2.2.2 Components of Neural Networks
The human brain on an average contains 86 billion neurons approximately [10]. A biological neuron consists of thin fibers, and those are known as dendrites. Dendrites receive incoming signals. The cell body, “soma” responsible for processing input signals and to decide firing/nonfiring of neurons to output signal. Processed signals output from neurons received by “axon” and passes it to relevant cells.
Artificial neuron called also as “perceptron” is a fundamental component of neural network, which is a mathematical function of a real-world problem with binary outputs. The neurons are systematically organized into two or more than two layers. One layer of neurons are connected to immediately preceding neurons layer and immediately succeeding neuron layer. The first (input) layer receives the external data, and the last (output) layer ultimately produces result. Each artificial neuron receives input from input layer, process the weights and sums and pass the sum through a nonlinear mathematical relation to produce output. In between them are one or more hidden layers ( Figure 2.1). Weights are multiples of respective input values arranged in an array. To achieve a final value of prediction, bias is added to the weighted sum. The size of the correction values to adjust for errors by the model is known as a learning rate. Activation function decides whether or not a neuron is fired [11]. The neural network uses previous step output data values for the network training and minimizes the error between observed and estimated. The process readjusts the weights at each interaction of neuron. The training will stop after reaching the optimal learning rate [12, 13]. The higher learning rate reduces the time for training, and ultimate accuracy is low. Lower learning rate takes longer time and higher accuracy.
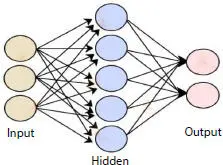
Figure 2.1 Architecture of artificial neural network (original figure).
2.2.3 Types and Suitability of Neural Networks
The artificial neural networks are usually selected based on the mathematical functions and output parameters. Among the different types of artificial neural networks, some of the most important kinds of the neural networks are discussed in this section.
A feed-forward neural network (FFNN) is an artificial neural network and is one of the simple type of neural network. In which, the input data travels in only one direction no loop or cycle formation. In an FFNN, every neuron (perceptron) in one layer is connected with each node in the immediate layer. As a result, each and every node is fully connected. This systematic arrangement of FFNN generates output by output layer. The number of hidden layers may arrange in between input and output layers and do not have a connection with the outer environment. These neural networks may or may not have a hidden layer. Common applications are pattern recognition, speech recognition, data compression, computer vision, and so on. If an FFN network uses more than one hidden layer, it is called a deep feed-forward network. By adding more hidden layers, overfitting will be reduced and improved generalization. The synaptic operation order in a hidden neuron, the ANNs were classified as first order, second, third, or higher order [14]. The back loops are absent in the FFN network. To reduce the error value in prediction, the back propagation algorithm may be used. The weights between the input hidden and output layers can be adjusted by using back propagation algorithm through learning rate and momentum. Then, the error value is back propagated from output layer to the input layer [15]. Back propagation algorithm was adopting widely for forecasting problems with the networks [16, 17]. Radial Basis Network (RBN)s behave as feed forward networks using other functions (radial basis function) to activate the network. Radial Basis Networks determine the gap between the generated output and target output. The logistic (sigmoid) function produces output value between 0 and 1. An RBN cannot be used for continuous value. Radial basis function considers the distance from the center to a point. The main advantage of RB neural networks is universal approximation and faster learning rate.
Recurrent neural network (RNN) uses previous information in current iterations. The principle of the RNN is keeping output and feeding the output back to input layer to help in estimating the output of the layer. In this type of neural network, hidden layers every neuron receives an input with a specific time delay. Recurrent neural network is required more time with low computational speed. These types can be used in time series anomaly detection, speech recognition, speech synthesis, and robot control. Long-/ short-term memory networks (LSTM) use a memory cell that processes data in RNNs. Gate recurrent units (GRUs) are different from LSTMs with similar models and produce equally better results. Extreme learning machines (ELMs) determine the output weights by choosing hidden nodes randomly. Extreme learning machine networks learn the output weights in only one step, and assigned weights are never updated. These algorithms work faster than the other general NN algorithms.
Convolution neural networks (CNN) are primarily used for image classification, image clustering, time series forecasting and object recognition. Deconvolutional networks (DCN) are CNNs that work in anopposite process. The major drawbacks of conventional neural networks are low learning rate and all the parameters tuning iteratively. In Hopfield network (HN), every neuron in network is directly connected with other neurons. The HNs are used to save memories and patterns and also applied in optimization problems. A Kohonen neural network (KN) also known as self-organizing maps is an unsupervised algorithm. This is very useful for multidimensional scattered data. It gives output in one or two dimensions only, so it is treated as a method of dimensionality reduction. This self-organizing process has different phases. A small weight is initialized to each neuron. In the second phase, the close neuron is the “winning neuron,” and the other neurons are connected to the winning neuron. The KN networks use more competitive learning than error correction learning.
2.3 Application of Neural Networks in Agriculture
2.3.1 Potential Applications of Neural Networks in Agriculture
Various ANN techniques are suitable to use in agriculture. The widely accepted neural network includes radial basisfunction neural network (RBFNN), backpropagation neural network (BNN), convolutional neural network (CNN), recurrent neural network (RNN), and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) for different applications. These NNs are also used in combination with remote sensing classification, rice mapping [17, 18]. Rice mapping is done by combining MS Sentinel 2 and Sentinel 1 SAR band using the LSTM network and dynamic time warping distance approach [19]. Detailed crop classification and mapping is the area for high scope of NN application [20, 21]. A ANN-based model combining a CNN and generative adversarial network (GAN) is used for crop classification with advantages of few data requirement and high flexibility [22]. A CNN-based approach with fused MODIS NDVI data, multitemporal Landsat, and synthetic phenological variable classifies a land accurately into small patches [23]. The methodology for crop classification using deep learning models was framed [24]. They proposed CNN model from multiple Landsat and Sentinel-1 images. Cropland was classified by a LSTMRNN model using Landsat imagery with high accuracy [25]. Wheat production was forecasted and compared the performance of different training methods using an ANN model [26].
Читать дальше













