9.5.1.1. Fedora Documentation
The Fedora Docs project ( http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/DocsProject ) produces release notes, installation and configuration guides, and other documentation, and is always looking for writers, editors, and readers willing to provide feedback. Other members of the Fedora Docs team develop the tool chain used to manage the documentation and transform it into various forms.
9.5.1.2. Fedora Translation
Since Fedora software is used globally, messages and controls within the software, documentation, and web sites all require translation into many languages. The Fedora Translation project exists to do this translation and to develop and refine the tools necessary to manage translated text. The Fedora Translation web site is found at http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/L10N .
L10N in the Translation URI stands for localization (translation into specific languages). I18N stands for internationalization (technologies that enable use of software in multiple locales). The numbers in the abbreviations refer to the quantity of letters removed.
If you have RPM packages that aren't included in Fedora Core or Fedora Extras, you can become a Fedora Extras contributor and make those packages available to other Fedora users. The Fedora Extras project has set up strict standards and a rigorous review process to protect the quality of the Extras repository, so participating in this project requires a certain level of skill and commitment. To streamline the process, Fedora Extras uses a sponsorship process, which pairs experienced members with newcomers during their first package submission. The web site http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Extras/Contributors describes the process of becoming a Fedora Extras contributor.
9.5.2.1. ...Fedora-related projects that have sprung up outside of the official Fedora community?
There are a number of Fedora-related projects that are not part of the official Fedora project, and these projects are also staffed by volunteers:
Derivative distributions
There are over 60 Linux distributions derived from Fedora Linux, and yet others that are derived from Red Hat Enterprise Linux (Red Hat's enterprise Linux distribution, which shares a common root with Fedora). These distributions tailor Fedora to meet specific community, linguistic, or hardware requirements.
Other repositories
The Livna, ATrpms, and RPMforge repositories interoperate with the Fedora Core and Extras repositories (although not necessarily with each other).
The Fedora Unity project
Fedora Unity provides web sites with guides and technical notes on various Fedora-related issues. It also produces what it terms respins of the Fedora Core CDs and DVDs, incorporating updates released since the official Fedora Core release dates.
9.5.3. Where Can I Learn More?
The Fedora projects page: http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Projects/
Linux distributions derived from Fedora: http://distrowatch.com/dwres.php?resource=independence#fedora
External repositories: http://rpm.livna.org/ , http://atrpms.net/ , and http://rpmforge.net/
The Fedora Unity Project: http://fedoraunity.org/
Chapter 10. Advanced Installation
There are thousands of different computer configurations, and thousands of different ways in which computers are used. The Fedora installer, Anaconda, is up to the challenge: although the default installation procedure is straightforward, Anaconda can also perform automated installations, set up complex storage layouts involving RAID and LVM, handle different types of installation media and network installation servers, and provide a rescue mode for the recovery of disabled systems.
This chapter deals with these advanced installation features. It also looks at GParted, a partition resizing tool, and GRUB, the bootloader used by Fedora that can be extensively customized.
10.1. Resizing a Windows Partition
Many computers are sold with some version of Microsoft Windows preinstalled, claiming the entire disk. In order to install Fedora in a dual-boot configuration, it is necessary to reduce the size of the Windows partition to free up some space.
10.1.1. How Do I Do That?
Fedora does not provide a good tool for resizing Windows partitions. Fortunately, there is a very good open source tool available, GParted.
Always back up your data before adjusting partitions.
Download the 26 MB GParted LiveCD from http://gparted.sourceforge.net/livecd.php and burn it onto a CD or DVD. Insert the disc into the system to be resized, and then start (or restart) the system; the screen shown in Figure 10-1 will appear.
Figure 10-1. GParted LiveCD boot screen

You may need to adjust the BIOS boot options to force the system to boot from the disc.
Press Enter. The system will ask you to select your language, as shown in Figure 10-2 , and then to select the keyboard type, as shown in Figure 10-3 .
Figure 10-2. Language selection screen
Figure 10-3. Keyboard selection screen
The software will then prompt you for your display resolution, as shown in Figure 10-4 ; select the default unless you're using an old monitor.
Do not select 640x480 resolution; the GParted window will not fit on the screen.
Figure 10-4. Display resolution selection screen
You should also select the default for the display color depth, as shown in Figure 10-5 , unless you find that the default does not work with your system.
Figure 10-5. Display color-depth selection screen
The GParted screen in Figure 10-6 will now appear, displaying a list of all of the partitions on the first hard disk drive. If you wish to edit the partitions on another drive, click on the drive menu in the upper-right corner of the screen and select that drive.
Figure 10-6. GParted main window
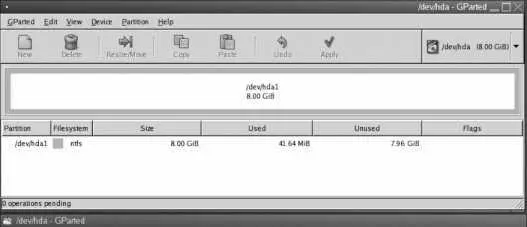
Click on the partition that you wish to resize, and then click on the Resize/Move button at the top of the window. In the resizing dialog shown in Figure 10-7 , select the new size for the partition by dragging the end of the partition, by entering the new partition size, or by entering the amount of free space that you wish to have after repartitioning. Click Next.
Figure 10-7. Entering a new partition size
The resize option will appear in a list of queued tasks at the bottom of the main window. Click the Apply button at the top of the window, and then click Apply on the confirmation dialog shown in Figure 10-8 .
Читать дальше



















