Hi there -- just dropping you a quick note viatelnet. Hope your day is going well.
-Chris .
250 2.0.0 k22I7BTo016133 Message accepted for delivery
QUIT
221 2.0.0 concord2.proximity.on.ca closing connection
Notice the blank line separating the email headers from the message bodyjust like HTTP transfers. The HTTP format is derived from the email format.
You can also send mail by sending it to the standard input of a sendmail process:
$ /usr/bin/sendmail chris@concord2.proximity.on.caSubject: Test II
Did you remember to renew the domain registration?If not, please take care of this before next Tuesday.[Ctrl-D]
Outbound mail is queued in /var/spool/mqueue /. Inbound mail is delivered via procmail to users' mailboxes in /var/spool/mail/ . The mailboxes are simply text files containing all of the messages concatenated end to end; this format is sometimes called mbox format .
The /etc/mail/sendmail.mc file used for configuration is an m4 macro file. It is interpreted by the m4 command using files in /usr/share/sendmail-cf/m4/ to build /etc/mail/sendmail.cf . While it is possible to construct the sendmail.cf file by hand, it's typically eight times as long as the sendmail.mc file and uses a very cryptic structure. Here's a snippet:
R< > $+ $: < > < $1 <> $&h > nope, restore +detail
R< > < $+ <> + $* > $: < > < $1 + $2 > check whether +detail
R< > < $+ <> $* > $: < > < $1 > else discard
R< > < $+ + $* > $* < > < $1 > + $2 $3 find the user part
R< > < $+ > + $* $#local $@ $2 $: @ $1 strip the extra +
R< > < $+ > $@ $1 no +detail
R$+ $: $1 <> $&h add +detail back in
Most system administrators would much rather deal with sendmail.mc than sendmail.cf .
7.6.3.1. ...using an alternate MTA?
Postfix is an alternate MTA shipped as part of Fedora. For most users, sendmail will work well, but if you are familiar with Postfix configuration you may want to use it instead.
You can easily switch between sendmail and Postfix using the alternatives command:
# alternatives --config mta
There are 2 programs which provide 'mta'.
Selection Command
-----------------------------------------------
*+ 1 /usr/sbin/sendmail.sendmail
2 /usr/sbin/sendmail.postfix
Enter to keep the current selection[+], or type selection number:
2
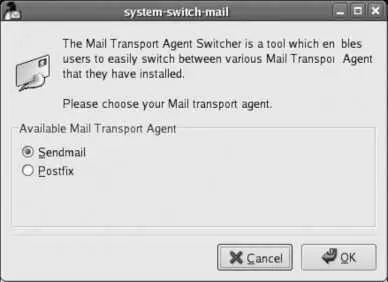
You can also switch graphically, using the system-switch-mail command available through the menu option System→Administration→Mail Transport Agent Switcher (this requires the somewhat obscure package system-switch-mail ). The window shown in Figure 7-20 will be displayed; select the MTA you wish to use and click OK.
Figure 7-20. The Mail Transport Agent Switcher tool.
7.6.3.2. ...fetching mail from a remote mailbox?
If you're using Fedora at a location that does not have a permanent Internet connection with a static IP address, incoming email cannot be delivered directly to sendmail. Instead, you'll have to arrange for the email to be delivered to mailboxes on another system and then pick up the mail from that system.
Many MUAs such as Evolution will directly access remote mailboxes, but sometimes you want to have that mail flow through the local mail system so that alias handling and procmail processing take place.
Fetchmail can retrieve mail from a remote mailbox and feed it to sendmail on the local system. To configure Fetchmail, create the file ~/.fetchmailrc using a text editor. Here is a simple configuration:
# Check for email at five-minute (300-second) intervals
set daemon 300
# Poll the system fedorabook.com using the POP3 protocol
poll fedorabook.com with protocol POP3 :
# Describe how the usernames on this machine relate
# to the usernames on fedorabook.com
user chris here is chris.tyler there, password " FedoraRules! "
user diane here is diane.tyler there, password " BiggestSecret ";
This will fetch the mail for two users from one server using the Post Office Protocol, Version 3 (POP3). Fetchmail can retrieve mail using many different protocols and has an uncommonly readable configuration syntax; consult its extensive manpage for the gritty details.
Once you have set up the ~/.fetchmailrc file, execute the fetchmail command:
$ fetchmail
It will run in the background until you stop it by running fetchmail with the -q option:
$ fetchmail -q
fetchmail: background fetchmail at 8025 killed.
To make fetchmail run automatically whenever you log in, place it in your ~/.bash_profile .
7.6.4. Where Can I Learn More?
The manpages for sendmail , procmail , procmailrc , fetchmail , procmailex , and postfix (check the See Also section for a long list of other manpages related to postfix )
The files in the /usr/share/doc/sendmail* , /usr/share/doc/fetchmail* , /usr/share/doc/procmail* , and /usr/share/doc/postfix* directories
The sendmail web site: http://www.sendmail.org
The fetchmail web site: http://www.catb.org/~esr/fetchmail
The procmail web site: http://www.procmail.org
The postfix web site: http://www.postfix.org
RFC 2142 defines a standard list of aliases that should exist on any Internet server: http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2142.txt
7.7. Configuring IMAP and POP3 Email
Having mail delivered to the system mailboxes in /var/spool/mail is fineas long as the users are using an MUA running on the Fedora system. If a user is running his MUA on another systemEvolution on another Fedora system in the local network, or perhaps Outlook on a Windows machinethen the user needs IMAP or POP3 access to the remote mailbox.
Fedora's Dovecot server provides IMAP and POP3 access.
When freshly installed, Dovecot will not successfully start. Dovecot requires security certificates to enable encrypted communications. There are three solutions to this problem:
Buy a certificate
A certificate is signed by a certificate authority (CA), whotheoreticallyis trusted by both the client and server. The CA certifies that the parties to whom certificates are issued are who they say they are, therefore eliminating the possibility of a malicious party between the client and the server masquerading as the server.
Читать дальше













