help mitigate the worst impacts of high dimensionality.
1.3.1.3 Working With Data Sets
The most popular method is to split the original data into two or more data sets at random or using statistical approaches. A portion of the data is used to train the model, whereas a second subset is used to assess the model’s accuracy. It is vital to remember that while in training mode, the model never sees the test data. That is, it never uses the test data to learn or alter its weights. The training data is a set of data that represent the data that the ML will consume to answer the problem it was created to tackle. In certain circumstances, the training data have been labeled—that is, it has been “tagged” with features and classification labels that the model will need to recognize. The model will have to extract such features and group them based on their similarity if the data is unlabeled. To improve the generalization capability of the model, the data set can be divided into three sets according to their standard deviation: training sets, validation sets, and testing sets. The validation set is used to verify the network’s performance during the training phase, which in turn is useful to determine the best network setup and related parameters. Furthermore, a validation error is useful to avoid overfitting by determining the ideal point to stop the learning process.
Читать дальше
















