Write a program to read data from the terminal, then increase this data by one and send it back to the terminal. For example, if the user enters character “A,” then character “B” should be displayed on the terminal. Assume that a MAX232-type voltage level converter chip is converting the microcontroller signals to RS232 levels. Figure 4.23 shows the circuit diagram of this example.
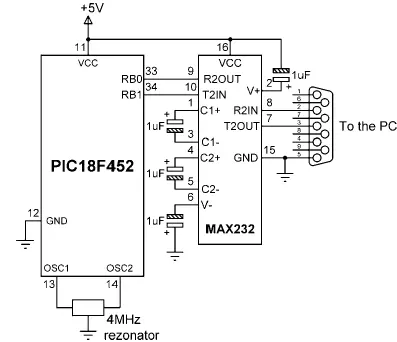
Figure 4.23: Circuit diagram of Example 4.13
Solution 4.13
The MAX232 chip receives the TX signal from pin RB1 of the microcontroller and converts it to RS232 levels. Comparably, the serial data received by the MAX232 chip is converted into microcontroller voltage levels and then sent to pin RB0. Note that correct operation of the MAX232 chip requires four capacitors to be connected to the chip.
The required program listing is shown in Figure 4.24 (program SERIAL.C). At the beginning of the program, function Soft_Uart_Init is called to configure the serial port. Then an endless loop is formed using a for statement. The Soft_Uart_Read function is called to read a character from the terminal. After reading a character, the data byte is incremented by one and then sent back to the terminal by calling function Soft_Uart_Write.
/********************************************************************
READING AND WRITING TO SERIAL PORT
==================================
In this program PORTB pins RB0 and RB1 are configured as serial RX and
TX pins respectively. The baud rate is set to 9600. A character is received
from a serial terminal, incremented by one and then sent back to the
terminal. Thus, if character "A" is entered on the keyboard, character "B"
will be displayed.
Programmer: Dogan Ibrahim
File: SERIAL.C
Date: May, 2007
**********************************************************************/
void main() {
unsigned char MyError, Temp;
Soft_Uart_Init(PORTB, 0, 1, 9600, 0); // Configure serial port
for (;;) // Endless loop
{
do {
Temp = Soft_Uart_Read(MyError); // Read a byte
} while (MyError);
Temp++; // Increment byte
Soft_Uart_Write(Temp); // Send the byte
}

Figure 4.24: Program listing of Example 4.13
4.3.4 Hardware USART Library
The universal synchronous asynchronous receiver transmitter (USART) hardware library contains a number of functions to transmit and receive serial data using the USART circuits built on the PIC microcontroller chips. Some PIC18F-series microcontrollers have only one USART (e.g., PIC18F452), while others have two USART circuits (e.g., PIC18F8520). Hardware USART has an advantage over software-implemented USART, in that higher baud rates are generally available and the microcontroller can perform other operations while data is sent to the USART.
The hardware USART library provides the following functions:
• Usart_Init
• Usart_Data_Ready
• Usart_Read
• Usart_Write
Usart_Init
The Usart_Init function initializes the hardware USART with the specified baud rate. This function should be called first, before any other USART functions. The only parameter required by this function is the baud rate. The following example call sets the baud rate to 9600:
Usart_Init(9600);
Usart_Data_Ready
The Usart_Data_Ready function can be called to check whether or not a data byte has been received by the USART. The function returns a 1 if data has been received and a 0 if no data has been received. The function has no parameters. The following code checks if a data byte has been received or not:
if (Usart_Data_Ready())
Usart_Read
The Usart_Read function is called to read a data byte from the USART. If data has not been received, a 0 is returned. Note that reading data from the USART is nonblocking (i.e., the function always returns whether or not the USART has received a data byte). The Usart_Read function should be called after calling the function Usart_Data_Ready to make sure that data is available at the USART. Usart_Read has no parameters. In the following example, USART is checked and if a data byte has been received it is copied to variable MyData :
char MyData;
if (Usart_Data_Read()) MyData = Usart_Read();
Usart_Write
The Usart_Write function sends a data byte to the USART, and thus a serial data is sent out of the USART. The data byte to be sent must be supplied as a parameter to the function. In the following example, character “A” is sent to the USART:
char Temp = 'A';
Usart_Write(Temp);
The following example illustrates how the hardware USART functions can be used in a program.
Example 4.14
The serial port of a PC (e.g., COM1) is connected to a PIC18F452 microcontroller, and terminal emulation software (e.g., HyperTerminal) is operated on the PC to use the serial port. The microcontroller’s hardware USART pins RC7 (USART receive pin, RX) and RC6 (USART transmit pin, TX) are connected to the PC via a MAX232-type RS232 voltage level converter chip. The required baud rate is 9600. Write a program to read data from the terminal, then increase this data by one and send it back to the terminal. For example, if the user enters character “A,” then character “B” should be displayed on the terminal. Figure 4.25 shows the circuit diagram of this example.
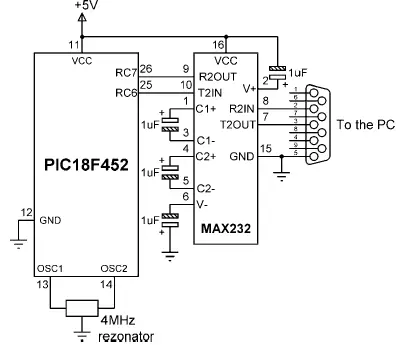
Figure 4.25: Circuit diagram of Example 4.14
Solution 4.14
The required program listing is shown in Figure 4.26 (program SERIAL2.C). At the beginning of the program, function Usart_Init is called to set the baud rate to 9600. Then an endless loop is formed using a for statement. The Usart_Data_Ready function is called to check whether a character is ready, and the character is read by calling function Usart_Read . After reading a character, the data byte is incremented by one and then sent back to the terminal by calling function Usart_Write .
/*******************************************************************
READING AND WRITING TO SERIAL PORT VIA USART
============================================
In this program a PIC18F452 microcontroller is used and USART I/O pins are
connected to a terminal through a MAX232 voltage converter chip. The baud
rate is set to 9600. A character is received from a serial terminal,
incremented by one and then sent back to the terminal. Thus, if character “A”
is entered on the keyboard, character “B” will be displayed.
Programmer: Dogan Ibrahim
File: SERIAL2.C
Date: May, 2007
*********************************************************************/
void main() {
unsigned char MyError, Temp;
Читать дальше















