afterward?
List regions?
Label them on a map?
Describe geographical differences?
There are so many choices!
Depending on what you want students to be able to DO at the end of a lesson, it will help us choose the right action verb for writing an instructional objective.
Instructional objectives often will depend on the overall curriculum plan and the level of the learners, but it also involves the teacher’s influence in designing a lesson.
Are you fed up with using the same old methods to introduce your lesson topic?

Do you ever have trouble writing learning objectives for your lessons? Often we know what we want our students to learn, but more importantly, we need to decide what we want our students to be able to do after a particular lesson or class.
The ABCD method of writing objectives is an excellent way to structure instructional objectives. In this method, «A» is for the audience, «B» is for behavior, «C» for conditions, and «D» is for the degree of mastery needed.
Example: -«Given a sentence written in the past or present tense, the student will be able to re-write the sentence in future tense with no errors in tense or tense contradiction (i.e., I will see her yesterday.).» The key here is to use verbs that indicate a clearly observable and measurable action. Appropriate action verbs for the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains are listed below.
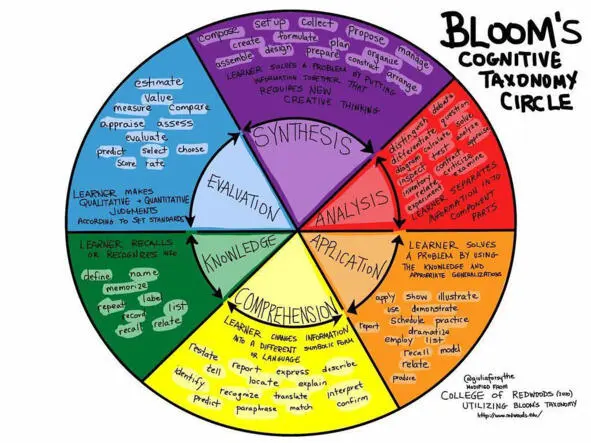
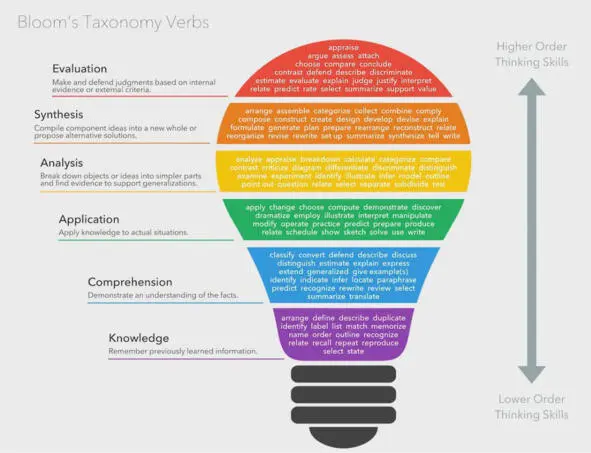
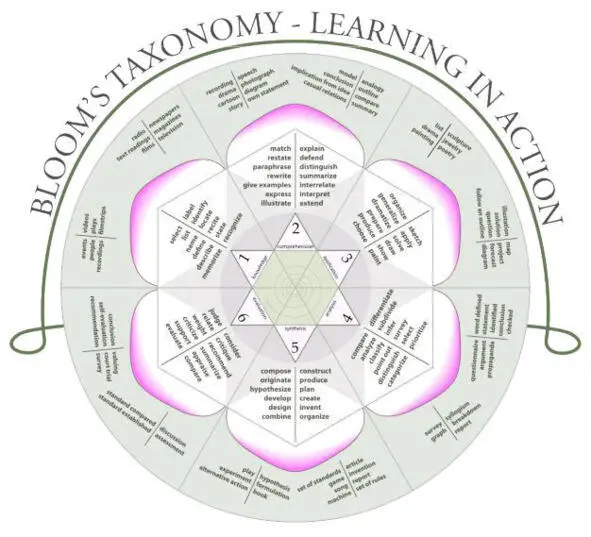
Bloom’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive DomainBloom’s taxonomy of cognitive learning, originated by Benjamin Bloom and collaborators in the 1950s, describes several categories of cognitive learning.
This taxonomy was revised in 2001 by Anderson and Krathwohlto change the category names from nouns to verbs, and to switch the Evaluation and Synthesis levels in the hierarchy.

Many people also call the analysis, synthesis/create, and evaluation categories «problem-solving.»
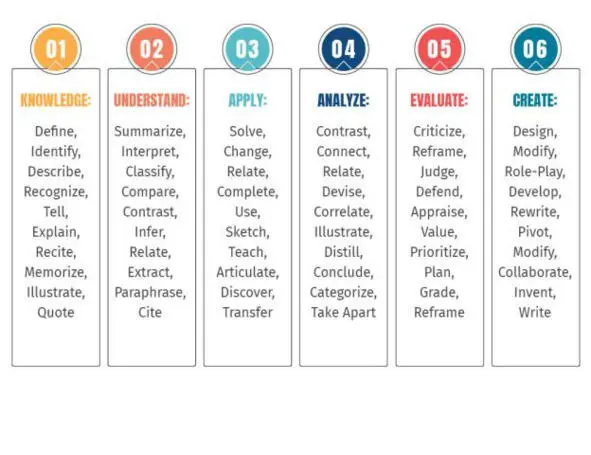
ACTION VERBS APPROPRIATE FOR EACH LEVEL OF
BLOOM’S/ANDERSON & KRATHWOHL’S TAXONOMY (Cognitive
Domain)
Remember:Define Identify List Name Recall Recognize Record Relate Repeat Underline
Understand:Choose Cite examples of Demonstrate use of Describe Determine
Differentiate between Discriminate Discuss Explain Express Give in own words Identify
Interpret Locate Pick Report Restate Review Recognize Select Tell Translate Respond
Practice Simulates
Apply:Apply Demonstrate Dramatize Employ Generalize Illustrate
Interpret Operate Operationalize Practice Relate Schedule Shop Use Utilize Initiate
Analyze:Analyze Appraise Calculate Categorize Compare Conclude Contrast Correlate Criticize
Deduce Debate Detect Determine Develop Diagram Differentiate Distinguish Draw
conclusions Estimate Evaluate Examine Experiment Identify Infer Inspect Inventory Predict
Question Relate Solve Test Diagnose
Evaluate:Appraise Assess Choose Compare Critique Estimate Evaluate Judge Measure Rate Revise Score Select Validate Value
– Lesson Design and Planning from scratch
– Create:Arrange Assemble Collect Compose Construct Create Design Develop Formulate Manage Modify Organize Plan Prepare Produce Propose Predict Reconstruct Set-up Synthesize Systematize Devise
Krathwohl and Bloom’s Taxonomyof the Affective Domain Krathwohl and Bloom’s 1964 taxonomy of the affective domain describes several categories of affective learning.
AFFECTIVE TAXONOMY Level Definition
Example
Receiving Being aware of or attending to something in the environment. Individual reads a book passage about civil rights. Responding Showing some new behaviors as a result of experience . Individual answers questions about the book, read another book by the same author, another book about civil rights, etc. Valuing Showing some definite involvement or commitment. The individual demonstrates this by voluntarily attending a lecture on civil rights. Organization Integrating a new value into one’s general set of values, giving it some ranking among one’s general priorities. The individual arranges a civil rights rally.
Characterization by Value Acting consistently with the new value . The individual is firmly committed to the value, perhaps becoming a civil rights leader
ACTION VERBS APPROPRIATE FOR EACH LEVEL OF KRATHWOHL & BLOOM’S TAXONOMY (Affective Domain)
ReceivingAccept Attend Develop Recognize RespondingComplete Comply Cooperate Discuss Examine Obey Respond Valuing Accept Defend Devote Pursue Seek OrganizationCodify Discriminate Display Order Organize Systematize Weigh Characterization by ValueInternalize Verify
Psychomotor Domain The following is a synthesis of the taxonomies of Simpson (1972), Dave (1970), and Harrow (1972).
ACTION VERBS APPROPRIATE FOR THE PSYCHOMOTOR TAXONOMYBend Calibrates Constructs Differentiate (by touch) Dismantles Displays Fastens Fixes Grasp Grinds Handle Heats Manipulates Measures Mends Mixes Operate Organizes Perform (skillfully) Reach Relax Shorten Sketches Stretch Write
– PSYCHOMOTOR TAXONOMY Level Definition Example Observing Active mental attending of a physical event.
– The learner watches a more experienced person. Other mental activity, such as reading may be a pert of the observation process.
– Imitating Attempted copying of a physical behavior. The first steps in learning a skill. The learner is observed and given direction and feedback on performance.
– Movement is not automatic or smooth.
– Practicing Trying a specific physical activity over and over. The skill is repeated over and over. The entire sequence is performed repeatedly.
– Movement is moving towards becoming automatic and smooth.
– Adapting Fine-tuning.
– Making minor adjustments in physical activity in order to perfect it. The skill is perfected.
Topics to Get Your Students Talking – And Topics to Avoid

You might not believe how many things there are to say about food, but you’ll be surprised. You can discuss their favorite and least favorite food (for lower-level classes), what they have and haven’t tried, the strangest thing they’ve tried, and what they can cook
Читать дальше




















