Many of these features are especially useful for embedded applications. It is not uncommon for embedded products to require portable or battery-powered configurations. The Pentium M has enjoyed popularity in this application space because of its power- and thermal-management features.
The Freescale MPC7448 contains what is referred to as a fourth-generation PowerPC core, commonly called G4. [18] 32-bit and 64-bit refer to the native width of the processor's main facilities, such as its execution units, register file and address bus.
This high-performance 32-bit processor is commonly found in networking and telecommunications applications. Several companies manufacture blades that conform to an industry-standard platform specification, including this and other similar stand-alone Freescale processors. We examine these platforms in Section 3.3, "Hardware Platforms," later in this chapter.
The MPC7448 has enjoyed popularity in a wide variety of signal-processing and networking applications because of the advanced feature set highlighted here:
• Operating clock rates in excess of 1.5GHz
• 1MB onboard L2 cache
• Advanced power-management capabilities, including multiple sleep modes
• Advanced AltiVec vector-execution unit
• Voltage scaling for reduced-power configurations
The MPC7448 contains a Freescale technology called AltiVec to enable very fast algorithmic computations and other data-crunching applications. The AltiVec unit consists of a register file containing 32 very wide (128-bit) registers. Each value within one of these AltiVec registers can be considered a vector of multiple elements. AltiVec defines a set of instructions to manipulate this vector data effectively in parallel with core CPU instruction processing. AltiVec operations include such computations as sum-across, multiply-sum, simultaneous data distribute (store), and data gather (load) instructions.
Programmers have used the AltiVec hardware to enable very fast software computations commonly found in signal-processing and network elements. Examples include fast Fourier Transform, digital signal processing such as filtering, MPEG video coding and encoding, and fast generation of encryption protocols such as DES, MD5, and SHA1.
Other chips in the Freescale lineup of stand-alone processors include the MPC7410, MPC7445, MPC7447, MPC745x, and MPC7xx family.
3.1.4. Companion Chipsets
Stand-alone processors such as those just described require support logic to connect to and enable external peripheral devices such as main system memory (DRAM), ROM or Flash memory, system busses such as PCI, and other peripherals, such as keyboard controllers, serial ports, IDE interfaces, and the like. This support logic is often accomplished by companion chipsets , which may even be purpose-designed specifically for a family of processors.
For example, the Pentium M is supported by one such chipset, called the 855GM. The 855GM chipset is the primary interface to graphics and memorythus, the suffix-GM. The 855GM has been optimized as a companion to the Pentium M. Figure 3-1 illustrates the relationship between the processor and chipsets in this type of hardware design.
Figure 3-1. Processor/chipset relationship
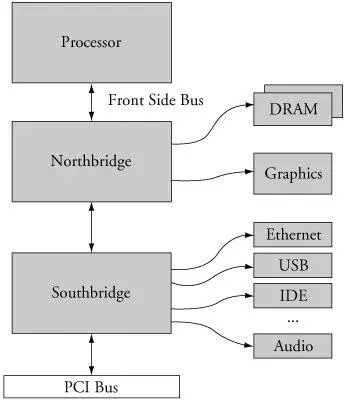
Note the terminology that has become common for describing these chipsets. The Intel 855GM is an example of what is commonly referred to as a northbridge chip because it is directly connected to the processor's high-speed front side bus (FSB). Another companion chip that provides I/O and PCI bus connectivity is similarly referred to as the southbridge chip because of its position in the architecture. The southbridge chip (actually, an I/O controller) in these hardware architectures is responsible for providing interfaces such as those shown in Figure 3-1, including Ethernet, USB, IDE, audio, keyboard, and mouse controllers.
On the PowerPC side, the Tundra Tsi110 Host Bridge for PowerPC is an example of a chipset that supports the stand-alone PowerPC processors. The Tsi110 supports several interface functions for many common stand-alone PowerPC processors. The Tundra chip supports the Freescale MPC74xx and the IBM PPC 750xx family of processors. The Tundra chip can be used by these processors to provide direct interfaces to the following peripherals:
• DDR DRAM, integrated memory controller
• Ethernet (the Tundra provides four gigabit Ethernet ports)
• PCI Express (supports 2 PCI Express ports)
• PCI/X (PCI 2.3, PCI-X, and Compact PCI [cPCI])
• Serial ports
• I2C
• Programmable interrupt controller
• Parallel port
Many manufacturers of chipsets exist, including VIA Technologies, Marvell, Tundra, nVidia, Intel, and others. Marvell and Tundra primarily serve the PowerPC market, whereas the others specialize in Intel architectures. Hardware designs based on one of the many stand-alone processors, such as Intel x86, IBM, or Freescale PowerPC, need to have a companion chipset to interface to system devices.
One of the advantages of Linux as an embedded OS is rapid support of new chipsets. Linux currently has support for those chipsets mentioned here, as well as many others. Consult the Linux source code and configuration utility for information on your chosen chipset.
3.2. Integrated Processors: Systems on Chip
In the previous section, we highlighted stand-alone processors. Although they are used for many applications, including some high-horsepower processing engines, the vast majority of embedded systems employ some type of integrated processor, or system on chip (SOC). Literally scores, if not hundreds, exist to choose from. We examine a few from the industry leaders and look at some of the features that set each group apart. As in the section on stand-alone processors, we focus only on those integrated processors with strong Linux support.
Several major processor architectures exist, and each architecture has examples of integrated SOCs. PowerPC has been a traditional leader in many networking- and telecommunications-related embedded applications, while MIPS might have the market lead in lower-end consumer-grade equipment. [19] These are the author's own opinions based on market observation and not based on any scientific data.
ARM is used in many cellular phones. These represent the major architectures in widespread use in embedded Linux systems. However, as you will see in Chapter 4, "The Linux Kernel: A Different Perspective," Linux supports more than 20 different hardware architectures today.
PowerPC is a Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) architecture jointly designed by engineers from Apple, IBM, and Motorola's semiconductor division (now an independent entity spun off as Freescale Semiconductor). Many good documents describe the PowerPC architecture in great detail. Consult the " Suggestions for Additional Reading " at the end of this chapter as a starting point.
PowerPC processors have found their way into embedded products of every description. From automotive, consumer, and networking applications to the largest data and telecommunications switches, PowerPC is one of the most popular architectures for embedded applications. Because of this popularity, there exists a large array of hardware and software solutions from numerous manufacturers targeted at PowerPC.
Some of the examples later in this book are based on the AMCC PowerPC 440EP Embedded Processor. The 440EP is a popular integrated processor found in many networking and communications products. The following list highlights some of the features of the 440EP:
Читать дальше













