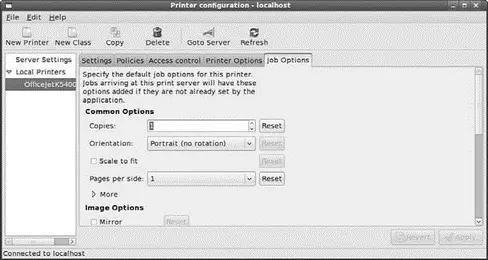
FIGURE 8.8 Configure how system-config-printerhandles print jobs that are submitted to it using the Job Options tab.
When you make changes, make sure to click the Apply button in the bottom right-hand corner of system-config-printerin order to restart CUPS and for the changes to take effect. Click Quit from the Action menu when you're finished.
Related Fedora and Linux Commands
The following commands help you manage printing services:
► accept — Controls print job access to the CUPS server via the command line
► cancel — Cancels a print job from the command line
► cancel — Command-line control of print queues
► disable — Controls printing from the command line
► enable — Command-line control CUPS printers
► lp — Command-line control of printers and print service
► lpc — Displays status of printers and print service at the console
► lpq — Views print queues (pending print jobs) at the console
► lprm — Removes print jobs from the print queue via the command line
► lpstat — Displays printer and server status
► system-config-printer — Fedora's graphical printer configuration tool
► http://www.linuxprinting.org/— Browse here for specific drivers and information about USB and other types of printers.
► http://www.hp.com/wwsolutions/linux/products/printing_imaging/index.html— Short but definitive information from HP regarding printing product support under Linux.
► http://www.cups.org/— A comprehensive repository of CUPS software, including versions for Fedora.
► http://www.pwg.org/ipp/— Home page for the Internet Printing Protocol standards.
► http://www.linuxprinting.org/cups-doc.html— Information about the Common UNIX Printing System (CUPS).
► http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~ghost/— Home page for the Ghostscript interpreter.
For any operating system to have mass-market appeal, it has to have a number of games that are compatible with it. Let's face it, no one wants to use computers just for word processing or databases — they want to be able to use them as a source of relaxation and even fun! This chapter looks at the state of Linux gaming and tells you how to get some of the current blockbusters up and running in a Linux environment. We even show you how to run Windows-based games under Linux.
A number of games come as part of the Fedora distribution, and they are divided into three distinct camps: KDE games, GNOME games, and X games. Our favorites are Planet Penguin Racer and Frozen Bubble (see Figure 9.1), but there are a few others for you to choose from. The best part, of course, is trying each one and seeing what you think. Many other free games are available across the web, so go to Google and see what you come up with.

FIGURE 9.1 Be very careful; Frozen Bubble can become extremely addictive!
However, games for Linux do not stop there — a few versions of popular Windows-based games are being ported across to the Linux platform, including Doom 3, Unreal Tournament 2004, and Quake 4. These three popular games have native Linux support and in some cases can run at similar, if not better, speeds than their Windows counter parts.
Finally, an implementation of the Wine code, called Cedega, is optimized especially for games. This uses application interfaces to make Windows games believe they are running on a Windows platform and not a Linux platform. Bear in mind that Wine stands for "Wine is not an emulator," so do not start thinking of it as such — the community can get quite touchy about it!
A historical gripe of Linux users has been the difficulty involved in getting modern 3D graphics cards working under Linux. Thankfully, since ATI (one of the major graphics card vendors) was bought up by AMD, they have released a true open source driver that is available to install under Fedora. NVIDIA also supports Linux, albeit by using closed source drivers. This means that Fedora does not ship with native 3D drivers for NVIDIA cards. It is fairly easy to get hold of the driver and install it; the Livna.org site has RPMs that are ready and waiting to be installed using yum.
Installing Proprietary Video Drivers
Fedora does not provide the official NVIDIA or ATI display drivers because they are closed source and Fedora is committed to delivering a totally free (as in speech) distribution. You can download the latest official drivers from http://www.nvidia.com/object/linux.html or from http://www.ati.com/. If you encounter problems with the NVIDIA drivers in particular, check out http://www.nvnews.net/vbulletin/forumdisplay.php?f=14 for more help. The NVIDIA staff do contribute to that forum, so you should be able to find expert help when you need it.
Bear in mind that if you go down the "official" route, you will have to take certain steps. It would be great to be able to access the drivers through yum, so much so that the Livna repository now has prepackaged the drivers into an RPM that is easily downloaded as long as you have the Livna repository enabled for yum.
CAUTION
The Livna repository is home to not only a wide range of kernel modules and drivers for many popular items of hardware, but also contains a number of legally question able packages that are not enabled in Fedora by default, including native MP3 support. If you are using Fedora for personal use, you should not have any real problems, but make sure to check before you start installing packages from Livna onto a corporate workstation or server!
To get the NVIDIA driver using yum, you need to have enabled the Livna repository (see Chapter 34, "Advanced Software Management," for more information on setting up repositories). At the command line, type
# yum install kmod-nvidia
and press Enter. After a few seconds, yum retrieves and downloads the latest NVIDIA driver that is appropriate for your current kernel version. After it finishes installing the packages, you have to restart your machine to take advantage of the improvements.
Installing the ATI driver is much the same because Livna.org also has a set of drivers available for ATI hardware. As with the NVIDIA driver, you need to be a super user and enter the following command:
# yum install kmod-fglrx
A restart of the system is necessary before you can make full use of the 3D capabilities of your card.
CAUTION
Both sets of graphics card drivers are very dependent on the kernel version you are running. Every time you update your kernel, you also have to update your driver. If you have used the kmod-*package from Livna, it should automatically update when you run yum upgrade.
Installing Popular Games in Fedora
It's a common misconception that Linux doesn't do games. In fact, that assumption is very wrong, as you are about to see. In this section, we walk through how to install five popular games that you can play within Fedora. Make sure that you have followed the earlier instructions on how to install graphics drivers for your graphics card; otherwise, you are likely to struggle with the likes of Doom 3, Unreal Tournament 2004, and Quake 4.
Читать дальше







![Andrew Radford - Linguistics An Introduction [Second Edition]](/books/397851/andrew-radford-linguistics-an-introduction-second-thumb.webp)






